The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) is an independent, not-for-profit organization that sets standards and offers pathways to accreditation for healthcare organizations. JCAHO, now known as The Joint Commission, advocates for the continuous improvement of healthcare quality and safety standards by conducting surveys, identifying areas for improvement, and offering platforms to support performance improvement.
The Joint Commission accredits a range of healthcare facilities, including hospitals, nursing care centers, home care providers, behavioral healthcare organizations, and ambulatory care providers. Each facility must meet specific criteria to earn accreditation, focusing on patient safety and quality standards of care.
One of The Joint Commission's initiatives to monitor performance measurement is the Oryx initiative, which began in 1997. This program allows healthcare organizations to meet their performance measurement requirements by utilizing various measurement systems. Hospitals and long-term care facilities, for instance, can choose from over 200 approved measurement systems operated by different organizations.
To maintain their accreditation, healthcare organizations must report on a specified number of clinical measures relevant to their patient population. The Joint Commission has established an advisory council to continuously review the measurement systems included in the Oryx initiative and select a set of core measures for each accreditation program.
The Oryx initiative is just one example of The Joint Commission's commitment to improving healthcare quality and safety through performance measurement and accreditation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Name of Initiative | The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO) |
| Description | JCAHO is an independent, not-for-profit organization that sets standards and offers pathways to accreditation for healthcare organizations. |
| Goal | To advocate for the continuous improvement of the quality of care and standards of safety of healthcare practices. |
| Target Organizations | Hospitals, nursing care centers, home care providers, organizations providing behavioral healthcare, and ambulatory care providers. |
| Accreditation Process | Conducted by a team of accredited professionals including hospital administrators, doctors, nurses, medical technologists, and other healthcare professionals. |
| Survey Frequency | Every 39 months for healthcare organizations and every 24 months for laboratories. |
| Accreditation Validity | 3 years for healthcare organizations and 2 years for laboratories. |
| Performance Measurement | Healthcare organizations must specify how patient and performance data is generated and used to improve standards and practices. |
| Performance Goals | Include infection control, medication safety, error prevention and reporting, staff credentialing and certification, emergency management, patient rights, privacy, and education. |
| Patient Safety Goals | Include ambulatory care, behavioral care, critical access, home care, hospital care, lab services, nursing care, and office-based healthcare. |
What You'll Learn

Setting performance targets
Define Clear and Specific Targets
Clear and specific targets provide a detailed picture of what needs to be achieved. For example, "increase sales by 5% over the next 12 months" is more effective than a vague goal like "increase sales". Specific targets remove ambiguity and ensure everyone understands what they are working towards.
Set Realistic Yet Challenging Goals
Setting unrealistic targets can be demoralising and lead to failure. It is important to consider your capacity, resources, and competitors or industry benchmarks when setting targets. While you should aim high, the goals should be achievable with your current capabilities or with a reasonable amount of additional investment.
Support Top-Level Targets with Lower-Level Targets
Top-level targets, such as increasing company profits, need to be supported by lower-level targets across the delivery chain. This includes areas like customer satisfaction, product quality, and staff engagement. Inefficiencies in any of these areas can impact your ability to achieve the desired top-level results.
Monitor Lower-Level Targets
Setting targets at various levels of the organisation is important, but monitoring their achievement is crucial. Regularly tracking lower-level targets helps identify areas of improvement and ensures that issues are addressed promptly. This prevents frustration and increases the likelihood of achieving the desired top-level outcomes.
Engage Stakeholders
Involving stakeholders in the target-setting process is essential for creating a sense of ownership and commitment. It also allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the organisation's capabilities and resources. Engaging stakeholders from the beginning fosters a collaborative environment and increases the chances of achieving the set targets.
Utilise Performance Measurement Frameworks
Performance measurement frameworks provide structure and guidance for monitoring and assessing the results of your targets. They help program managers make informed decisions, take timely actions, and ensure that the information gathered effectively supports the evaluation process.
By following these considerations, organisations can set performance targets that are achievable, motivating, and aligned with their strategic goals. Regular monitoring, flexibility, and a focus on continuous improvement are key to successful performance target setting and implementation.
Battery-Sapping Security Apps: Monitor Your Usage
You may want to see also

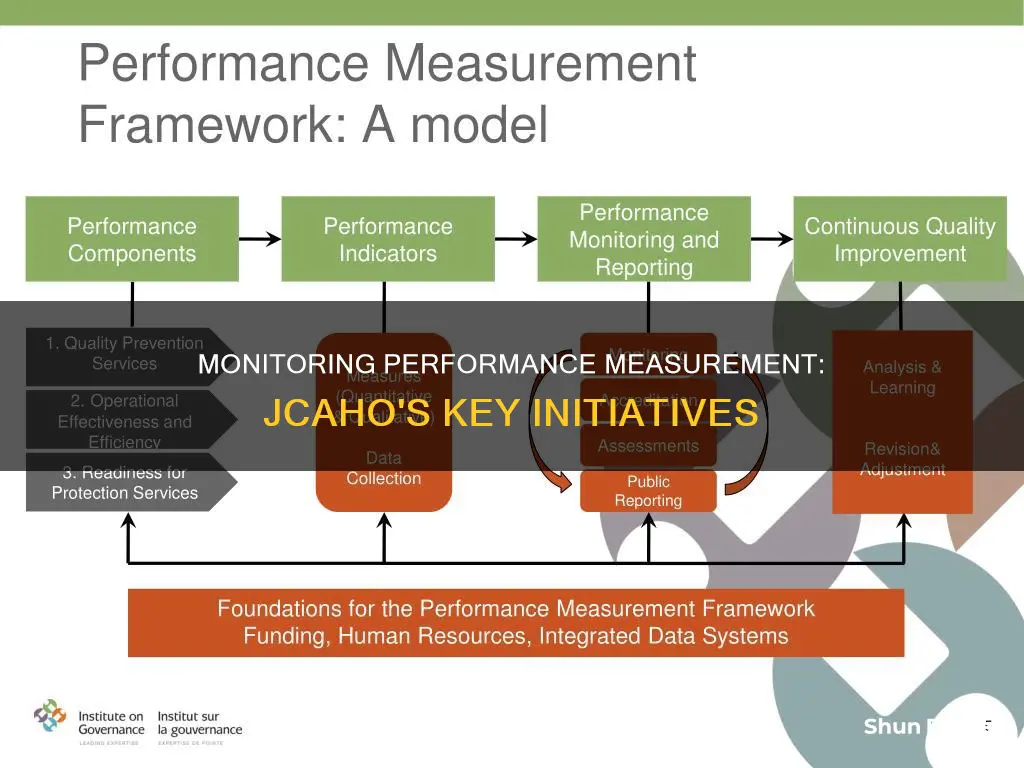
Creating a performance measurement framework
Performance measurement is a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and evaluating the progress of a project, program, or initiative toward achieving its desired outcomes, goals, and objectives. It is a powerful tool for planning and analysis and is often used to support program managers in monitoring the results and efficiency of their management.
The Purpose of a Performance Measurement Framework
A performance measurement framework identifies the indicators required to monitor and evaluate the performance of a program. Its purpose is to:
- Support program managers in continuously monitoring and assessing program results and the efficiency of their management.
- Enable informed decision-making and timely action regarding programs.
- Provide effective and relevant departmental reporting on programs.
- Ensure that the information gathered will effectively support an evaluation.
Steps to Develop a Performance Measurement Framework
- Identify your objectives: Clearly define your strategic and operational objectives. What are you trying to achieve? How does it align with your overall goals and priorities? Consider stakeholder expectations and needs, and ensure your objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
- Define your performance indicators (PIs): Determine the quantifiable metrics that reflect the quality, efficiency, effectiveness, and satisfaction of your project. Select PIs that are relevant, reliable, valid, and comparable. Balance input, output, outcome, and impact PIs. Input PIs measure resources and activities, while output PIs focus on deliverables and results. Outcome PIs assess short-term effects, and impact PIs evaluate long-term benefits.
- Set your performance targets: Establish specific values or ranges that indicate acceptable or optimal performance levels for each PI. Set targets that are realistic, achievable, and challenging. Consider baseline, benchmark, and best practice data to determine appropriate performance levels.
- Collect and analyze performance data: Gather accurate, timely, consistent, and complete performance data. Utilize appropriate methods and tools such as surveys, interviews, observations, tests, audits, reports, dashboards, and charts.
- Report and communicate performance results: Summarize and interpret your performance data in relation to your targets. Ensure that your results are clear, concise, relevant, and actionable. Use appropriate formats and channels to communicate your performance effectively to stakeholders and decision-makers.
- Review and improve your performance measurement framework: Periodically review and improve your framework based on feedback and lessons learned. Adjust your objectives, PIs, targets, data, results, and communication as needed. Address any changes or challenges in your project environment, such as scope, schedule, budget, quality, and stakeholder expectations.
Challenges and Considerations
When creating a performance measurement framework, it is important to address common challenges and considerations:
- Lack of understanding: Communicate the purpose of performance measurement and ensure that the right outcomes and measures are chosen. Encourage stakeholder participation to foster a shared understanding.
- Negative perception: Distinguish between performance measurement and performance management. Emphasize that it is an evaluation of tactics, not individuals. Create gap resolutions to address any shortcomings constructively.
- Resource constraints: Articulate the resources dedicated to performance measurement, including time, staff, and efforts. Highlight the connection between monitoring and resource allocation to demonstrate its importance.
- Data concerns: Ensure the availability of accurate and reliable data. Train and educate stakeholders in the data collection and analysis process. Select the "right" measures that are agreed upon by stakeholders.
- Lack of integration: Embed performance measurement into the organizational culture. Engage senior leadership to create buy-in and drive cultural change. Establish clear timelines and communication methods for sharing results.
Example Frameworks
There are various performance measurement frameworks available, such as:
- CPA Canada's PM4NPO: This framework consists of four stages: the balanced scorecard, reviewing and assessing, strategy map, and balanced scorecard. It helps organizations define their goals, identify efficiency and effectiveness, and establish metrics for success.
- Government of Canada's Performance Measurement Strategy Framework: This framework utilizes a logic model that follows individual projects, listing inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. It focuses on establishing indicators, data sources, targets, and responsibilities for each project and is known for its straightforward and easy-to-understand structure.
Tracking Business Goals: Strategies for Performance Monitoring
You may want to see also

Collecting and analysing data
Collecting and analyzing data is a crucial step in the performance measurement process, providing insights that drive decision-making and improvement. Here are some key considerations and best practices for effective data collection and analysis:
Planning and Preparation:
- Define clear objectives: Understand why data is being collected and what specific information is needed to meet those objectives.
- Identify data sources: Determine the data sources required, such as transaction records, website visits, mobile applications, customer feedback, and industry reports.
- Select appropriate methods: Choose suitable data collection methods such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, observations, or automated data collection tools.
- Ensure data quality: Implement measures to ensure data accuracy and address issues like errors, inconsistencies, or missing data.
Data Collection:
- Collect relevant data: Focus on gathering data that is directly relevant to your objectives to avoid wasting time and resources.
- Utilize technology: Leverage technology and automated data collection functions in business applications, websites, and mobile apps to streamline the process.
- Combine multiple sources: Collect data from multiple sources to gain a comprehensive understanding, including internal systems and external data providers.
- Incorporate feedback loops: Encourage feedback through surveys, social media tracking, and customer interviews to understand their experiences and perspectives.
Data Analysis:
- Quantitative and qualitative analysis: Analyze both quantitative data (numbers, statistics) and qualitative data (descriptions, opinions) to gain a holistic understanding.
- Statistical procedures: Apply statistical operations to quantitative data to identify relationships, patterns, and trends.
- Comparison and correlation: Compare data with other groups or variables to identify connections and correlations that provide valuable insights.
- Visual representation: Use charts, graphs, and visual inspection to identify patterns or discontinuities in the data over time.
- Data transformation: Convert qualitative data into quantitative data when appropriate to facilitate analysis and identify patterns.
Data Utilization:
- Address findings: Interpret the results and address any issues or unexpected findings. Identify areas where your initiative is successful and areas that need improvement.
- Continuous improvement: Use the insights gained from data analysis to adjust and improve your processes, products, or services continuously.
- Communicate results: Share the findings and insights with relevant stakeholders to demonstrate transparency and build trust.
- Monitor key performance indicators: Continuously track and evaluate relevant performance indicators to measure progress and identify areas for further improvement.
Hooking Up Raspberry Pi: Monitor Connection Guide
You may want to see also

Reporting and communicating results
Performance measurement is a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of projects, programs, and initiatives. It is a crucial tool for organizations to demonstrate accountability, make informed strategic decisions, and drive continuous improvement.
The Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO), also known as the Joint Commission, plays a vital role in monitoring and improving the performance of healthcare entities. They conduct surveys, identify areas for improvement, and offer platforms to support performance enhancement. The commission's accreditation process involves a comprehensive assessment of various aspects of healthcare organizations, including patient safety, quality standards of care, infection control, medication safety, staff credentialing, and patient privacy.
When it comes to reporting and communicating results, there are several key steps and considerations:
Data Collection and Analysis:
- Identify the relevant data sources within and outside the organization, such as reports, budgets, logbooks, meeting minutes, surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Ensure data consistency and provide explanations for any changes in measurement methods or adjustments in the data.
- Analyze data by identifying patterns, trends, and relationships. Utilize graphs, charts, and tables to present the data effectively.
- Compare actual results with anticipated outcomes, targets, or benchmarks to identify variances.
Communication and Reporting:
- Determine the target audience for the report, including internal stakeholders, executives, board members, staff, external stakeholders, and the general public.
- Utilize various communication channels such as meetings, websites, social media, newsletters, annual reports, press releases, and media outlets to reach the intended audiences.
- Structure the report effectively by providing background information, describing the performance measurement process, presenting results, and explaining their context.
- Include graphs, charts, and tables to support the interpretation of results and discuss the relationship between activities, outputs, and outcomes.
- Be transparent and unbiased when presenting results, including both successes and areas for improvement.
- Provide recommendations and corrective actions based on the findings to improve future performance.
- Maintain open communication with stakeholders throughout the process, keeping them informed of progress and achievements.
By following these steps and considerations, organizations can effectively communicate the results of their performance measurement initiatives, build trust with stakeholders, and drive continuous improvement in their operations.
Micca Origen G2: Hooking Up to Studio Monitors
You may want to see also

Improving strategic decision-making
Performance measurement is a crucial tool for management and oversight, aiming to improve outcomes by focusing on quantifiable measures. It is designed to support the achievement of corporate goals and strategies and provide valuable insights for further development and adjustment.
Performance measurement is an essential aspect of strategic decision-making as it offers a systematic approach to collecting, analyzing, and evaluating data to ensure a project stays "on track" and achieves its desired outcomes. Here are some ways in which performance measurement can improve strategic decision-making:
- Informed decision-making: Performance measures provide critical information to support strategic decisions about an organization's operations and performance. They offer insights into what is working well and what needs improvement, enabling leaders to make data-driven choices.
- Flexibility and adaptability: By regularly monitoring performance, organizations can identify areas where they need to be more flexible and adapt their strategies accordingly. This is especially important when dealing with complex and dynamic environments, as it allows for course correction to stay aligned with goals.
- Accountability and transparency: Performance measurement fosters accountability by demonstrating the effectiveness of plans and activities in achieving desired outcomes. It also increases transparency, as stakeholders can clearly see the impact of decisions and strategies.
- Continuous improvement: Performance measurement encourages a culture of continuous improvement. By regularly reviewing performance data, organizations can identify areas for enhancement and develop "best practices" to apply to future initiatives.
- Effective resource allocation: Performance measurement helps inform resource allocation by identifying areas of strength and weakness. It enables leaders to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that successful initiatives receive the necessary support and that struggling areas get the attention they need.
- Enhanced communication: Performance measurement improves communication by providing a common framework for discussing an organization's progress and challenges. It allows stakeholders to engage in meaningful conversations about goals and strategies, fostering a collaborative environment.
- Goal-setting and strategy development: Performance measurement is integral to the goal-setting process. By reviewing performance data, organizations can set realistic, achievable goals and develop strategies that are aligned with their desired outcomes.
- Identifying key performance indicators (KPIs): Performance measurement involves defining KPIs that are measurable, traceable, and directly linked to the success of organizational goals. These KPIs provide a clear framework for evaluating success and help identify areas that need improvement.
- Comparative analysis: Performance measurement allows for comparisons over time, across different groups, or with competitors. This comparative analysis provides context and helps identify areas of relative strength and weakness, informing strategic decisions.
- Risk management: Performance measurement can help identify and mitigate risks. By tracking key indicators, organizations can spot potential issues before they become full-blown crises, enabling proactive decision-making to minimize negative impacts.
By utilizing performance measurement effectively, organizations can make more informed, data-driven strategic decisions. It provides a factual basis for decision-making, ensuring that choices are rooted in evidence rather than intuition or guesswork. This, in turn, can lead to improved outcomes and a stronger competitive position.
Eliminating Grid Alignment from Your Desktop Monitor
You may want to see also