G-Sync is a technology developed by NVIDIA that eliminates screen tearing and minimises display stutter and input lag. It works by matching the refresh rate of your monitor to the framerate of the game you're playing. If you want to enable G-Sync on your ASUS monitor, you'll need to make sure your monitor allows G-Sync and that you have an NVIDIA graphics card. You can then enable G-Sync in your monitor's built-in menus and in Windows.
What You'll Learn

Check your monitor is G-Sync compatible
To check if your monitor is G-Sync compatible, you must first determine whether your monitor is labelled as such. All monitors that support G-Sync will have it clearly labelled in the title (model name) or description.
If you are unsure, you can check by opening the Nvidia Control Panel on your Windows computer. Right-click on your desktop screen and click on Nvidia Control Panel. From the menu bar, go to Display and select Show indicator for G-Sync. The indicator will appear on the screen to let you know whether G-Sync is turned on or off.
Depending on the type of monitor you are using, the menu item could state Show indicator for G-SYNC, Show indicator for G-SYNC Compatible, or Show indicator for G-SYNC/G-SYNC Compatible. If G-Sync is not turned on, you can enable it by clicking on the 'Enable G-SYNC G-SYNC Compatible' checkbox.
Additionally, to check if your monitor is working as expected, you can refer to benchmark tests available online. It is also recommended to set the resolution and refresh rate to maximum for enhanced performance.
Resetting Your ASUS Monitor: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Ensure you have the right hardware
To enable G-Sync on an ASUS monitor, you need to ensure you have the right hardware. G-Sync is a function developed by NVIDIA to eliminate screen tearing and minimize display stutter and input lag. It can support most games, but a few may not perform well with the function enabled.
To use G-Sync, you will need a monitor that supports the G-Sync feature, such as the PG series model. The monitor must support a Display Port 1.2 connection directly from the GPU.
In terms of GPUs, you will need an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 650 Ti BOOST GPU or higher for a desktop PC. For a laptop, you will need an NVIDIA GeForce GTX 980M, GTX 970M, or GTX 965M GPU or higher.
Additionally, your system must be running Windows 7, 8.1, or 10 or above.
If you have the compatible hardware, you can then proceed to enable G-Sync.
Monitoring Electrical Usage: Individual Breakers and Their Secrets
You may want to see also

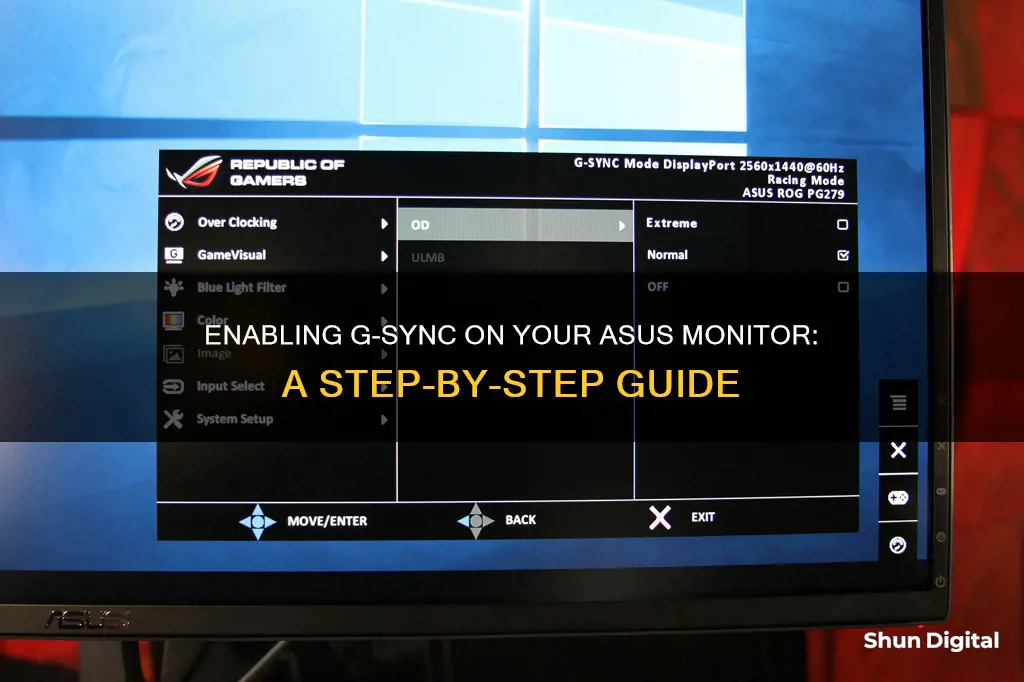
Enable G-Sync in your monitor's settings
To enable G-Sync in your monitor's settings, you must first ensure that your monitor is G-Sync compatible. G-Sync is a technology developed by NVIDIA that eliminates screen tearing and minimises display stutter and input lag by matching the refresh rate of your monitor to the framerate of the game you are playing.
To check if your monitor is G-Sync compatible, look for the G-Sync label on your monitor or its packaging. NVIDIA also maintains an active database that you can sort by manufacturer and model.
Once you have confirmed that your monitor is G-Sync compatible, you can then enable G-Sync in your monitor's settings. The specific steps to do this may vary depending on the brand and model of your monitor, so you may need to refer to your monitor's manual. However, here are some general steps you can follow:
- Use the on-display buttons to locate the adaptive sync/G-Sync options in your monitor's settings.
- Toggle G-Sync on.
- Adjust any other display settings as needed, such as the refresh rate and brightness.
- Open the NVIDIA Control Panel on your computer. You can do this by right-clicking on your Windows desktop and selecting NVIDIA Control Panel.
- In the NVIDIA Control Panel, look for Display settings in the sidebar and click on "Set up G-Sync".
- Click the box that says "Enable G-Sync".
- Choose whether to enable G-Sync for full-screen mode or windowed mode, or both.
- If you have multiple monitors, set your G-Sync monitor as the primary display.
- Adjust your game settings to align with your monitor's settings, such as the framerate and refresh rate.
By following these steps, you should be able to successfully enable G-Sync in your monitor's settings and take advantage of the smoother gaming experience that it provides.
Monitoring Device Usage: Securing Your Home WiFi
You may want to see also

Enable G-Sync in Windows
To enable G-Sync in Windows, you must first ensure that your monitor supports G-Sync. Support is common, even on monitors that are not marketed as gaming models, but it is not automatic. Check for the G-Sync label on your monitor or its packaging, or refer to the active database maintained by NVIDIA, which can be sorted by manufacturer and model.
Once you have confirmed that your monitor supports G-Sync, follow these steps:
- Right-click on your Windows desktop.
- Click on the NVIDIA Control Panel. In Windows 11, you may first need to click "Show more options".
- Look for Display settings in the sidebar and click on "Set up G-Sync".
- Click the box marked "Enable G-Sync".
- Choose whether to enable G-Sync for full-screen or windowed modes, or both.
- If you have more than one monitor, set your G-Sync monitor as the primary display. To do this, right-click on your desktop, select Display settings, click on "Identify" next to the monitors being shown, and select "Make this my main display" for the G-Sync monitor.
G-Sync should now be active. However, you may need to adjust additional settings within individual games. To do this, locate the game's graphics settings and adjust the refresh rate options to match your monitor. Look for an FPS limiter (or FPS cap) and set the FPS to the value of your refresh rate or below. For example, if you have a 144Hz monitor, the FPS should be capped at 144, 120, or 60fps.
Additionally, if G-Sync is enabled, V-sync should be disabled as they accomplish similar things, but only G-Sync can dynamically adjust both the framerate of your graphics card and the refresh rate of your monitor.
Internet Monitoring: How Often Are We Tracked Online?
You may want to see also

Adjust game settings
G-Sync should be active now, but you may need to tweak additional in-game settings. At the least, you'll want a game's framerate (measured in frames per second, or FPS) to match your monitor's refresh rate. If the FPS exceeds that refresh rate, you won't like the results. Explore the menus to find a game's graphics settings, then adjust the refresh rate options to match your monitor. Next, look for an FPS limiter (a.k.a. an FPS cap). If there is one, the FPS should be set at or below the value of your refresh rate. If you have a 144Hz monitor, for example, the FPS should probably be capped at 144, 120, or even 60fps. Keep in mind that your PC may (and probably will) run slower than that cap anyway, depending on the game you're playing, its detail levels, and how powerful your CPU and GPU are. Your monitor might be capable of 144fps, but most (current) PCs can't reach that if they're running Cyberpunk 2077 at maximum detail.
You may need to experiment with other game settings as well, such as V-sync. If G-Sync is on, V-sync should probably be disabled—it tries to accomplish the same thing, but only G-Sync (and FreeSync) can dynamically adjust both the framerate of your graphics card and the refresh rate of your monitor.
To ensure that your G-Sync is working properly, you can grab the Pendulum demo from Nvidia. For the best results, you may want to tweak settings in individual games, including running them in exclusive full-screen mode where possible. Your primary goal is to ensure that your frame rate remains inside the refresh rate range your monitor supports for G-Sync compatibility.
If you’re frequently getting above the maximum limit, consider limiting the maximum frames output in your game’s graphics/display menu. If, on the other hand, you find you’re frequently dipping below the lowest threshold of supported refresh rates, you may want to drop some of the graphics settings in your game to consistently yield higher FPS.
Monitoring Memory Usage: A Guide for Node.js Developers
You may want to see also







