VMware vSphere is a virtualization platform that transforms data centres into aggregated computing infrastructures. The vSphere Web Client is a tool that allows users to monitor the performance of their virtual environment and locate the source of potential issues and current problems. It provides performance data on system resources such as CPU, memory and storage. The vSphere Web Client also offers advanced performance charts that display multiple data sets in one panel to evaluate different resource statistics. These charts can be exported in various formats, including PNG, JPEG and CSV.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Performance data | CPU, Memory, Storage, etc. |
| Performance Monitoring Command-line Utilities | Access detailed information on system performance through the command line |
| Events, Alerts, and Alarms | Configure alerts and alarms and specify actions for the system to take |
| System logs | Contain additional information about activities in the vSphere environment |
| Monitor tab | Click the Monitor tab, then Performance |
| Available views | Depend on the type of object; for views with many charts in a large environment, the vSphere Web Client distributes charts across multiple pages |
| Time range | Select a predefined or custom time range |
What You'll Learn

Performance data on system resources
VMware vSphere is a virtualization platform that transforms data centers into aggregated computing infrastructures, including CPU, storage, and networking resources. It provides tools to monitor the health and performance of your virtual environment.
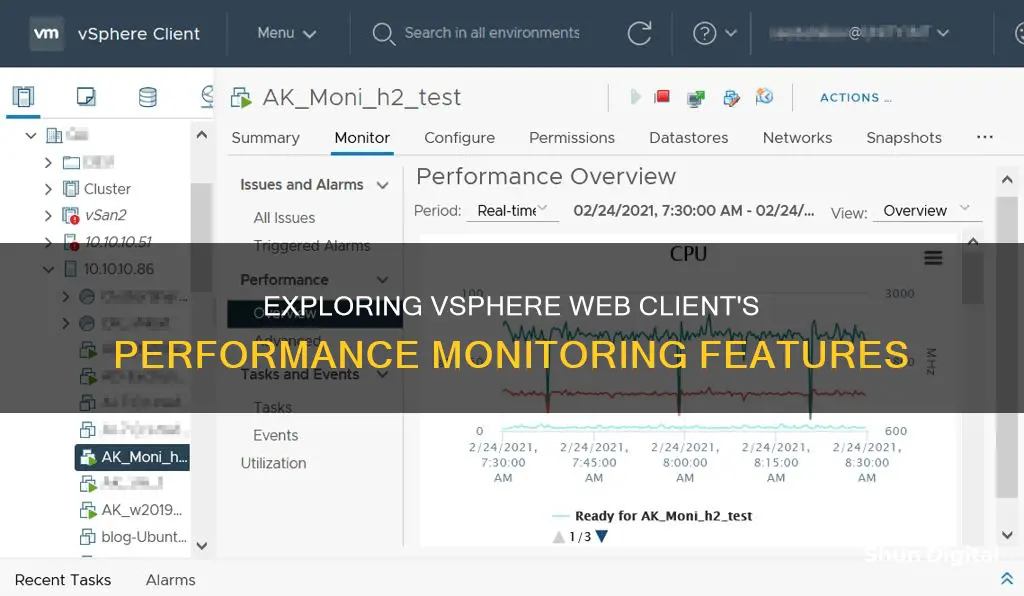
The vSphere Client offers performance charts that display real-time health and performance data of inventory objects. These charts can be customized to add additional metrics and different time spans. For example, administrators can monitor CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O.
VSphere also provides advanced performance charts that support data counters not available in other charts. These charts can be viewed by navigating to an inventory object, clicking the "Monitor" tab, and selecting "Performance". The historical data displayed depends on the collection interval and statistics level set for the vCenter Server.
In addition, vSphere includes command-line utilities that provide detailed information on system performance. One such tool is esxtop, which allows administrators to view resource, health, and performance metrics of virtual machines and ESXi hosts with sampling intervals as short as two seconds.
With these features, administrators can gain valuable insights into the performance of their system resources and make informed decisions to ensure the optimal performance of their virtual environment.
Troubleshooting Monitor Issues: Button Panel or Power Supply?
You may want to see also

Performance Monitoring Command-line Utilities
Performance-monitoring command-line utilities provide a detailed look at how ESX/ESXi uses resources in real time. There are two main command-line utilities: resxtop and esxtop. Both utilities can be started in one of three modes: interactive (default), batch, or replay. The key difference between the two is that resxtop can be used remotely or locally, while esxtop can only be started through the service console of a local ESX host.
Resxtop and esxtop are command-line utilities that provide a detailed, real-time view of how ESXi uses resources. They offer insights into resource utilisation, allowing administrators to monitor and optimise the performance of their virtualised environment.
Using the esxtop utility, administrators can access information about CPU, memory, disk, and network utilisation directly from the ESXi host. This enables them to identify potential bottlenecks or areas where resources may need to be reallocated for optimal performance.
On the other hand, the resxtop utility provides similar functionality but with the added flexibility of being accessible remotely or locally. This utility is particularly useful for monitoring resource utilisation across multiple ESXi hosts in a distributed environment. With resxtop, administrators can gain insights into CPU load, memory usage, disk I/O, and network traffic without needing physical access to each individual host.
In addition to resxtop and esxtop, VMware also offers performance monitoring capabilities for virtual machines running Microsoft Windows operating systems. The VMware Tools package includes performance counters that integrate with the Windows Perfmon utility. This integration enables administrators to view detailed performance data, such as CPU utilisation, memory usage, and disk activity within the Windows operating system. By leveraging these performance counters, administrators can fine-tune the performance of their virtual machines and ensure efficient utilisation of resources.
Cleaning LCD Monitors: Removing Dust Easily
You may want to see also

Events, alerts and alarms
Events, alerts, and alarms are an important part of the vSphere Web Client performance monitoring toolkit. They allow administrators to stay on top of the health and performance of their virtual environment, helping them to quickly identify and troubleshoot any issues that may arise.
With the ability to configure alerts and alarms, administrators can set specific triggers and specify the actions the system should take when those triggers are activated. This could include sending notifications or taking automatic remedial action to mitigate potential problems. Alerts can be set up to provide a quick overview of the health of the system, allowing administrators to easily identify which hosts are healthy and which are experiencing problems.
The vSphere Web Client also provides access to detailed system performance information through the command line. This includes system logs, which contain valuable data about activities in the vSphere environment. This information can be used to gain deeper insights into the performance of both physical hardware and virtual devices, helping administrators make informed decisions about resource allocation and optimisation.
Performance charts, available for datacenter, cluster, host, resource pool, vApp, and virtual machine objects, provide a visual representation of resource statistics. Administrators can select a valid inventory object and choose from overview or advanced charts to monitor different aspects of system performance. These charts can be customised by selecting specific time ranges and data collection intervals, making it easier to spot trends and identify potential areas of concern.
Powering Your LCD Monitor with a Power Bank
You may want to see also

System logs
The vSphere Client system log files can be used to resolve technical issues. The location of these logs depends on the type of vCenter Server system being used. For a vCenter Server that runs on Windows, the logs can be found at C:\ProgramData\VMware\vCenterServer\logs\vsphere-client\logs. For a vCenter Server Appliance, the logs are located at /var/log/vmware/vsphere-client/logs. The main log file for both systems is vsphere_client_virgo.log.
The vSphere Web Client logs are grouped by component and purpose. For example, the log file vsphere_client_virgo.log contains all communication between underlying Flex endpoint connections, internal tasks, and events. The log file localhost_access_log.
It is important to note that the vSphere Client and vSphere Web Client have different log file locations and structures. As such, it is crucial to refer to the appropriate documentation or support resources to locate the relevant log files for the specific vSphere client in use.
Ultimate Guide to Buying the Perfect Monitor
You may want to see also

Overview and advanced performance charts
The vSphere Client is a web browser-based application that enables users to monitor their virtual environment by visualising key metrics with performance charts, setting alarms on metrics, and viewing tasks and events. Performance charts are available for inventory objects, which include virtual machines, ESXi hosts, clusters, and resource pools.
To access performance charts in the vSphere Client, users need to select an inventory object, click the "Monitor" tab, and then click "Performance". From there, they can choose either "Overview" or "Advanced" charts. By default, both types of charts display real-time data collected in 20-second intervals over the past hour. However, users can also view different intervals, such as the last day, week, or month, using the interval dropdown menu above the performance charts.
The available views and specific metrics categories in the overview and advanced performance charts depend on the type of inventory object being observed. For example, when observing an ESXi host, users can select the "Home" view, which displays key resource metrics, or the "Virtual Machines" view, which provides a breakdown of the virtual machines running on that host with the highest CPU, memory, disk, and network usage.
Unlocking Freesync: Understanding Your Monitor's Range
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
VMware vSphere is VMware's virtualization platform, which transforms data centers into aggregated computing infrastructures that include CPU, storage, and networking resources.
The vSphere Web Client is a Flex-based GUI that can be used to perform tasks related to monitoring and performance in the vSphere environment.
The vSphere Web Client allows users to access detailed information on system performance through the command line and quickly identify which hosts are healthy and which are experiencing problems. It also provides performance charts for various objects, including datacenters, clusters, hosts, and virtual machines, offering an overview of different resource statistics.
In addition to the vSphere Web Client, VMware offers command-line utilities, events, alerts, and alarms for performance monitoring. System logs are also available to provide additional information about activities in the vSphere environment.