Monitoring the temperature of your AMD Radeon graphics card is essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent overheating. High GPU temperatures can reduce performance and even lead to system shutdowns. AMD Radeon graphics cards come with a built-in performance monitoring tool that allows users to track their GPU temperature and other crucial performance statistics. To access this tool, users can press Alt + R or right-click on the desktop and select AMD Adrenalin. Within the software, users can navigate to the Performance tab to view real-time metrics such as GPU temperature, utilization, clock speeds, and fan speed. Additionally, AMD's software provides the ability to log performance data for further analysis. For a more comprehensive view of system performance, users can utilize third-party tools such as MSI Afterburner, which is compatible with AMD Radeon graphics cards and offers features like overclocking and temperature logging.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Software | AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition, Radeon Settings app, Wattman overclocking tool, Radeon Overlay, Radeon Software |
| --- | --- |
| Windows OS | Windows 10, 11 |
| --- | --- |
| Windows Task Manager | Ctrl + Shift + Esc, Crtl + Alt + Delete, right-click on the Windows Start menu icon |
| --- | --- |
| Windows Task Manager Performance Tab | GPU section |
| --- | --- |
| Radeon Overlay | Alt + R, Ctrl + Shift + 0 |
| --- | --- |
| Wattman overclocking tool | Right-click on the Windows desktop, Radeon Settings, Gaming > Global Settings > Global Wattman |
| --- | --- |
| Third-party tools | MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, HWiNFO64, HWInfo, NZXT CAM, SpeedFan, Open Hardware Monitor, LibreHardwareMonitor |
What You'll Learn

Windows Task Manager
To monitor your AMD Radeon graphics card's performance and temperature in the Windows Task Manager, follow these steps:
- Open Task Manager: You can do this by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc on your keyboard, or by right-clicking on the Windows Start menu icon and selecting Task Manager from the menu.
- Navigate to the Performance Tab: Once Task Manager is open, click on the "Performance" tab at the top.
- Locate your GPU: In the left-hand pane, scroll down and locate your GPU. It should be listed under the Graphics section. If you have multiple GPUs, you may need to find the correct one by its name.
- Check the Temperature: The temperature of your AMD Radeon GPU will be displayed near the bottom of the Task Manager window, or in the list of components on the left. You can also click on the GPU in the left pane to see more details, including the current temperature and usage, in the right pane.
- Ensure Dedicated GPU: It is important to note that the Task Manager's temperature monitoring feature currently only supports dedicated GPUs. If you are using an integrated graphics card, you may not be able to see the temperature in Task Manager.
- Update Graphics Driver: To see the temperature in Task Manager, you may need to update your graphics driver to support version 2.4 or higher of WDDM (Windows Display Driver Model). You can check your current WDDM version by pressing WIN + R and entering "dxdiag". The WDDM version will be listed under the Display tab.
By following these steps, you can use the Windows Task Manager to monitor the performance and temperature of your AMD Radeon graphics card. This can help you ensure that your GPU is operating within acceptable temperature ranges and maintain optimal system performance.
Connecting Xbox to a Monitor Without HDMI: Alternative Methods
You may want to see also

AMD Radeon Settings
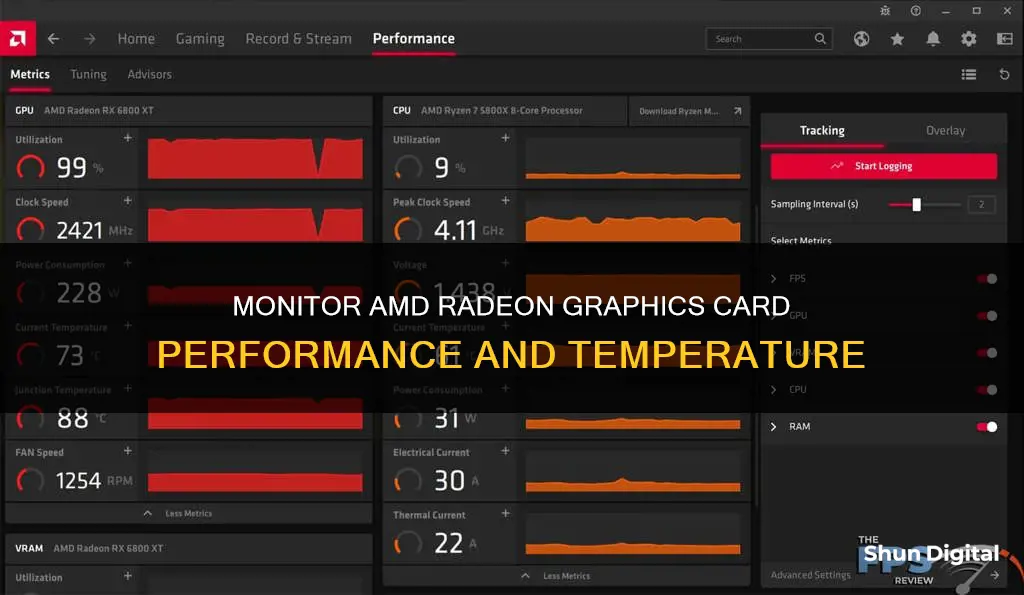
To monitor the performance of an AMD Radeon graphics card, you can use the AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition. This software allows users to monitor the performance of their AMD Radeon Series Graphics and compatible CPUs. Users can also customise the performance metrics they want to monitor, which are then represented by graphs and meters over a period of time.
To access the AMD Software, click the Start button on the Taskbar, then search for and select the app. Once the app is open, search for "Metrics" and click on the "Performance Metrics" result. By default, the performance metrics will be displayed using a grid view, but you can switch to a list view by clicking the icon. To show other performance stats, select Additional Metrics.
The right panel of the app provides tracking options, including the ability to enable or disable the metric gauge, graph and overlay, as well as the ability to log performance stats by saving them to a file for later analysis. You can also adjust the sampling interval, which is the rate at which the software polls for new data.
The performance metrics that can be monitored in real-time include:
- Frame Rate (reported in frames per second or FPS)
- Frame Time (reported in FPS)
- 99th% FPS (reported in FPS)
- Stutter Rate (reported in percentage)
- GPU Utilization (reported in percentage)
- GPU Clock Speed (reported in Megahertz or MHz)
- Total Board Power (reported in Watts or W)
- GPU Current Temperature (reported in degrees Celsius or °C)
- GPU Junction Temperature (reported in °C)
- GPU FAN Speed (reported in revolutions per minute or RPM)
- GPU Memory Utilization (reported in Megabytes or MB)
- GPU Memory Clock Speed (reported in MHz)
Additionally, AMD Radeon graphics cards also have a Radeon Overlay feature, which can be activated by pressing Alt + R. This overlay provides tools to adjust game settings and includes a Performance Monitoring tool that displays the GPU temperature and other crucial information while gaming.
Ideal Triple Monitor Setup: Size and Resolution
You may want to see also

Radeon Overlay
The Performance Monitoring tool within Radeon Overlay displays the GPU temperature, along with other crucial information, while users are playing games. To activate the tool, summon the Radeon Overlay by pressing Alt+R and select which performance metrics you want to monitor in the Overlay's Performance Monitoring section. Once set up, the Performance Monitoring tool can be brought up by pressing Ctrl+Shift+0.
The Performance Monitoring tool allows users to select the metrics they want to monitor, including:
- Frames per second (FPS)
- GPU utilisation (%)
- GPU engine clock (MHz)
- GPU memory clock (MHz)
- GPU temperature (°C)
- GPU power (W)
- GPU fan speed (RPM)
- CPU utilisation (%)
- VRAM utilisation (GB)
- System RAM utilisation (GB)
The Performance Monitoring tool also allows users to customise the on-screen display, including the location, size, transparency, number of columns, and text colour of the metrics.
Monitoring Linux Memory Usage: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Wattman Overclocking Tool
Wattman is an overclocking tool for AMD Radeon graphics cards. It is included in the Radeon Software Crimson driver pack and offers a range of features for tweaking and fine-tuning graphics cards.
To access Wattman, open the Radeon Settings app and click on the Gaming tab, then Global Settings, and finally the Global Wattman tab. Wattman features a real-time graphing tool called "Histogram", which maps out the activity level, current core clock speed, memory frequency, temperature, and fan speed of the graphics card. This allows users to monitor all the crucial measurements needed while overclocking.
Wattman also offers per-app Profile settings, allowing users to profile performance while specific games are running for up to 20 minutes at a time. This feature integrates with the overclocking capabilities of Wattman, which can be applied on a per-game basis. Users can overclock their graphics cards in more demanding games while reducing the target temperature in less strenuous titles.
Wattman provides granular control over clock speeds and voltages, allowing users to configure up to seven performance states to their preferences. It also includes controls for the power limit, fan speed, and target temperature of the graphics card.
The tool also enables "undervolting", which involves reducing voltages to maintain stability at stock clock speeds, potentially improving power efficiency. Additionally, the Frame Rate Target Control (FRTC) feature helps save power by capping the maximum frame rate of the GPU, ensuring that the graphics card does not render more frames than the monitor can display.
Overall, Wattman is a powerful and versatile tool for overclocking AMD Radeon graphics cards, offering a range of customisation options and performance-tracking features.
Asus ProArt Display: Graceful, Professional Monitors for Creative Pros
You may want to see also

Third-party tools
While Windows 10 and 11 have native ways to monitor GPU temperatures, third-party tools offer more robust GPU temperature monitoring options.
MSI Afterburner
MSI Afterburner is a versatile tool that works with both Nvidia GeForce and AMD Radeon graphics cards. It offers an overlay that displays GPU temperature and other performance statistics while you are in-game. It also allows you to log performance statistics.
EVGA Precision X1
EVGA Precision X1 has similar features to MSI Afterburner and AMD Radeon Software, but it exclusively supports Nvidia GPUs. It also supports logging temperature data to a file.
HWiNFO64
HWiNFO64 provides real-time data about every component in your system, including GPU temperatures. It also supports logging any metrics it can display.
Open Hardware Monitor
Open Hardware Monitor is a reliable tool that can monitor GPU temperatures and manually adjust fan speed.
SpeedFan
SpeedFan is another reliable tool for monitoring GPU temperatures, voltages, fan speeds, and reducing noise.
Eradicating Resonance: Studio Monitor Optimization Techniques
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can use the AMD Adrenalin software, which is available to download on the official AMD website. Once installed, you can launch the software by pressing Alt + R or by right-clicking on your desktop and selecting "AMD Adrenalin". Navigate to the Performance tab, where you will find real-time metrics for your GPU, including temperature, utilisation, clock speeds, power consumption, and fan speed.
There are several third-party tools available, including HWInfo, Open Hardware Monitor, and SpeedFan. These tools allow you to monitor not only your GPU temperature but also other facets of your PC, such as clock speeds, voltage, and RAM timings.
Monitoring your GPU temperature is crucial to ensure it stays within acceptable ranges. High GPU temperatures can reduce performance and even cause system shutdowns. Additionally, keeping an eye on your GPU temperature can help you identify any potential issues with your GPU or PC.
Ideally, your GPU temperatures should stay below 80 degrees Celsius. Occasional spikes above 80 degrees are okay, but if your GPU regularly runs at 90 degrees or higher, it may be at risk of damage or a shortened lifespan.