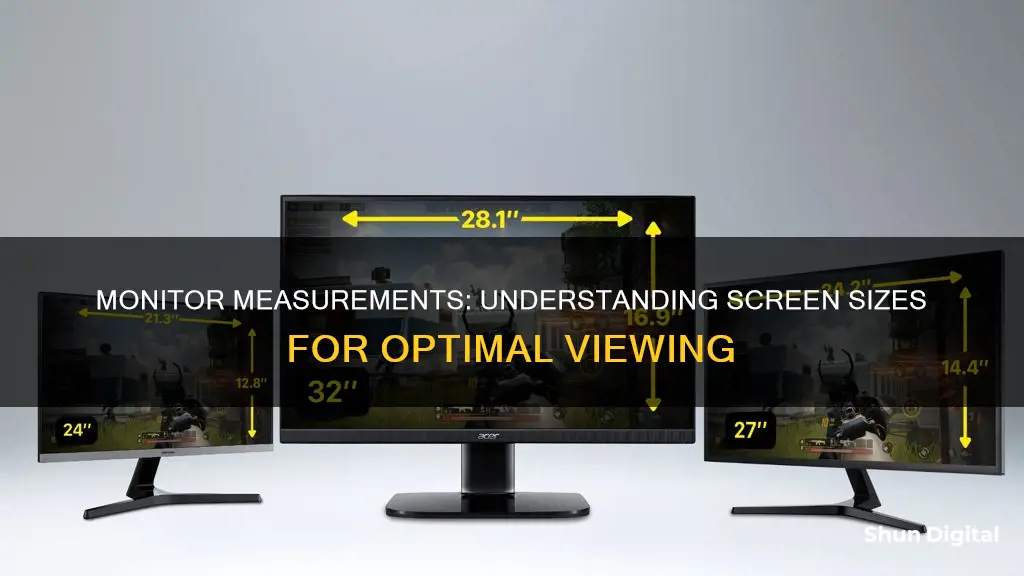
Knowing the size of your monitor is important for various reasons, such as choosing the right wallpaper or ensuring compatibility with your setup. The standard way to measure a monitor's size is by its diagonal length, typically in inches. This can range from 11.6 inches for a laptop screen to 55+ inches for a TV used as a monitor. While there are standard display sizes, it is always recommended to physically measure your monitor to get an accurate size, as some may have unique dimensions.
What You'll Learn

How to measure your monitor
To measure the size of your monitor, you will need a measuring tape or a ruler.
The size of a monitor is the length of the diagonal of the monitor, measured in inches. This is different from the screen resolution, which is measured in pixels.
To measure the diagonal distance, place the tape measure or ruler at the top-left corner of the screen and extend it to the bottom-right corner. If you start from the top-right corner, pull it straight to the bottom-left corner. Make sure to measure only the screen itself and not the bezel or frame around the screen.
Once you have the diagonal measurement, you can round it up or down to the nearest inch. This is the size of your monitor screen. For example, if the diagonal distance is 23.5 inches, you can round it up to 24 inches.
You can also use a simple mathematical equation to find the monitor size. First, measure the width and height of the screen in inches. Then, square the width and height and add the two numbers together. Finally, calculate the square root of this sum to get the diagonal measurement, which is the screen size.
For instance, if the width is 11.57 inches and the height is 6.51 inches, you would multiply the width by itself to get 133.8. Then, multiply the height by itself to get 42.38. Adding these together gives you 176.18. The square root of this sum is 13.27, which is the advertised size of a Dell XPS 13 laptop monitor.
If you are unable to measure your monitor, you can also check the model number, which may include the monitor size. For example, Acer S201HL means the monitor size is 20 inches. You can also search for your laptop model online, which should display the screen size in the specifications.
Adjusting Text Size on LG 27 Monitors: A Simple Guide
You may want to see also

Monitor size in relation to cost
The size of a monitor is usually measured by the diagonal length of its screen, from one corner to the opposite corner. This measurement is typically given in inches.
The cost of a monitor can vary depending on its size, features, and target audience. Here are some factors that influence the cost of a monitor in relation to its size:
- Basic vs. High-End Features: Larger monitors with basic features such as TN panel technology, lower resolutions, and fewer connectivity options tend to be more affordable. On the other hand, high-end monitors with features like IPS panels, 4K resolution, advanced ergonomics, and a wide range of ports will typically be more expensive.
- Target Audience: The cost of a monitor can also depend on who it is targeted towards. Budget monitors for basic tasks may cost around $100 or less, while professional-grade monitors for graphic designers or photographers can range from $500 to several thousand dollars.
- Size and Resolution Correlation: While size and resolution are independent factors, they often go hand in hand. Larger monitors usually support higher resolutions, and higher resolutions are more beneficial on bigger screens. As a result, the cost of a monitor can increase with both size and resolution.
- Graphics Card Requirements: The graphics card capabilities needed for a monitor can also impact its cost. Higher resolutions and faster refresh rates typically found on larger gaming monitors require more powerful graphics cards. This means that the overall cost of a high-end gaming setup, including the monitor and graphics card, will be higher.
- Brand and Quality: The brand and overall quality of the monitor can also influence its cost. Monitors from well-known brands with a reputation for high-quality products tend to be more expensive than lesser-known brands.
- Additional Features: Monitors with additional features such as built-in speakers, USB ports, adjustable stands, or touch-screen capabilities will usually be more expensive than those without these extras.
- Technology Advancements: As new technologies emerge, such as OLED or Mini LED, monitors incorporating these advancements will typically be more expensive than those with more traditional panels.
In summary, the cost of a monitor is influenced by a combination of its size, resolution, features, target audience, brand, and the technology used. When choosing a monitor, it's essential to consider your budget, specific needs, and the trade-offs between size and other specifications to find the best option for your setup.
Adjusting Screen Size: Reducing Monitor Display for Better Viewing
You may want to see also

The standard monitor size
The standard size of a monitor is typically measured by the diagonal length of its screen, usually in inches. This is the distance from one corner of the screen to the opposite corner. The standard size for monitors usually falls within the range of 19 to 34 inches, with some ultra-wide models extending beyond 40 inches.
The size of a monitor is an important factor in optimising your workspace or gaming setup. The larger screen provides a more immersive experience for gaming and media consumption, and can also reduce eye strain by providing a more comfortable viewing angle. Larger screens also allow for easier multitasking and side-by-side window arrangements, making them ideal for professionals such as graphic designers, video editors, and programmers.
The most common monitor size is 24 inches, which offers a good balance between screen space and desk space requirements. However, 27-inch monitors are also becoming increasingly popular for both home and office use.
It is worth noting that the size of a monitor is distinct from its resolution, which refers to the total number of pixels available on the screen and determines the level of detail that can be rendered. While larger monitors often support higher resolutions, the two factors are independent, and a single monitor can display a variety of resolutions depending on its video card.
When determining the size of your monitor, it is recommended to physically measure the diagonal length of the screen, excluding any bezels or frames. Alternatively, you can check the model number, specifications, or display settings on your computer to find the size.
How to Track Printer Ink Usage Efficiently
You may want to see also

How to find the screen size of your monitor
There are several ways to find the screen size of your monitor. Here are some methods that can help you determine the size:
Physically Measure the Screen
You can manually measure the size of your monitor using a measuring tape or a ruler. Follow these steps:
- Place the measuring tape or ruler at the top-left corner of the screen.
- Pull it diagonally to the bottom-right corner. Ensure that you only measure the screen itself and do not include the bezel (plastic edge) or frame.
- Note the diagonal measurement in inches or centimetres.
- If needed, you can also measure the height and width of the screen separately.
Check the Model Number
The monitor's size is sometimes included in the model number. For example, "Acer S201HL" indicates a 20-inch screen, where "20" after the "S" represents the screen size. Typically, the model number starts with one or two letters, followed by numbers, and the first two numbers after the letters indicate the screen size.
Review Device Specifications
For laptops, smartphones, and tablets, you can review the device specifications to find the screen size. Look for a section labelled "Screen", "Display", or something similar. The screen size will be listed in this section, usually in inches.
Check Online
If you are unable to find the screen size in the specifications, you can search for your device's model number online, which should provide the screen size information.
Use Display Settings (Windows)
If you are using a Windows computer, you can check the display settings:
- Right-click on your desktop and select "Display Settings".
- Click on "Advanced scaling settings" under "Scale and layout".
- On the Advanced scaling settings page, click on "Advanced sizing of text and other items".
- This will open the "Screen Resolution" settings in the Control Panel, where you can find the diagonal measurement of your screen.
Use System Report (Mac)
On a Mac, follow these steps:
- Go to the Apple menu in the top-left corner of your screen and choose "About This Mac".
- Click on "System Report" at the bottom of the window.
- In the System Report window, scroll down to the "Graphics/Displays" section and click on it.
- Here, you will find a list of all the displays connected to your Mac, including internal and external ones. Click on a display to check its resolution, and then use the resolution and aspect ratio to calculate the diagonal screen size.
By using one or a combination of these methods, you should be able to accurately determine the screen size of your monitor.
Calibrating Your ASUS Monitor: Perfect Color Display
You may want to see also

How to calibrate your monitor
To find out the size of your monitor, you can manually measure the distance from one corner of the screen's viewable area to the diagonally opposite corner. This is the standard way to measure monitor size.
Now, here is a detailed guide on how to calibrate your monitor:
Brightness & Contrast:
The 'Backlight' setting changes the amount of light your monitor outputs, making it brighter. Changing the backlight level does not significantly alter the accuracy of your screen, so you can set it to your preference. The brightness setting, on the other hand, affects how the monitor handles darker colours. If set too high, blacks will look grey, and the image will have less contrast. If set too low, the blacks will get "crushed", meaning instead of showing distinct near-black steps of grey, the monitor will show them as pure black.
Picture Mode:
The picture mode presets usually alter most of the image settings. If you are not using a colorimeter for calibration, this is an important setting to adjust as it can be difficult to enhance your monitor's colour accuracy otherwise. The 'Standard' or 'Custom' preset is generally the best option, while some monitors also offer an "sRGB" picture mode to enhance image accuracy.
Sharpness:
Adjusting the sharpness changes the appearance of edges on-screen. Having it too low will result in a blurry image, while setting it too high will give the picture an odd look with strange-looking edges. The default setting is usually fairly accurate, but if you are not satisfied, you can set it to the maximum and then lower it until no strange pattern forms between the lines and shapes of the test image.
Colour Temperature:
The colour temperature adjusts the overall picture's temperature. A cooler temperature gives a blue tint, while a warmer temperature gives a yellow or orange tint. A 6500k colour temperature is generally recommended as it is the standard for most screen calibrations and is equivalent to midday light.
White Balance:
White balance refers to the balance of colours across different shades of grey. While it is not possible to adjust these settings without the necessary equipment, you can keep them at their defaults to avoid making things worse.
ICC Profiles:
If you calibrate your monitor using a tool, it will likely create a calibration profile that ends in .icm. This is an ICC profile, a reference table that your computer's programs can use to display content accurately on your screen. While Apple's macOS handles these profiles well, Windows and Windows applications tend to be inconsistent in their usage.
Additional Settings:
Some monitors feature a 'Game Mode' or 'Low Input Lag Mode', which lowers the monitor's input lag without altering image quality, making it more responsive. Many monitors also have a blue light filter, often called 'Low Blue Light' or 'Reader Mode', which reduces eye strain and is built into most desktop operating systems.
Troubleshooting an ASUS Monitor with No HDMI Signal
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To measure the size of your monitor, you need to measure the distance from one corner of the screen to the diagonally opposite corner. This is the standard way to measure monitor size.
Desktop computer monitors are available in sizes ranging from 13 to 43 inches. Some users may use their TV as a monitor, with screen sizes of 55 inches or more. Laptop screens generally range from 11.6 to 17 inches.
You can find the screen size of your monitor by checking the model number. The monitor size is usually included in the model number. For example, Acer S201HL means the monitor size is 20 inches.
To find the resolution of your monitor, right-click on your desktop and select Display Settings. Under Scale and Layout, you will find a setting for Resolution.