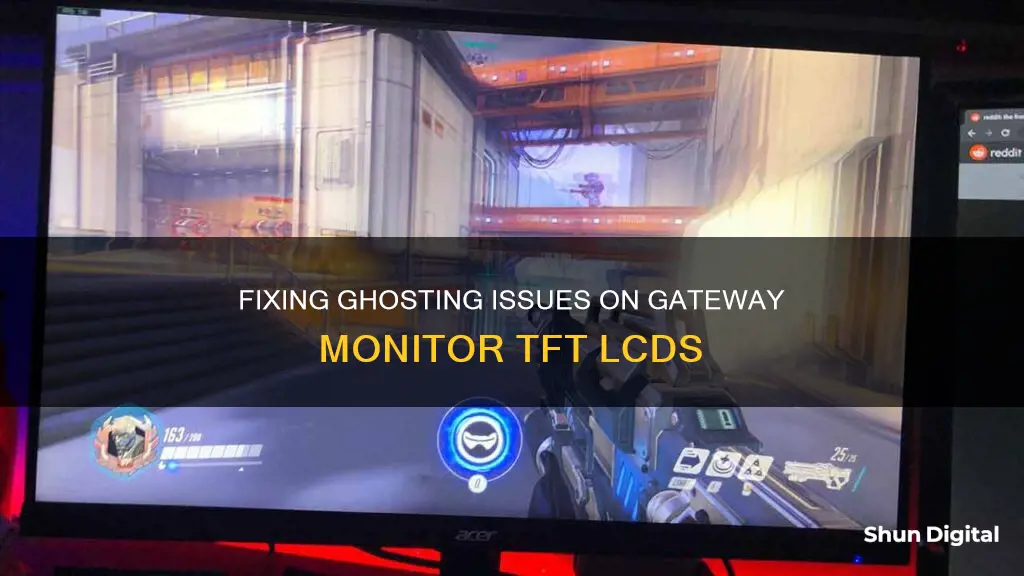
Ghosting on a monitor is when a moving object leaves traces of where it has been on the screen. It is a common issue, especially for gamers who haven't configured their gaming monitors correctly. It is caused by a slow response time from the monitor, which results in a trail of pixels behind a moving object, almost like a motion blur. This can be fixed by performing some preliminary checks, updating graphics card drivers, modifying monitor display settings, modifying graphics card settings, and checking for monitor damage.
What You'll Learn

Adjust monitor settings
Adjusting your monitor settings can be an effective way to stop ghosting on your Gateway monitor. Here are some detailed instructions to help you with the process:
Set a Higher Refresh Rate:
- Right-click on your desktop and select "Display Settings".
- Click on "Advanced Display Settings".
- Find the "Refresh Rate" option and select the highest available value from the drop-down menu.
- Close the Settings app and restart your computer to apply the changes.
Adjust Response Time Settings:
- Use the buttons on your monitor to access the settings menu.
- Look for the "Response Time" setting and change it to the fastest or lowest available value, preferably 5 milliseconds or lower.
- On some monitors, this setting may be called "Overdrive" or "Advanced Motion Acceleration" (AMA). If you find these options, turn them on and adjust the values if possible.
Disable Certain Settings:
- Go to your monitor's settings or your graphics card's menu.
- Look for settings such as "Noise Reduction", "Dynamic Contrast", "Perfect Clear", and "Motion Smoothing".
- Disable or turn off these settings, especially if you experience ghosting when viewing darker images.
Change Display Profile:
- Access your monitor's settings using the buttons on the monitor.
- Look for a menu where you can change display profiles.
- Select a profile designed for gaming, such as "Gamer", "FPS", or "RTS".
Enable Motion Blur Reduction:
- Many monitors have motion blur reduction features that can help reduce ghosting.
- Check your monitor's settings for motion blur reduction options.
- Enable these features to minimize ghosting and improve visual clarity.
Use a Screensaver:
- Set up a screensaver on your monitor to prevent the continuous display of static images, which can contribute to ghosting.
- A screensaver will keep your pixels cycling and prevent them from staying in the same position for too long.
By following these steps and adjusting your monitor settings, you should be able to significantly reduce the ghosting effect on your Gateway TFT LCD monitor.
Troubleshooting an ASUS 144Hz Monitor Not Reaching 144Hz
You may want to see also

Use a screensaver
Using a screensaver is an effective way to prevent ghosting on your Gateway monitor. A screensaver is a computer program that activates when your device is idle, filling the screen with moving images or patterns.
The original purpose of screensavers was to prevent burn-in on CRT or plasma monitors, which occurs when the same image is displayed for long periods. Although modern LCD screens are not susceptible to burn-in, screensavers are still useful for preventing ghosting.
To prevent ghosting, ensure your screensaver activates after your device has been idle for no longer than 20 minutes. You can also customise your screensaver to display moving images, which is the most effective solution to avoid ghosting. This can be as simple as displaying a bouncing ball instead of a static one.
In addition to preventing ghosting, screensavers can also be used for entertainment, password protection, and running useful background tasks such as virus scans.
How to Track Printer Ink Usage Efficiently
You may want to see also

Turn off the display
Turning off the display is one of the ways to prevent ghosting on a Thin-Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display (TFT LCD) monitor. Ghosting is a common phenomenon in these monitors, where an image remains faintly visible even after it has been replaced by a new one. This issue arises when certain pixels in the LCD do not immediately revert to their inactive state, causing a "ghost" of the previous image to persist.
To prevent and address this issue, it is recommended to turn off the display, even for a short amount of time. Doing so allows the pixels to reset and can help reduce the occurrence of ghosting. Turning off the display for a few hours occasionally should be sufficient. This is particularly effective when combined with other measures, such as using screen savers and adjusting the motherboard's voltage to match the LCD screen.
Additionally, it is important to avoid displaying static or high-contrast images for extended periods, as this can contribute to the ghosting issue. The slow response time of liquid crystals is the primary cause of ghosting, and by avoiding static images, you can help prevent the pixels from becoming less responsive to change.
It is also recommended to regularly clean your screen. You can do this by creating a completely white image and moving it around the screen for several hours without turning on the backlight. This can help extend the lifespan of the backlight LEDs and reduce the likelihood of ghosting.
By following these measures, you can effectively prevent and reduce ghosting on your TFT LCD monitor.
Standard Monitor Size: Understanding the 1280x1024 Resolution
You may want to see also

Check monitor cables
To check for issues with your monitor cables, you should:
- Inspect the cable for any signs of damage, including fraying or other physical damage.
- Check the connectors on both ends of the cable for signs of corrosion or damage.
- Try using a different cable to see if the issue persists.
- If you're using an HDMI cable, consider switching to a DisplayPort cable, as this offers better video quality.
If you suspect that the issue may lie with other connected devices, try the following:
- Disconnect any wireless devices connected to your system one at a time to see if this improves the ghosting issue.
- Move any wireless devices further away from your monitor to reduce potential signal interference.
- Ensure that any devices connected to your PC, such as printers or speakers, are not causing the issue by testing with them disconnected.
Wall Mounting Your ASUS: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Update graphics card drivers
Updating your graphics card drivers is an important step in troubleshooting monitor ghosting issues. This is especially true if you play games regularly, as it is possible that a bug or compatibility issue is the root of the ghosting problem.
Identify Your Graphics Card
Before updating your graphics card driver, you first need to identify which graphics card your computer is using. This can be done by following these steps:
- Click on the Windows Start button.
- Type "System Information" into the search box and press Enter.
- In the System Information dialog box, expand the "Components" entry and select "Display".
- On the right panel, the graphics display adapter will be listed in the "Adapter Type" or "Adapter Description" entries.
- Update Graphics Card Driver
Once you have identified your graphics card, you can proceed to update the driver. Here are the steps to update your graphics card driver in Windows:
For Windows 11:
- Open the Windows Start menu and type "Device Manager". Click Open.
- Click "Display adapters", then right-click your graphics card and select "Update Driver".
- Select "Search automatically for updated driver software".
- Your computer will scan for available updates and download and install them automatically.
- Once the updated driver is installed, you will be informed and asked to restart your PC.
For Windows 10:
- Click Start, type "Device Manager", and click Open.
- Click "Display adapters" and select your graphics card.
- Open the Driver tab, click "Update Driver", and select "Search automatically for updated driver software".
- Alternatively, you can select "Browse my computer for driver software" to choose a driver that you have already downloaded. Then click "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer".
- Click "Have Disk" > "Browse" to navigate to the folder that contains the new driver. Click "Next".
- You can now explore the new graphics control panel to learn about new features or adjust settings.
For Windows 7:
- Right-click on the Computer icon on your desktop and choose "Properties".
- Open "Device Manager".
- Go to "Audio, Video and Game Controller".
- Look for an entry for your graphics card, which will be listed under the "Display Adapters" heading.
- Double-click on the entry for your graphics card and switch to the Driver tab.
- Click "Update Driver" and select "Search automatically for updated driver software".
- If no new drivers are found, repeat steps 1-3 and select "Browse my computer for driver software".
- Windows will now prompt you for a driver location. If you haven't downloaded a driver yet, you can skip to the next section to learn how to get your graphics drivers.
- If you have found the right driver but it didn't come with an installer, extract the file from the directory you downloaded it from. The file will likely end in ".inf".
- Click "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer".
- Click "Have Disk" and then "Browse". Find the folder of the new graphics driver you downloaded and double-click on the ".inf" file.
- Click "Next" to install the driver. Your display may go blank temporarily during the installation.
- You can now explore the new options provided by the manufacturer in the graphics control panel.
- Get Graphics Drivers from Official Websites
If you are unable to find updated drivers using the methods above, you can manually download the driver directly from the graphics hardware manufacturer's website. Make sure to download the driver that matches your graphics adapter. Here are the websites for the three major graphics driver makers:
- Intel: intel.com
- NVIDIA: nvidia.com
- AMD: amd.com
Download the drivers from the appropriate website and install them using the provided setup program.
Monitoring Data Usage: Strategies for Effective Data Management
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Ghosting occurs when the pixel response time of the monitor is too low, causing visual artifacts. It can also be caused by a faulty monitor cable, unoptimized monitor settings, or other devices interfering with the monitor-to-PC connection.
Try updating your graphics card drivers, modifying your monitor's display settings, and checking for any damage to the monitor cable. You can also try adjusting the monitor's refresh rate and response time, and enabling motion blur reduction features.
Image retention is commonly temporary and reversible, with an image temporarily displayed on the screen even when the content has changed. Burn-in is a form of permanent image retention that is harder to fix.
Use a screensaver to keep the pixels cycling, power off the display when not in use, and keep the display brightness as low as possible.
Avoid placing high-contrast patterns side-by-side in a fixed image, use a background with bright colors, and apply motion to the screen.