Performance Monitor is a tool that can be used to check on the performance of your system and identify how different programs affect system performance. It can tell you how system resources are being managed and provide other configuration information that might be useful. It can also collect and log data in files for analysis later.
Performance Monitor allows you to view and analyse application and hardware data to fix system performance-related problems. You can also customise what data to collect in log files, define alerts, generate reports, and replay collected performance data in many ways.
Performance Monitor can be used to monitor virtually anything on your computer. You can monitor processor, hard drive, memory, and network usage. You can also add counters to monitor applications and hardware performance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Graph display | Flexible and configurable |
| Counter configuration | Simplified |
| Graphs | Can be printed when saved as HTML files |
| System Monitor | Portable |
| System Monitor display | Toolbar, area where counter values are displayed, legend, value bar, timer bar |
| Toolbar | Type of display, data source, counters, data updates, highlighting chart or histogram data, importing or exporting counter settings, configuring other System Monitor properties |
| Shortcut menu | Add Counters, Save As, Properties |
| Data source | View Current Activity, View Log File Data |
| Histogram and reports | Useful for simplifying graphs with multiple counters |
| Line graphs | More informative for identifying trends |
| Scale | Can be adjusted to enhance the visibility of counter data in the chart |
| Performance Monitor | Can be used to view and analyze application and hardware data to fix system performance-related problems |
| Data Collector Sets | Can be used to create custom sets containing performance counters and alerts based on specific criteria |
What You'll Learn

How to open Performance Monitor
There are several ways to open the Performance Monitor on a Windows device.
Using the Start Menu
One way to access the Performance Monitor tool is via the Start Menu. For Windows 10, click on the Windows icon on the taskbar, scroll down the list of apps until you see the Windows Administrative Tools folder, and click to expand it, then find and click on the Performance Monitor shortcut.
For Windows 11, click on the Windows icon, then click on All Apps. Scroll down to the All Apps list until you see the Windows Tools shortcut and click on it. The Windows Tools window will open, and you will see the Performance Monitor shortcut. Double-click on this shortcut to open the app.
Using Search
You can also use the search function to open Performance Monitor. For Windows 10, click or tap inside the search bar or press the Windows key on your keyboard. Type "perfmon" or "Performance Monitor", then press Enter or click/tap on the appropriate search result.
In Windows 11, the process is the same; just click or tap inside the search box, type "Performance Monitor" or "perfmon", and press Enter.
Using the Command Line
If you need to start Performance Monitor from the command line, you can do so by opening Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal and typing "perfmon" or "perfmon.exe" in the command line.
Using the Run Command
Another quick method is to press the Windows + R keys on your keyboard to open the Run window. In the Open field, type "perfmon" and press Enter on the keyboard or click OK.
Using Computer Management
Performance Monitor is also included in the Computer Management app, which is a useful tool for troubleshooting problems with your Windows computer. Open Computer Management, and you will find the Performance section in the menu tree on the left side of the Computer Management window, in the System Tools section above Device Manager. Click on Performance to access the full Performance Monitor tool.
Monitoring Digital Ocean: Data Transfer Usage Insights
You may want to see also

How to use Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor is a tool that can be used to view and analyse application and hardware data to fix system performance-related problems. It can be used to monitor resource usage and server processes, including how often the CPU is being used, how much memory is being used, and more.
Opening Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor can be opened in three ways:
- Open Start, search for Performance Monitor, and click the result.
- Use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command, type "perfmon", and click OK.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu, select Computer Management, and click on Performance.
Using Performance Monitor
When you first open the tool, it will display a system summary with real-time data about memory, network adapter, physical disk, and processor usage. On the left, you will find the navigation pane with access to Performance Monitor, Data Collector Sets, and Reports.
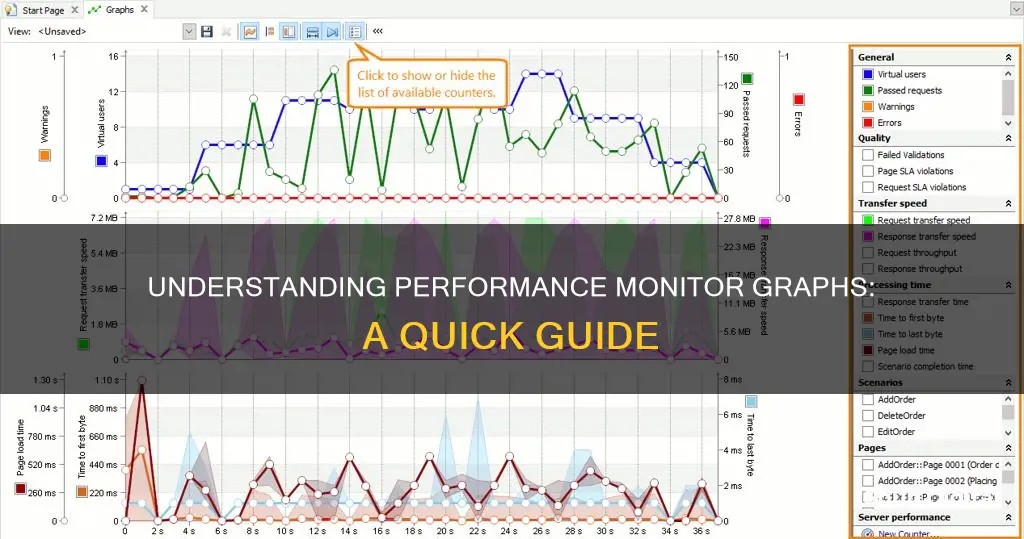
Performance Monitor initially displays a single counter, which is typically the "Processor Time" counter, showing the processor load in the last 100 seconds. You can add other counters to monitor different aspects of your computer by clicking the green plus button above the Performance Monitor graph.
Customising Performance Monitor
Once you have set up your counters, you can customise various aspects of the data shown in the graph. To do this, double-click on one of the counters to open the Performance Monitor Properties window. From here, you can select the counter you want to customise, and choose the colour, scale, width, and style.
You can also change the graph's style by clicking the "Change graph type" in the toolbar and selecting from the available views, including Line, Histogram bar, and Report.
Data Collector Sets
Performance Monitor includes Data Collector Sets, which allow you to create custom sets containing performance counters and alerts based on specific criteria. To create a custom Data Collector Set:
- Expand Data Collector Sets in Performance Monitor.
- Right-click "User Defined", select New, and click on Data Collector Set.
- Name your Data Collector Set and select "Create manually (Advanced)".
- Choose whether to create data logs or create a Performance Counter Alert.
- Set the counter interval rate and select the specific counters you want to capture.
- Click "Add" and select the counters you want to add to the "Added Counters" box.
- Specify a location to save the data.
- Select a user to run the data collector set as.
Best Places to Buy Ultrawide Monitors: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

How to add new counters
To add new counters to monitor applications and hardware performance on your computer, follow these steps:
- Open the Performance Monitor. On Windows, you can do this by searching for "Performance Monitor" in the Start menu and clicking the result. Alternatively, you can use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command, type "perfmon", and click OK.
- In the left menu, click "Performance Monitor" under "Monitoring Tools".
- At the top of the "Performance Monitor" pane, click the "View Current Activity" icon.
- To add counters, right-click in the report area and click "Add Counters". This will open the "Add Counters" window.
- Click the green plus button above the "Performance Monitor" graph.
- Select "Local computer" or the name of your computer from the drop-down menu.
- Select and expand the category of the item you want to monitor. For example, if you want to monitor network performance, select the "Network Adapter" category.
- Select the counters you want to monitor. For example, you might select "Bytes Total/sec" to monitor network performance. If you want to add multiple counters, hold the Ctrl key and click to select each item. You can also check the "Show description" option to get more information about each counter.
- If applicable, select the instances you want to monitor. For example, for the "Network Adapter" category, you can choose to monitor one or multiple network adapters simultaneously.
- Click the "Add" button, then click "OK" to confirm and add the new counters.
Once you've added the counters, you can customize the Performance Monitor view by changing the colour, scale, width, and style of the data displayed in the graph.
Connecting LG Monitor to MacBook Air: A Simple Guide
You may want to see also

How to customise the counter view
To customise the counter view in Performance Monitor, you can change the graph type, the graph duration, the sampling rate, the colour, width and style of the lines, and the view's general settings.
- To switch between the views, select the graph type button drop-down and select the preferred view. The three display options are Report, Line and Histogram.
- To configure the views, click the Properties button or right-click on the chart and select Properties.
- The General tab will allow you to set the sampling rate and the graph duration. The sampling rate affects how often new data is added to the graph, and the graph duration affects the x-axis on the line graph.
- The Data tab allows you to add or remove counters, and choose the colour, width and style of the lines for each counter.
- The Graph tab allows you to select the view and alter the view's general settings. You can keep the bar moving across the screen at the point of the current data by selecting the "Wrap" setting.
- The vertical and horizontal grids add lines to the grid to help interpret the numbers. You can also add or remove the x and y axis labels.
LCD Monitors: Hazardous or Harmless?
You may want to see also

How to use Data Collector Sets
Data Collector Sets are used to collect multiple data sets on-demand or over a period of time. They can be created and configured by an administrator or automatically by the operating system. The data collected can be used to generate detailed reports and recommended fixes for performance issues.
To create a custom Data Collector Set:
- Open Server Manager.
- Expand the node Diagnostics | Performance | Data Collector Sets.
- Right-click User Defined and choose New | Data Collector Set. This will launch the New Data Collector Set wizard.
- Enter a descriptive name for the Data Collector Set and choose the Create Manually option.
- Select the types of data you want to collect, such as Performance counter and System configuration information. Then click Next.
- Add the relevant performance counters, such as % Processor Time. Keep the default sample interval or adjust it as needed.
- The Data Collector Set will use registry keys to determine system configuration information. You can add keys in the Registry Keys window.
- Click Finish.
To run a Data Collector Set:
- Right-click the Data Collector Set and choose Start.
- To stop the Data Collector Set, right-click and choose Stop.
You can also create a Data Collector Set using a template or the Performance Monitor. When using a template, select Create from a template and choose from Basic, System Diagnostics, or System Performance options. When using the Performance Monitor, right-click the Performance Monitor node, click New, and select Data Collector Set. Type a name, select a folder, and specify a user account.
Removing the Bezel from Your ASUS Monitor: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can open the Performance Monitor by searching for it in the search field on the taskbar, using the Windows key + R shortcut and typing "perfmon", or by using the Windows key + X shortcut, selecting Computer Management, and clicking on Performance.
Click the green plus button above the Performance Monitor graph, select your computer from the drop-down menu and expand the category of the item you want to monitor. Select the counters you want to monitor, click "Add", and then "OK".
Double-click one of the counters to open the Performance Monitor Properties window, and select the counter you want to customise on the "Data" tab. Choose the colour, scale, width, and style you want to use, and repeat for each item you want to customise.
Click the "Change graph type" button in the toolbar and select one of the available views: Line, Histogram bar, or Report.
Right-click on the graph and select "Save settings as". The settings will be saved as an HTM file, which can be opened using Internet Explorer or by copying and pasting the content into Performance Monitor.