Monitoring your CPU usage is an important way to know if you're getting the best performance out of your processor. In Windows, there are several ways to do this, from quick and simple to more detailed. Here are some methods to monitor CPU usage in Windows:
- Using Task Manager: Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc and go to the Performance tab. You can also sort the processes by CPU usage to identify which process is causing high usage.
- Using the System Tray: Look for the CPU usage icon in the bottom right corner of the screen. A computer with high CPU usage will have an icon indicating the amount of used and available CPU.
- Using the Command Prompt: Open the Command Prompt and type wmic cpu get loadpercentage to see the current CPU usage percentage.
- Using Third-Party Tools: Tools like Process Explorer, Task Manager Deluxe, and CPU-Z can provide more detailed information about CPU usage and help identify which programs and processes are using the most CPU.
- Using Resource Monitor: Search for Resource Monitor and open the CPU tab to see the processor's usage, including how much of the CPU is available and what is running.
- Using Performance Monitor: This tool allows you to study how apps perform in real-time or by collecting data for later analysis. With this, you can identify apps behaving abnormally.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Keyboard shortcut to open Task Manager | Ctrl + Shift + Esc |
| Alternative keyboard shortcut to open Task Manager | Ctrl + Alt + Del, then click Task Manager |
| Alternative way to open Task Manager | Right-click the Windows button, select Task Manager |
| Alternative way to open Task Manager | Right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager |
| Task Manager column to click on to see CPU usage | CPU |
| Alternative Task Manager column to click on to see CPU usage | Performance > CPU |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Use the System Tray in the bottom right corner of the screen |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Open the Command Prompt and type "wmic cpu get loadpercentage" |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Use a third-party tool such as Process Explorer, Task Manager Deluxe, or CPU-Z |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Use the Resource Monitor and select the CPU tab |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Use Performance Monitor and select the Performance Monitor tab |
| Alternative way to see CPU usage | Use HWInfo64 |
What You'll Learn

Using Task Manager
The Task Manager is a useful tool to monitor your Windows 10 computer's performance in real-time. It can be opened in several ways:
- Right-click the Taskbar and click on Task Manager.
- Open Start, search for Task Manager and click the result.
- Use the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keyboard shortcut.
- Use the Ctrl + Alt + Del keyboard shortcut and click on Task Manager.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the power-user menu and click on Task Manager.
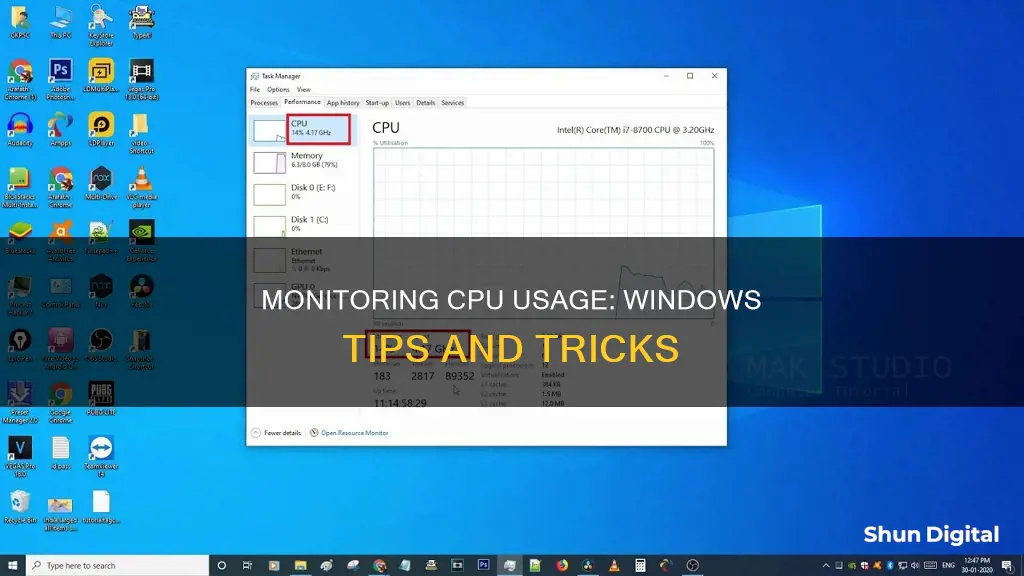
Once opened, the Task Manager window defaults to the Processes tab. If you see a single list of process names in the Name column, you can expand any instances of grouped processes. To check the CPU usage, select the CPU column header to sort the list by CPU usage, with the arrow pointing down to sort the data from highest to lowest consumption.
The Performance tab in Task Manager provides a detailed, real-time overview of the performance of your computer, including CPU and memory usage, as well as hard drive, network, and Bluetooth information. The CPU section provides details about the processor and resource utilisation. The graph shows the overall utilisation of the processor over a 60-second period. You can also view a graph for each core of your processor by right-clicking inside the section and selecting "Logical processors".
The Memory section offers a view of the RAM usage by the system and applications. There are two graphs: the first shows total memory usage over a 60-second period, and the second shows the amount of memory currently allocated. The Disk section provides important information about hard drive usage, including the hard drive activity and transfer speeds over a 60-second period.
The Task Manager also provides a separate section for each Ethernet or Wi-Fi adapter installed on your computer, even for virtual network adapters. There is only one graph in this section that shows the throughput of the adapter over a 60-second period.
The Performance tab also includes a Bluetooth section, which will show more information when you connect your phone or another device and begin transferring data.
Monitoring Power Usage: Simple Steps for Your Home
You may want to see also

Using Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor is a tool that displays information about hardware and software resources in real-time. It is included in several versions of Windows and can be used to monitor CPU usage and utilisation.
To open the Resource Monitor, you can use the following methods:
- Use Windows-R to open the run box. Type resmon.exe, then hit Enter.
- Use Windows-R to open the run box. Type perfmon.exe /res, then hit Enter.
- On Windows 10, select Start > All Apps > Windows Administrative Tools > Resource Monitor.
- On previous versions of Windows, select Start > All Programs > Accessories > System Tools > Resource Monitor.
- Open the Windows Task Manager with Ctrl-Shift-Esc. Switch to the Performance tab, then select "Open Resource Monitor".
The Resource Monitor interface has five tabs: Overview, CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network. The Overview tab provides a summary of resource usage, including CPU and memory usage, disk utilisation, and network use in real-time.
To monitor CPU usage in detail, switch to the CPU tab. Here, you will find a list of processes, along with Services, Associated Handles, and Associated Modules. You can filter the data by processes to see links between processes, services, and other files on the system. The graphs on the CPU tab show the usage of each core, Service CPU usage, and total CPU usage.
The Associated Modules section lists files such as dynamic link libraries used by a process, while Associated Handles point to system resources such as files or Registry values. Right-clicking on any process in the CPU tab will display a context menu with options to end the process, suspend or resume processes, and run an online search.
The Memory tab focuses on memory usage and provides a physical memory view, visualising the distribution of memory on the Windows machine. It lists processes along with their name, process ID, hard faults, and various memory-related information.
The Disk tab lists disk activity for processes and storage information. It shows the disk usage for each running process and provides a reading of each process's disk read and write activity. The Storage listing shows all available drives, their available and total space, and active time. The graphs on this tab visualise the disk queue length, indicating the number of requests for the disk and helping to identify if disk performance is keeping up with I/O operations.
Finally, the Network tab lists network activity, TCP connections, and listening ports. It provides detailed information on the network activity of any running process, including remote servers that processes connect to, bandwidth usage, and local listening ports.
Monitoring Data Usage on Your MacBook Pro: A Guide
You may want to see also

Using Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor is a tool that allows you to study how applications perform in real-time or by collecting data for later analysis. With this tool, you can identify which apps are behaving abnormally and, hopefully, why.
Opening Performance Monitor
To open Performance Monitor, you can:
- Open Start, search for Performance Monitor, and click the result.
- Use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command, type "perfmon", and click OK.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu, select Computer Management, and click on Performance.
When you first open the tool, it will display a system summary with real-time data about memory, network adapter, physical disk, and processor usage.
On the left, you'll find the navigation pane with access to Performance Monitor, Data Collector Sets, and Reports.
Performance Monitor will initially display a single counter, typically the "Processor Time" counter, which shows the processor load in the last 100 seconds. However, you can add other counters to monitor virtually anything on your computer.
Adding Counters
To add new counters to monitor applications and hardware performance on your computer, do the following:
- Click the green plus button above the Performance Monitor graph.
- Select Local Computer or the name of your computer from the drop-down menu.
- Select and expand the category of the item you want to monitor.
- Select the counters you want to monitor.
- If applicable, select the instances you want to monitor.
- Click the Add button.
- Click OK to confirm and add the new counters.
Customising Performance Monitor View
Once you have configured all the counters you want to monitor, you can also customise various aspects of the data shown in the graph.
To customise the Performance Monitor view:
- Double-click one of the counters to open the Performance Monitor Properties window.
- On the "Data" tab, select the counter you want to customise.
- At the bottom, choose the colour, scale, width, and style you want to use.
- Repeat steps 2 and 3 for each item you want to customise.
Additionally, you can change the graph's style by clicking "Change graph type" in the toolbar and selecting one of the available views, including Line, Histogram bar, and Report.
Performance Monitor Counters
- % Disk Time to monitor the time a drive is taking to complete read and write requests.
- % Interrupt Time to monitor the time the CPU takes to complete hardware requests (interrupts).
- % Committed Bytes in Use to monitor the total memory currently in use by your system.
- Bytes Received/sec, Bytes Sent/sec, Bytes Total/sec to see how much bandwidth is being used by your wireless or Ethernet adapter.
- % Usage and % Usage Peak to monitor how page files are being utilised.
Monitoring Xbox Usage: Remote Control for Parents
You may want to see also

Using Xbox Game Bar
The Xbox Game Bar for Windows 10 has been updated to include a Resources widget that can track which applications are using your system resources, including Random Access Memory (RAM), Central Processing Unit (CPU), and Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). This widget can be pinned to your desktop, allowing you to monitor resource usage while you continue gaming or working.
The widget provides an overview of the top tasks and their associated impacts, rating them as low, medium, or high. This simple rating system helps you quickly identify which applications are consuming the most resources.
In addition to the Resources widget, the Xbox Game Bar also includes a Performance widget. While the Resources widget focuses on specific applications, the Performance widget monitors overall system utilization. This widget has also been updated to include GPU utilization and GPU memory usage, in addition to its previous capabilities.
If you are a gamer, the Xbox Game Bar is a useful tool as it allows you to monitor resource usage without ever having to tab out or leave your game. You can even close resource-intensive applications directly from the widget, helping you free up resources without interrupting your gaming experience.
To access these widgets, simply open the Xbox Game Bar on your Windows 10 device. If you cannot see the widgets, check for updates in the Microsoft Store app and install the latest version of the Xbox Game Bar.
Monitoring GPU Usage: MSI Afterburner Guide
You may want to see also

Using HWInfo64
HWInfo64 is a popular and comprehensive PC monitoring tool that can be used to monitor your CPU usage in Windows. It provides in-depth hardware information and real-time system monitoring, including CPU, GPU, and system metrics. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to use HWInfo64 to monitor your CPU usage:
Download and Install HWInfo64:
Go to the HWInfo website and download the latest version of HWInfo64. Once the download is complete, install the program by following the installation wizard.
Launch HWInfo64:
Open the HWInfo64 application. The program will automatically start scanning your system and gathering information about your hardware, including your CPU.
Navigate to the CPU Section:
In the HWInfo64 interface, look for the "CPU" section. This section will provide you with detailed information about your CPU, such as its model, speed, temperature, and usage.
Monitor CPU Usage:
Within the "CPU" section, you'll find various metrics related to CPU usage. This includes the current CPU usage percentage, the number of cores and threads, and the individual core usage. You can monitor these metrics in real time to get an understanding of your CPU's performance.
Customize the Interface:
HWInfo64 allows you to customize the interface to suit your needs. You can rearrange the order of the sensors, hide or display specific sensors, and even change the color scheme. This customization can help you focus on the CPU metrics that are most important to you.
Enable On-Screen Display (OSD):
HWInfo64 offers an on-screen display feature that allows you to view monitoring metrics directly in your games or other full-screen applications. With the OSD, you can track CPU usage, GPU temperature, or any other supported metrics without alt-tabbing out of your game.
Set Up Notifications and Alerts:
HWInfo64 can also provide you with notifications and alerts for specific system events or when certain thresholds are met. For example, you can set up an alert to notify you if your CPU usage exceeds a certain percentage, helping you identify potential performance issues.
Generate Reports:
HWInfo64 allows you to generate detailed reports of your system's hardware and performance. These reports can be exported in various formats and are useful for troubleshooting, system comparisons, or sharing your system specifications with others.
By following these steps, you can effectively use HWInfo64 to monitor your CPU usage in Windows. Remember to update HWInfo64 regularly to take advantage of the latest features and improvements.
Monitoring Plex CPU Usage: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc or Ctrl + Alt + Delete and then click Task Manager from the options presented. Alternatively, you can find the Task Manager via the Start Menu or the Taskbar: Right-click the Windows button or the Taskbar and select Task Manager.
Open the Task Manager and select the Performance tab. Select CPU to see a graph of what percentage of your total CPU power is in use. To see which apps are using the CPU the most, open the Processes tab.
Click on the Performance tab of Task Manager, click CPU, then hover your mouse over the charts showing your CPU cores, right-click, and select Graph Summary View. You can resize it to fit your desktop.
Open the Start menu, then search for Resmon and open the Resource Monitor. Select the CPU tab to view the processor's usage.
Open Search from the taskbar and type Performance Monitor. Open the first entry in the list to launch this tool. Select the Performance Monitor tab to see the CPU performing in real time.







