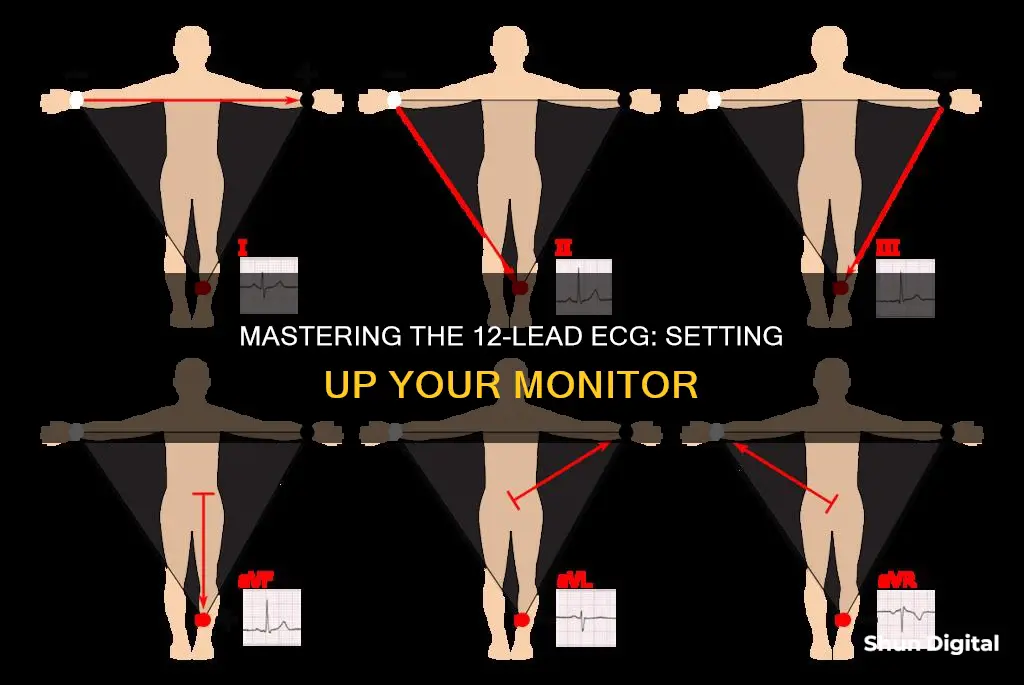
A 12-lead monitor is a vital tool for patient care, providing a continuous graphic picture of electrical activity in the heart. To hook one up, you must first position the patient supine, or in a Semi-Fowler's position if they cannot tolerate lying flat. Next, expose the area where the electrodes will be placed and select the appropriate electrodes for your machine. Prepare the skin by removing hair and oils, and then apply the electrodes. For a 12-lead ECG, the electrode placement must be exact, so follow the rules for placement carefully. Finally, connect the electrode wires to the monitor and acquire the ECG.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Positioning of patient | Ideally supine, but Semi-Fowler's position (partially reclined) is also acceptable |
| Electrode placement | On the limb, between the shoulder and wrist, not over bony prominences or large muscle groups; chest leads must be exact |
| Electrode selection | Check use-by date, ensure conductive gel hasn't dried out, style may vary depending on the EKG machine |
| Skin preparation | Remove body hair and oils with a razor and alcohol pad respectively; rub area with gauze if there is excessive dead or dry skin |
| Display preferences | Duplicate displays, extend displays, or show only on one display |
| Primary display | Can be selected in System Settings/Preferences or Displays |
What You'll Learn

Understanding the benefits of connecting a monitor to a laptop
Connecting a monitor to a laptop can be highly beneficial in many ways. Here are some of the key advantages:
Enhanced Productivity and Focus
A dual monitor setup extends your laptop screen, providing more visual workspace. This setup allows you to work with multiple applications or documents side by side, reducing the need to switch between tabs frequently. Consequently, you can improve your productivity and maintain better focus by minimising distractions.
Improved Ergonomics and Viewing Experience
A larger screen offers a better viewing experience, especially when watching movies or playing games. On a smaller laptop screen, your eyes have to work harder to focus, which can lead to eye strain. With a bigger monitor, you'll have a more comfortable and ergonomic setup, reducing the risk of neck and back complaints after long work sessions.
Convenience and Portability
Monitors are easy to connect to laptops using common interfaces such as HDMI or USB-C. Additionally, if you need a portable solution, companies like Asus offer lightweight and durable portable monitors specifically designed for travel, providing you with a convenient option for working or gaming on the go.
Replication of Traditional Office Setup
If you're used to working on a desktop with multiple monitors in your office, having an additional monitor for your laptop can replicate that traditional setup. This is especially beneficial if you need to work remotely or travel frequently, as it provides a similar working environment, enhancing your overall computing experience.
Power Delivery
When you connect your laptop to a monitor using a USB-C cable, you can also benefit from power delivery. This setup can solve the issue of your laptop's battery draining during the day. A monitor with at least 65W of power delivery is typically sufficient, but remember to ensure your laptop has a compatible USB-C port or adapter.
Monitoring Bandwidth Usage: A Guide for D-Link Routers
You may want to see also

Knowing the different types of cables and ports
- HDMI: This port transmits both audio and video signals, making it ideal for connecting a TV to a PC. HDMI is commonly found on modern home entertainment devices, such as flat-panel TVs and Blu-ray players.
- DVI: The Digital Visual Interface (DVI) port transmits video signals in digital format, ensuring high image quality. It supports both analog and digital signals and is perfect for older systems or for a 144Hz display at 1080p resolution.
- DisplayPort: DisplayPort is considered the best connector for transmitting audio and video signals. It can transmit 144Hz up to 4K resolution and often includes a USB channel, eliminating the need for a separate USB cable.
- VGA: The Video Graphics Array (VGA) port is an older, legacy video connector. It is typically only used when no other options are available, as newer digital standards offer superior image quality.
- USB-C: USB-C, also known as USB Type-C, is a versatile connector that can connect to various devices, including hosts, replacing connectors like USB-B and HDMI. It is commonly found on Macintosh computers and Windows PCs.
- Thunderbolt: Developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple, Thunderbolt allows the connection of external peripherals and monitors to a computer. Thunderbolt 3 uses the USB-C connector, while Thunderbolt 1 and 2 use the Mini DisplayPort connector.
- AV (RCA): This type of input is commonly found on electronic equipment that generates audio and visual signals, such as composite video. It receives analog signals through a connector known as an RCA type connector.
- NDI: Network Device Interface (NDI) is a format that enables the transmission of audio and video content via an ethernet network.
- SDI: SDI, or Serial Digital Interface, is a professional video signal format preferred in production environments due to its longer range (up to 300 feet) and reliability. It is typically transmitted through BNC cabling with specialised connectors.
When setting up a 12-lead monitor, it is important to ensure that the cables and ports match and are in good condition. Checking for fraying, broken wires, or discolouration is crucial to ensure optimal signal transmission and image quality.
Finding the Right MSI Monitor Size for You
You may want to see also

Setting up display preferences
Once you've connected your laptop to the monitor, it's time to set up your display preferences.
Windows
Right-click on the desktop screen and select "Display settings". In the "Multiple displays" section, you can choose how you want to use your displays:
- "Duplicate these displays" – It should show the same image on both displays
- "Extend these displays" – Increases your desktop across both displays
- "Show only on 1" or "Show only on 2" – Shows the image only on the selected display
Click "Apply" and then "Keep changes" when you're happy with the setup.
Mac
Click on the Apple menu and select "System Preferences". Click on "Displays" and then on the "Arrangement" tab.
To extend the desktop, drag the two display icons to your desired arrangement. To mirror the displays, check the "Mirror Displays" box.
Ubuntu Linux
Click "Activities" in the upper-left corner of the screen. This displays a search bar you can use to search for apps on your system. Type "Displays" in the search bar. Click "Displays" in the Settings menu.
Click and drag the monitors in the "Displays" panel to the position you have set up on your desk. Each display in the "Displays" panel is numbered, and the corresponding number is shown in the top-left corner of each display when the "Displays" panel is open.
Click the monitor you want to use as the primary display. The primary display is the one that contains the top bar and the "Activities" overview.
Keyboard Shortcuts
There are keyboard shortcuts you can use to more easily manage a dual (or more) screen setup:
- Windows: Windows key + P allows you to switch between multiple displays options.
- MacOS: Command key + F1 to switch between mirrored and extended desktop modes.
Cox Data Usage: Monitor and Manage Your Data
You may want to see also

Using adapters when needed
When connecting a laptop to a monitor, you may need to use an adapter if your laptop and monitor have different ports. Common adapters include HDMI to DisplayPort, DisplayPort to VGA, and USB-C to HDMI.
Firstly, purchase the appropriate adapter for your setup. Then, connect your laptop and monitor using the adapter and a compatible cable.
For example, if your laptop has a USB-C port and your monitor has an HDMI port, you would need to purchase a USB-C to HDMI adapter. You would then connect the adapter to your laptop's USB-C port and use an HDMI cable to connect the adapter to the monitor.
Using the correct adapters and cables is crucial to ensure a secure connection and optimal signal transmission between your laptop and monitor.
OptumRx: Prescription Monitoring for Customer Safety and Care
You may want to see also

Other tips for hooking up a monitor to a laptop
- Identify the available ports on both your laptop and the monitor. Common ports include HDMI, DisplayPort, DVI, and VGA. Ensure that your laptop and monitor have at least one port in common.
- Power off both devices before making any connections. This is a safety measure to prevent potential damage during the setup process.
- If your laptop and monitor do not share the same video connection, you can usually find an adapter that enables you to convert one of the above connections to the format you need.
- Make sure that your cable can support the resolution and refresh rate you want. A standard 18Gbps HDMI cable can handle 4K at 60Hz, but if you're a gamer, you'll probably want a 48Gbps HDMI cable that can transmit 4K at up to 120Hz. Remember, your monitor and laptop also need to support these display settings.
- If your laptop does not automatically recognize the monitor, you may need to initiate the connection yourself. On a PC, right-click on a blank spot on your desktop, select Display Settings, then click Detect. On a Mac, open System Preferences or System Settings, click Displays, then hold down the Option key and click Detect Displays.
- You can also use these menus to choose whether you want your two screens to mirror each other or extend, meaning they act as separate screens you can move between. If you extend the screens, you can also drag-and-drop the monitor icons so they're in the same positions they are in real life.
Choosing the Right-Sized Monitor for Your Conference Room
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Connecting your laptop to a 12-lead monitor can enhance your virtual experience. You can benefit from a larger screen size, improved resolution, dual-screen functionality, better ergonomics, enhanced performance, and increased longevity of your laptop.
First, understand the different cables and ports available. Common ports include HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, and Thunderbolt (usually found on Apple devices). Once you've identified the correct ports and cables, connect your laptop to the monitor and set up your display preferences.
Ensure you set the display settings correctly to maximise the resolution. Check that all power and data connections are secure. Use keyboard shortcuts (Windows key + P on Windows, Command key + F1 on macOS) to easily manage your dual-screen setup. Consider getting an external keyboard and mouse if you plan to use the 12-lead monitor as your main display.