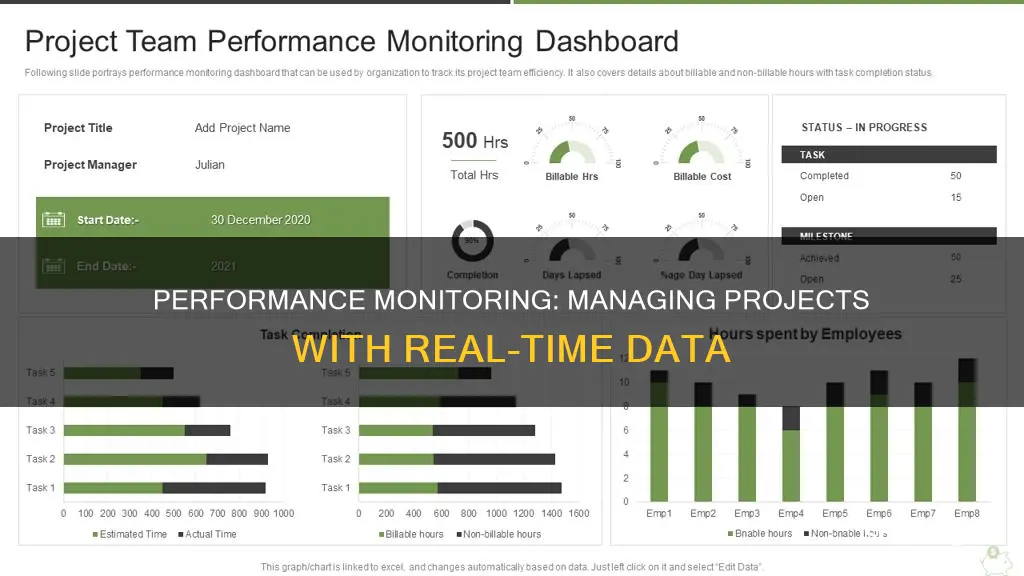
Performance monitoring is a key element of project management that involves tracking a project's metrics, progress, and associated tasks to ensure everything is completed on time, within budget, and according to project requirements and standards. It is a systematic recording of all the activities and tasks in a project for stakeholders, implementers, and beneficiaries. This process records the project's hurdles and gaps and provides complete control to improve its efficiency. It includes steps to identify and resolve issues to increase the efficiency of the project. Performance monitoring is essential for project success as it helps project managers make informed decisions and take corrective actions to achieve the project's goals.
What You'll Learn

Tracking project metrics, progress, and associated tasks
Define Project Metrics and KPIs:
Begin by clearly defining the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be tracked throughout the project. These KPIs should align with the project's goals and provide measurable values to evaluate success. Examples include net profit, overall cost, efficiency, timeline for deliverables, and budget adherence.
Collect and Analyse Data:
Establish methods for collecting data on project performance, such as self-reporting systems, weekly team meetings, or automated reporting tools. Ensure that data is collected consistently and stored in a centralised location for easy analysis. Analyse the collected data to identify any deviations from the project plan and to assess progress towards milestones.
Monitor Project Scope and Budget:
Keep a close eye on the project's scope to ensure that it remains within the initial boundaries. Monitor resource allocation, budget utilisation, and task completion to identify potential scope creep. Regularly evaluate the budget to ensure that expenditures remain within the allocated funds and to identify any areas where adjustments may be needed.
Identify Risks and Issues:
By tracking project metrics and progress, project managers can proactively identify potential risks and issues. Look for deviations from the project plan, unexpected delays, or budget overruns. Address these issues promptly and implement corrective actions to get the project back on track.
Maintain Regular Communication:
Effective communication is essential for successful project monitoring. Hold regular meetings with team members and stakeholders to discuss progress, address concerns, and make necessary adjustments. Ensure that everyone involved in the project is aware of the current status, milestones achieved, and any changes to the project plan.
Utilise Project Monitoring Tools:
Take advantage of project management software and tools specifically designed for project monitoring. These tools can help automate data collection, provide visual representations of project progress, and facilitate collaboration among team members. Examples include Trello, Wrike, and Monday.com.
Conduct Regular Evaluations:
Evaluate the project's progress at regular intervals to identify areas that require improvement. Assess whether the project is meeting its goals and KPIs, and make any necessary adjustments to timelines, budgets, or resource allocation.
By following these instructions and best practices, project managers can effectively track project metrics, progress, and associated tasks, ensuring that projects are completed successfully, within the defined scope, and on time and within budget.
Transforming LCD Monitors: TV Conversion Without a Tuner
You may want to see also

Monitoring budgets in relation to schedules
Performance monitoring is a key element in project management, providing an effective means of measuring a project's progress, its components, and the adequacy and timeliness of the provision and use of funds. Monitoring budgets in relation to schedules is an essential aspect of performance monitoring, helping project managers make informed decisions, maintain communication among stakeholders, and keep the project on track. Here are some detailed paragraphs on this topic:
Understanding the Relationship Between Budgets and Schedules
The relationship between budgets and schedules is integral to successful project management. A project budget outlines the financial plan for all project expenditures, while the schedule determines the timeline for completing various tasks and achieving milestones. These two aspects are interlocked, as an increase in one often leads to an increase in the other. For example, if a project falls behind schedule, it may require additional resources and incur higher costs to get back on track. Therefore, effective performance monitoring involves regularly tracking both budgetary and scheduling aspects to identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments.
Developing a Project Budget
Developing a comprehensive and reliable project budget is crucial for effective performance monitoring. This involves understanding the individual cost elements and logistics of budget tracking. Project managers need to consider how the overall budget number is derived, how costs will be spread across project milestones, and how to handle scenarios where the project goes over or under budget. Additionally, it is essential to learn from past projects to make future budget estimates more accurate. Techniques such as bottom-up and top-down budgeting, three-point estimates, and parametric estimation can be used to estimate project costs accurately.
Monitoring Budgetary Performance
Performance monitoring involves regularly tracking actual spending against the budget to identify any variances. Project managers can use tools like the Earned Value Method (EVM) to evaluate budgetary performance and calculate cost variances. By drilling down into specific work packages or activities, managers can identify problems or potential issues and develop solutions. Variances can be further analysed to understand the reasons behind them and make informed decisions. This proactive approach helps keep the project on track financially and ensures that resources are used efficiently.
Communicating Budgetary Information to Stakeholders
Effective performance monitoring also involves communicating budgetary information to stakeholders. This includes providing regular updates on the project's financial status, addressing any concerns or requests for clarification, and collaborating on solutions when budgetary challenges arise. Stakeholder communication fosters trust and confidence in the project's financial management and ensures that everyone is aligned with the project's goals and objectives. It also helps secure continued support and investment from stakeholders, as they feel involved in the decision-making process.
Adjusting the Budget and Schedule
Performance monitoring is an ongoing process that requires flexibility and adjustments. As projects progress, unexpected events or changes may impact the budget or schedule. Project managers need to be prepared to handle these deviations and make necessary corrections. This may involve utilising contingency reserves, following change control processes, and constantly evaluating and updating the budget and schedule based on project progress. By integrating risk management strategies into budgetary planning, managers can proactively address potential financial challenges and make informed decisions to keep the project on track.
Protecting Your Data: Stop ISPs Monitoring Your Usage
You may want to see also

Identifying potential risks to project performance
Performance monitoring is a key element of project management, providing managers with real-time status reporting that helps them make decisions and maintain communication with stakeholders. It involves measuring project performance by reviewing the project plan, identifying potential problems, and implementing changes. This process is essential for keeping a project on schedule and within budget, as well as managing risks and avoiding scope creep.
Understand Common Project Risks
Firstly, it is important to be aware of the types of risks that commonly affect projects. These include:
- Scope creep or scope risk: This occurs when the initial project objectives are not well-defined, and stakeholders change requirements during the project.
- Performance risk: This happens when the project underperforms compared to initial expectations, often due to time constraints or miscommunication among team members.
- Cost risk: This is the risk of the project exceeding the allocated budget, which can be mitigated by detailed budgeting and regular budget reviews.
- Time risk or project schedule risk: This refers to the risk of tasks taking longer than expected, impacting the overall timeline and potentially the budget and performance.
- Resource risk: This risk involves not having sufficient resources, including time, skills, money, or tools, to complete the project.
- Operational risk: Changes in company or team processes, such as shifts in team roles or management, can create distractions and impact project timelines.
- Communication risk: Ineffective or untimely communication between team members and stakeholders can lead to loss of data, misinformation, or project disruptions.
- Technology risk: The rapid evolution of technology poses challenges in data security, compliance, and information security, and may require additional training and resources.
Conduct Risk Analysis
Perform a risk analysis to identify, evaluate, and prioritize potential risks. This involves brainstorming and listing all possible risks, assessing their likelihood and potential impact, and developing a risk response strategy. Tools such as a probability matrix or a risk register can assist in this process.
Monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs provide data on timelines, budgets, and quality, enabling project managers to make informed decisions and identify potential risks. Regularly tracking these metrics can help identify deviations from the project plan and take corrective actions.
Encourage Open Communication
Effective communication between team members, stakeholders, and clients is crucial for identifying potential risks. Regular updates and discussions about deliverables, roadblocks, feedback, and timelines can help uncover issues before they become major problems.
Utilize Project Monitoring Tools
Project management software and platforms can automate data collection, streamline workflows, and provide real-time visibility into project progress. These tools enable the collection of accurate and up-to-date data, facilitating more effective risk identification and management.
Removing Delta Monitor Shower Handle: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Verifying a project's scope
Performance monitoring in project management involves tracking and evaluating the progress and performance of a project to ensure it stays on course and meets its goals and objectives. An essential aspect of performance monitoring is verifying the project's scope, which ensures that the project delivers what it set out to achieve and confirms that the project's deliverables are acceptable. Here are some key considerations and steps to effectively verify a project's scope:
Begin by thoroughly reviewing and understanding the project scope statement. This document outlines the project's objectives, deliverables, constraints, and assumptions. It is crucial to have a clear understanding of what the project aims to accomplish and the scope's boundaries. Ensure that all stakeholders, including the project team, customers, and sponsors, agree on and approve the scope statement.
Next, establish clear and concise criteria to evaluate the project's deliverables. These criteria should be aligned with the project's objectives and define the acceptable standards for each deliverable. They may include quality standards, performance metrics, or customer satisfaction metrics. Develop a comprehensive checklist or evaluation framework that covers all critical aspects of the deliverables.
Throughout the project, maintain open and frequent communication with all stakeholders. Regularly seek feedback, input, and evaluations from customers, end-users, and sponsors to ensure that the project's deliverables meet their expectations and requirements. Encourage stakeholders to provide timely notifications of any changes or discrepancies in the project's scope and address them promptly.
Develop a process to validate and verify each deliverable against the established criteria. This may involve inspections, tests, demonstrations, or reviews by subject matter experts, quality assurance teams, or external auditors. Ensure that the verification process is rigorous and unbiased to identify any deviations from the scope or quality standards.
During the verification process, thoroughly document all findings, issues, and deviations from the project's scope or quality standards. Maintain a transparent and detailed record of the verification process, including the methods used, personnel involved, and outcomes. This documentation is crucial for project evaluation, stakeholder communication, and future reference.
If discrepancies or issues are identified during verification, initiate a scope change control process. Evaluate the impact of each deviation and determine whether a scope change is necessary. Follow a well-defined process for approving, managing, and communicating scope changes, ensuring that they are appropriately justified, documented, and accepted by all stakeholders.
Finally, continuously monitor the project's environment and external factors that may impact the scope. Stay vigilant for any changes in technology, market conditions, regulations, or customer needs that could affect the project's objectives or deliverables. Proactively address these factors and adjust the scope, if necessary, to ensure the project remains relevant and aligned with its original goals.
By diligently verifying the project's scope, project managers can ensure that the project delivers the expected outcomes, meets quality standards, and satisfies stakeholder requirements. Effective performance monitoring and scope verification help mitigate risks, control costs, and ultimately contribute to the project's success and positive outcomes for all involved parties.
Direct Wiring Method: LCD Monitor and Transformer Connection
You may want to see also

Ensuring work doesn't exceed the initial project scope
Performance monitoring is an integral part of project management, providing real-time status reporting that helps project managers make decisions and maintain communication among stakeholders. It involves tracking a project's metrics, progress, and associated tasks, ensuring that work is completed on time, within budget, and according to project requirements. Crucially, it helps prevent scope creep by ensuring that work doesn't exceed the initial project scope.
Define the Project Scope
Firstly, it is essential to define the project scope clearly and explicitly. The project scope sets the boundaries and outlines the goals, deadlines, and deliverables. It is crucial to involve all relevant stakeholders in this process and ensure everyone is on the same page. A well-defined project scope statement should include the project's objectives, deliverables, constraints, exclusions, and assumptions.
Prevent Scope Creep
Scope creep occurs when project deliverables exceed the initial scope, leading to potential delays, overwork, and low-quality outputs. To prevent scope creep, create a solid project scope statement and share it with stakeholders as early as possible. Throughout the project, refer back to the project scope document to ensure you stay on track and identify any new elements that weren't part of the original plan.
Establish a Change Control Process
Implement a change control process to manage any changes or additions to the project scope. This process should include a mechanism for submitting change requests, a review process involving key stakeholders, and a system to judge whether changes will be accepted, denied, or deferred.
Monitor Project Scope
Regularly monitor the project scope to ensure that any changes are verified and documented. Update relevant documents, such as the project scope statement and work breakdown structure. Also, determine any necessary adjustments to timelines and budgets due to scope changes.
Effective Communication
Maintain open and transparent communication with team members, stakeholders, and clients. Encourage regular updates on deliverables, roadblocks, feedback, and timelines. This will help identify potential issues early on and ensure that everyone is aligned with the project scope.
Use Project Monitoring Tools
Utilize project monitoring tools and software to streamline workflows, collect data and feedback, and generate reports. These tools can help track performance, identify risks, and make data-driven decisions to keep the project within the initial scope.
By following these strategies, project managers can effectively ensure that work doesn't exceed the initial project scope, reducing the risk of delays, budget overruns, and scope creep.
Identifying Monitor Ports: VGA or DVI?
You may want to see also







