Performance monitoring in health and safety is a vital component of any health and safety management strategy. It involves the analysis of safety processes and procedures to determine how well those systems function. Monitoring health and safety in the workplace allows for a more accurate assessment of existing controls and risks, which can be used to develop an effective plan of action. This process is essential for organisations to measure their performance against set Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), targets and objectives. It also ensures that hazards and risks are being controlled within an organisation.
What You'll Learn

Monitoring and reporting are vital parts of a health and safety culture
Monitoring and reporting are essential components of an effective health and safety culture in any organisation. It is a key part of any health and safety management strategy, allowing for a thorough assessment of existing controls and risks to develop a robust plan of action.
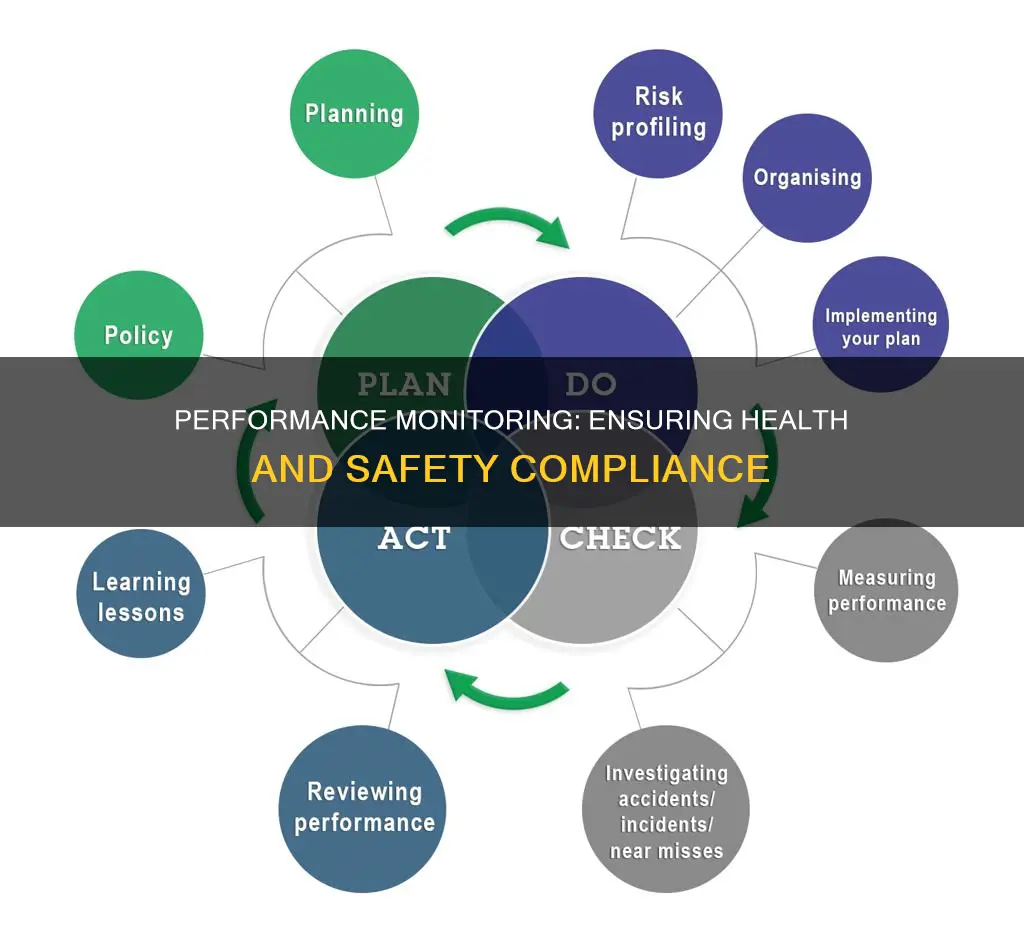
Health and Safety management systems typically follow a PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) model. Monitoring and review are integral to the 'Check' and 'Act' stages, ensuring that health and safety policies are effective and compliant with legal requirements. This process involves workers at all levels of the organisational structure, fostering a sense of ownership and improving morale.
Effective monitoring and reporting systems provide several benefits. Firstly, they ensure that hazards and risks are identified and controlled. This includes assessing the levels of risk, identifying potential hazards, evaluating safety policies, and conducting accident investigations. By doing so, organisations can reduce accidents and incidents, improve the working environment, and increase efficiency and productivity.
Additionally, monitoring and reporting allow organisations to measure their performance against key indicators, targets, and objectives. This includes tracking the frequency of incidents and near-misses, as well as analysing workforce experience, machine maintenance, safety equipment features, and technical specification standards. This data enables organisations to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance health and safety practices.
Furthermore, monitoring and reporting facilitate continuous improvement. By periodically reviewing health and safety performance, organisations can identify areas where policies and procedures can be enhanced and make necessary changes. This includes learning from accidents, incidents, and ill-health data to prevent reoccurrence and improve overall health and safety culture.
Effective monitoring and reporting systems also promote involvement and engagement from employees. By encouraging employees to report unsafe conditions and hazardous situations, organisations can empower their workforce to take an active role in health and safety. This two-way feedback system not only improves safety but can also have additional benefits, such as increased productivity and employee satisfaction.
In conclusion, monitoring and reporting are indeed vital parts of a robust health and safety culture. They provide organisations with the tools to identify risks, measure performance, and continuously improve their health and safety practices, ultimately creating a safer and more productive work environment for all stakeholders.
Quickly Resize Images in Campaign Monitor with Simple Steps
You may want to see also

Safety performance indicators (SPI) and safety performance targets (SPT)
Performance monitoring is a critical component of health and safety management. It involves assessing existing controls and risks to develop an effective plan of action. Monitoring and reporting are essential elements of a health and safety culture, and they play a vital role in improving safety performance.
Safety Performance Indicators (SPIs) and Safety Performance Targets (SPTs) are crucial tools within performance monitoring. According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), an SPI is a "data-based parameter used for monitoring and assessing safety performance." SPTs are defined as "the planned or intended objective for safety performance indicator(s) over a given period."
SPIs are quantitative measures used to track safety performance over time. They help identify areas of strength and weakness in an organisation's safety systems, processes, and activities. Examples of SPIs include accident rates, incident rates, safety-related delays, and safety culture surveys. Identifying the most meaningful and effective SPIs can be challenging, and collecting data for them can be time-consuming.
SPTs, on the other hand, are specific, measurable goals that an organisation sets to improve safety performance. These targets help focus efforts and resources, ensuring that safety initiatives align with the organisation's overall goals. Setting ambitious SPTs or lacking necessary resources can make achieving these targets challenging. Additionally, monitoring and evaluating SPTs can be difficult without clear measurement methods.
To effectively utilise SPIs and SPTs, organisations must invest significant time, resources, and expertise. A culture of safety that promotes transparency and accountability is essential for success. Additionally, access to relevant data, tools, and resources is crucial for effective monitoring and evaluation of safety performance.
In summary, SPIs and SPTs are vital components of performance monitoring in health and safety. They provide measurable ways to assess and improve safety performance, ensuring that organisations can identify risks, set targets, and take appropriate actions to create safer environments for all stakeholders.
Monitoring Your ASUS Tablet: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Involving your workforce in health and safety
Performance monitoring in health and safety is an essential component of any health and safety management strategy. It involves assessing existing controls and risks to develop an effective plan of action. Monitoring and review are integral parts of the "check" and "act" steps of the PDCA (Plan, Do, Check, Act) system used in most safety management systems.
Now, involving your workforce in health and safety is a two-way process that encourages collaboration between employers and employees. Here are some detailed guidelines to achieve this:
Listen and Share Concerns:
Create an environment where employees feel comfortable voicing their concerns about health and safety. Listen to their perspectives and encourage open communication.
Joint Problem-Solving:
Engage in joint problem-solving by discussing issues and seeking solutions together. Address health and safety matters promptly and collaboratively.
Seek and Share Views and Information:
Encourage a culture of open dialogue where employees can express their views and share relevant information. Ensure that health and safety discussions are timely and inclusive.
Make Decisions Together:
Involve employees in decision-making processes related to health and safety. Empower them to contribute their ideas and participate in finding solutions.
Provide Training and Resources:
Offer health and safety training to employees and ensure they have the necessary resources to maintain a safe working environment. This includes providing personal protective equipment (PPE) and maintaining equipment to prevent accidents and health hazards.
Compliance with Regulations:
Familiarize yourself with health and safety regulations, such as the Safety Representatives and Safety Committees Regulations 1977, and the Health and Safety (Consultation with Employees) Regulations 1996. These regulations outline the legal duty of employers to consult and involve employees in health and safety matters.
Monitor and Evaluate:
Regularly monitor the effectiveness of health and safety measures and evaluate their impact. Collect feedback from employees and their representatives to identify areas for improvement. This can include conducting audits, inspections, and reviews to ensure compliance with health and safety standards.
Foster a Positive Health and Safety Culture:
Involving employees in health and safety can lead to additional benefits, such as improved productivity and employee morale. Encourage a culture where health and safety are prioritized, and employees are engaged in maintaining a safe working environment.
Removing Back Monitor Applications: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Safety assurance and risk controls
Safety assurance involves monitoring risk controls during operations to ensure they remain effective. This includes conducting internal audits, investigations, and utilising employee reporting systems to gather information. This information is then analysed and compared with existing norms and patterns to identify any trends or areas of concern. By doing so, organisations can proactively identify and address potential health and safety risks before they result in accidents or incidents.
Risk controls, on the other hand, refer to the measures put in place to mitigate identified risks. This includes both preventive and protective measures. Preventive measures aim to reduce the likelihood of a risk occurring, while protective measures focus on reducing the potential harm or impact of a risk. Examples of risk controls include providing personal protective equipment (PPE), implementing safe working procedures, and ensuring proper maintenance of equipment.
To ensure the effectiveness of risk controls, it is important to involve employees at all levels of the organisation. This includes providing training, fostering a culture of collaboration and open communication, and encouraging employee involvement in health and safety initiatives. By empowering employees to take ownership of health and safety, organisations can benefit from diverse perspectives and a more engaged workforce.
Additionally, it is crucial to periodically review and assess the effectiveness of risk controls. This involves monitoring and measuring performance, conducting audits, and learning from accidents, incidents, and near misses. By doing so, organisations can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance their health and safety management systems.
Furthermore, safety assurance and risk controls should be dynamic and adaptable to change. When introducing new procedures, products, or processes, organisations must consider the potential health and safety implications and make the necessary adjustments to their risk controls. This ensures that the organisation remains compliant with legal requirements and that employees are protected from potential hazards.
In conclusion, safety assurance and risk controls are critical aspects of health and safety management. By implementing effective monitoring systems, fostering a culture of safety, and adapting to change, organisations can create a safer working environment for their employees and mitigate the potential for accidents and incidents.
RF Monitor Buying Guide: Where to Purchase
You may want to see also

Safety data and monitoring methods
There are two main types of safety data collection methods: mandatory and voluntary reporting systems. Mandatory reporting systems require the disclosure of specific events, such as serious incidents and accidents, while voluntary reporting systems allow individuals to submit information about observed hazards or errors without legal obligation.
Safety monitoring methods can be categorised into several types:
- Safety audits and inspections: These focus on evaluating the integrity of safety management systems and their supporting processes. Audits are formal assessments conducted by trained individuals, while inspections are often carried out by supervisors or managers.
- Safety surveys: These examine procedures or processes related to specific operations, assessing the particular hazards and associated risks.
- Safety occurrence reporting and investigations: This involves the reporting and subsequent investigation of safety occurrences to identify root causes and implement corrective actions.
- Safety studies: These are comprehensive analyses that address broad safety concerns and are useful for identifying system safety deficiencies.
- Safety reviews: Conducted during the introduction of new technologies, procedural changes, or structural changes in operations, safety reviews are crucial for managing change and have clearly defined objectives.
Additionally, continuous monitoring of day-to-day activities and the systematic capture of data reflecting actual performance are also essential components of safety monitoring. This includes programmes such as Flight Data Monitoring, Line Operations Safety Audit (LOSA), and Normal Operations Safety Survey (NOSS).
When monitoring safety performance, it is important to consider various factors, including workforce experience, machine maintenance schedules, safety equipment features, technical specification standards, and compliance reporting. By tracking these indicators and analysing trends, organisations can improve their Environment, Health, and Safety (EHS) performance.
Furthermore, involving employees in health and safety monitoring can have additional benefits, such as increased productivity and improved morale. This can be facilitated through a two-way feedback system where employees can report unsafe conditions, and management can implement improvements and encourage employee engagement in safety initiatives.
Installing Pillow TFT LCD Monitor: A Simple Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Performance monitoring in health and safety is a process of evaluating the effectiveness of safety policies and procedures within an organisation. It involves checking risk levels, identifying hazards, and reviewing incident data to ensure the organisation meets its safety objectives and complies with legal requirements.
Performance monitoring is vital to ensure a safe working environment for employees. It helps to reduce accidents, improve efficiency and productivity, and save resources. Monitoring also allows organisations to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to enhance overall safety culture.
The frequency of performance monitoring depends on the nature of the organisation, the complexity of its operations, and the level of risk involved. Some organisations may monitor safety performance daily or weekly, while others may conduct quarterly or annual assessments. Continuous monitoring of day-to-day activities is also recommended to identify any immediate safety concerns.







