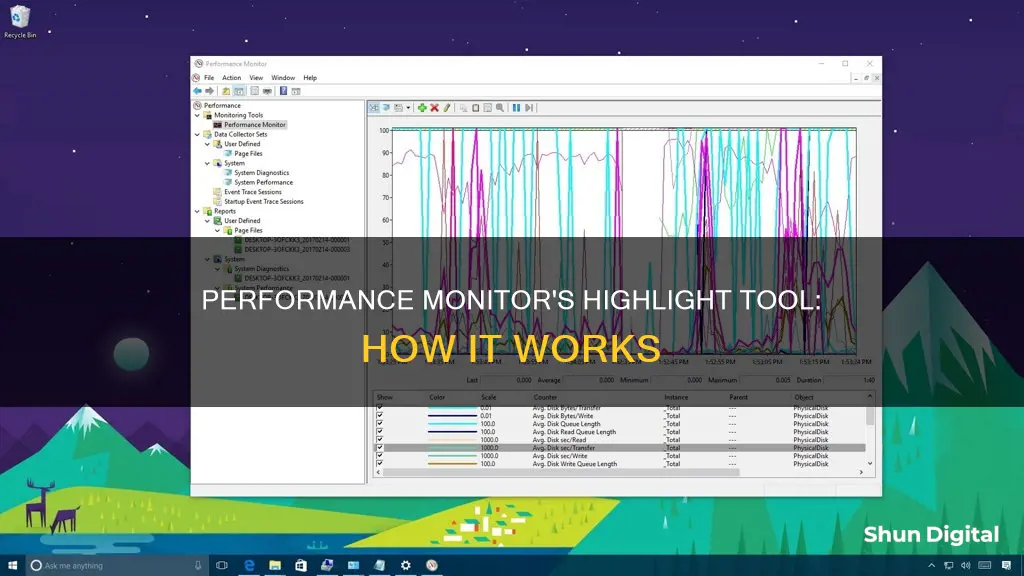
The Highlight tool in Performance Monitor allows you to select specific counters to monitor and highlight their data in the graph. This can be useful when you want to focus on specific performance metrics and compare them against each other. You can also change the colour of the highlighted data to make it stand out. This feature provides a visual way to identify trends and issues in your system's performance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Name | Performance Monitor |
| Type of tool | Performance monitoring tool |
| Operating System | Windows |
| Function | Measures system and application performance by collecting reliable performance data |
| Data Collection | Collects data in the background as the user uses the computer |
| Data Sampling | Allows the user to specify the values and time period of data sampling |
| Data Display | Allows the user to display data in various formats such as line graph, histogram bar, and report |
| Data Analysis | Provides controls and indicators to facilitate analysis of collected data |
| Data Comparison | Allows the comparison of performance data from multiple log files |
| Alerts | Can be set up to notify the user when a particular counter goes above or below a specific value |
| User Access | Requires the user to be a member of the Administrators group |
What You'll Learn

How to open the Performance Monitor tool
The Performance Monitor is a tool that can help you identify issues with your Windows computer or laptop's performance. It has been available on Windows operating systems since 1993. With it, you can monitor how your computer's processor, memory, or storage space are utilized and troubleshoot problems.
- Using the Search function: Click or tap inside the search bar or press the Windows key on your keyboard. Type "perfmon" or "Performance Monitor" and then press Enter or click/tap on the appropriate search result.
- Using the Start Menu: In Windows 10, click on the Windows icon from the taskbar, scroll down the list of apps until you see the "Windows Administrative Tools" folder, and click or tap on it to expand it, and then find and click/tap on the "Performance Monitor" shortcut. In Windows 11, click or tap the Windows icon to open the Start Menu, then click or tap "All apps", scroll down to the "All apps list" until you see the "Windows Tools" shortcut, and click or tap on it. The "Windows Tools" window will open, and you will see the "Performance Monitor" shortcut. Double-click or double-tap on this shortcut to open the app.
- Using the command line: Open Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal and type "perfmon" or "perfmon.exe" and hit Enter.
- Running the executable file: Go to "C:\Windows\System32\perfmon.exe" and double-click or double-tap on the file. Alternatively, you can open its location by using environment variables like "%WINDIR%\System32\perfmon.exe".
- Pinning the shortcut: If you use the Performance Monitor app frequently, you can pin its shortcut to the taskbar or the Start Menu. In Windows 10, open the Start Menu, scroll down the apps list to "Windows Administrative Tools", open this folder, and right-click or press and hold the "Performance Monitor" shortcut. In the contextual menu, choose "Pin to Start" or "More > Pin to taskbar". In Windows 11, click or tap inside the search box on the taskbar and type "performance monitor" or "perfmon", then right-click or press and hold on the search result and choose the option you want.
- Using the Run window: Press the Windows + R keys on your keyboard to open the Run window. In the Open field, type "perfmon" and press Enter on the keyboard or click OK.
- Creating a shortcut: If you prefer using a desktop shortcut, you can create a Performance Monitor shortcut yourself. Right-click or press and hold on the empty space on your desktop and choose "New > Shortcut". In the "Create Shortcut" window, type "perfmon" in the location field, press Next, give a name to your shortcut, and then press Finalize.
- Using File Explorer: Press Windows + E to open File Explorer in Windows 10 or 11. Then type "perfmon" in the address bar and press Enter on your keyboard.
- Using System Configuration: If you have opened System Configuration to manage the startup options for your computer, you can also use it to run Performance Monitor. Go to the "Tools" tab in System Configuration, select "Performance Monitor", and click or tap "Launch".
- Using Computer Management: Open the Computer Management app and find the "Performance" section in the menu tree on the left side of the window. It is in the "System Tools" section, just above "Device Manager". Click or tap on "Performance" to access the full Performance Monitor tool.
Syncing Wireless Keyboards to Monitors: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

How to use the Performance Monitor tool
Performance Monitor is a tool integrated into Windows operating systems that allows users to effectively measure system and application performance by collecting reliable performance data. It is a more advanced tool than Task Manager and can monitor virtually anything on your computer.
To open the Performance Monitor tool, you can:
- Open Start, search for Performance Monitor, and click the result.
- Use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command, type "perfmon", and click OK.
- Use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu, select Computer Management, and click on Performance.
When you first open the Performance Monitor, it will display a brief overview and a system summary with real-time data about memory, network adapter, physical disk, and processor usage. On the left, you will find the navigation pane with access to Performance Monitor, Data Collector Sets, and Reports.
Adding Counters
Performance Monitor initially displays a single counter, typically the "Processor Time" counter, which shows the processor load in the last 100 seconds. You can add other counters to monitor different aspects of your computer's performance. To do this, follow these steps:
- Click the green plus button above the Performance Monitor graph.
- Select "Local computer" or the name of your computer from the drop-down menu.
- Select and expand the category of the item you want to monitor. For example, if you want to monitor network activity, select the "Network Adapter" category.
- Select the counters you want to monitor. For instance, you can choose "Bytes Total/sec" to see how much bandwidth is being used.
- If applicable, select the instances you want to monitor. For the "Network Adapter" category, you can monitor one or multiple network adapters simultaneously.
- Click "Add", then "OK" to confirm and add the new counters.
Customizing the View
Once you have set up your counters, you can customize various aspects of the data shown in the graph. Here's how:
- Double-click one of the counters to open the Performance Monitor Properties window.
- On the "Data" tab, select the counter you want to customize.
- Choose the color, scale, width, and style you want to use.
- Repeat the above steps for each item you want to customize.
Additionally, you can change the graph's style by clicking the "Change graph type" button in the toolbar and selecting from options such as Line, Histogram bar, and Report.
Using Data Collector Sets
Performance Monitor also includes Data Collector Sets, which allow you to create custom sets containing performance counters and alerts based on specific criteria. Here's how to create a custom Data Collector Set:
- In Performance Monitor, expand "Data Collector Sets".
- Right-click "User Defined", select "New", and click "Data Collector Set".
- Type a descriptive name for the new set.
- Select the "Create manually (Advanced)" option.
- Choose the "Create data logs" option and check "Performance counter". You can also select other options as needed.
- Click "Add" and pick the performance counters you want to include.
- Configure the sample interval, which defines how often Performance Monitor will run and collect data. Shorter intervals will result in more frequent data logging.
- Save your set and close the window.
Once you've set up your custom Data Collector Set, you can right-click on it and select "Start" to run it or "Stop" to shut it down.
Viewing and Analyzing Data
After collecting data with Performance Monitor, you can view and analyze it using the Reports option. Go to "Reports" and select the report you want to see. When opening a custom report, you will see a recording of the data collected, which can still be helpful for analyzing your system's performance.
Performance Monitor also offers the ability to save settings for later use. To do this, right-click on the Performance Monitor graph and select "Save Settings As". The settings will be saved as an HTM file, which can be opened using Internet Explorer to load a functional instance of Performance Monitor in the web browser.
Tips for Using Performance Monitor
- Performance Monitor can be resource-intensive, so running it may impact your system's performance.
- It is important to choose the right counters to monitor. For example, monitoring "% Committed Bytes in Use" can help you determine if you have enough memory on your system.
- You can also use Performance Monitor to identify potential malware by monitoring network activity. If you notice high network activity when you're not using your internet connection heavily, it could indicate the presence of malware.
Lace Monitor Buying: Where to Purchase Your New Pet
You may want to see also

How to use Data Collector Sets
Data Collector Sets are
Uninstalling Zio Monitor: A Step-by-Step Guide to Removal
You may want to see also

How to add and remove performance counters
The Performance Monitor is a tool that allows you to view and analyse application and hardware data to fix system performance-related problems. You can also customise what data to collect in log files, define alerts, generate reports, and replay collected performance data in many ways.
To open the Performance Monitor on Windows 10, you can do a search for it in the Start menu, use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command and type "perfmon", or use the Windows key + X keyboard shortcut to open the Power User menu, select Computer Management, and click on Performance.
Adding Performance Counters
To add new counters to monitor applications and hardware performance on your computer, do the following:
- Click the green plus button above the Performance Monitor graph.
- Select Local Computer or the name of your computer from the drop-down menu.
- Select and expand the category of the item you want to monitor.
- Select the counters you want to monitor.
- If applicable, select the instances you want to monitor.
- Click the "Add" button, then "OK" to confirm.
Removing Performance Counters
To remove performance counters, you must have administrative privileges. From the following location, you can add or remove performance counters:
In ProficyServer.exe, enter the applicable command line:
ProficyServer [exe] /installperformancounters ProficyServer [exe] /uninstallperformancounters
If the counters are added or deleted after the server is started, the server and the performance monitoring tool (perfmon) must be restarted for this change to take effect.
Monitor Size: Your Unsuspected Digital Fingerprint
You may want to see also

How to use performance alerts
Performance alerts are an important feature of performance monitoring tools, allowing users to proactively identify performance issues and take necessary actions. Here's a guide on how to use performance alerts effectively:
Understanding Performance Alerts
Performance alerts are notifications that are triggered when a specific metric or condition is met. These alerts can be set up to monitor various aspects of a system's performance, such as processor load, memory usage, network activity, and more. For example, you can set an alert to notify you when the processor load exceeds a certain threshold or when the memory usage is consistently above 80%.
Customizing Alert Settings
Performance monitoring tools usually offer customization options for alerts. You can define the specific conditions that will trigger an alert, such as the threshold value, the duration of the issue, and the frequency of occurrence. Additionally, you can often choose how you would like to receive the alerts, such as via email, SMS, or through a third-party notification service.
Creating and Configuring Alerts
To create a performance alert, follow these general steps:
- Identify the Metric: Determine the specific metric or aspect of system performance you want to monitor, such as CPU usage, network latency, or response time.
- Set the Threshold: Define the value that will trigger the alert. For example, you might set an alert for CPU usage to go off when it exceeds 90% usage.
- Specify Alert Actions: Decide what should happen when the alert is triggered. This could include sending notifications to specific individuals or teams, logging the issue, or even taking automated corrective actions.
- Customize Alert Settings: Fine-tune the alert settings according to your requirements. This includes specifying the frequency of alerts, the format of the notifications, and any additional conditions or rules.
- Test and Adjust: Once the alert is set up, test it to ensure it works as expected. Make any necessary adjustments to the settings to optimize the alert's effectiveness.
Examples of Performance Alerts in Action
- Website Response Time: You can set a performance alert to notify you when your website's response time exceeds a certain threshold, such as 8 seconds. This can help you identify potential issues with your server or website code, ensuring a smooth user experience.
- High CPU Usage: If you want to monitor the CPU usage of your servers, you can set an alert for when the CPU usage goes above a certain percentage, such as 80%. This can help you identify overloaded servers or applications that are using excessive system resources.
- Memory Constraints: By setting a performance alert for memory usage, you can be notified when the available memory falls below a critical level. This allows you to take proactive measures, such as adding more memory or optimizing memory-intensive applications.
In conclusion, performance alerts are a powerful tool for maintaining optimal system performance. By following the steps outlined above and customizing alerts to your specific needs, you can ensure that you're promptly notified of potential issues, allowing you to take timely and effective corrective actions.
Choosing the Right-Sized Drawing Monitor for Your Needs
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The highlight tool in Performance Monitor allows you to select specific counters for isolated data display.
To highlight a counter in Performance Monitor, select the counter from the list of available counters and click the "Show" checkbox.
Highlighting a counter in Performance Monitor isolates the data for that counter, making it easier to focus on specific data of interest.
Yes, you can select and highlight multiple counters simultaneously in Performance Monitor.
To unhighlight a counter in Performance Monitor, simply deselect the "Show" checkbox for that counter.







