Lateral spread is a technique used by hackers to move through a network and find vulnerabilities, escalate access privileges, and reach their target. This process is also known as east-west movement and involves moving sideways from device to application, with the intent to move upwards in terms of access or deeper in terms of data. Lateral spread can be used to gain access to specific accounts or data, or to control as many devices as possible. This technique can be used for financial gain, data or proprietary information theft, or further criminal activity. Detecting and preventing lateral spread is critical to safeguarding an organization's network.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Lateral spread | A technique used to place the mean point of impact of two or more units 100 meters apart on a line perpendicular to the gun-target line |
| Lateral movement | A group of methods used by cybercriminals to explore an infected network to find vulnerabilities, escalate access privileges, and reach their ultimate target |
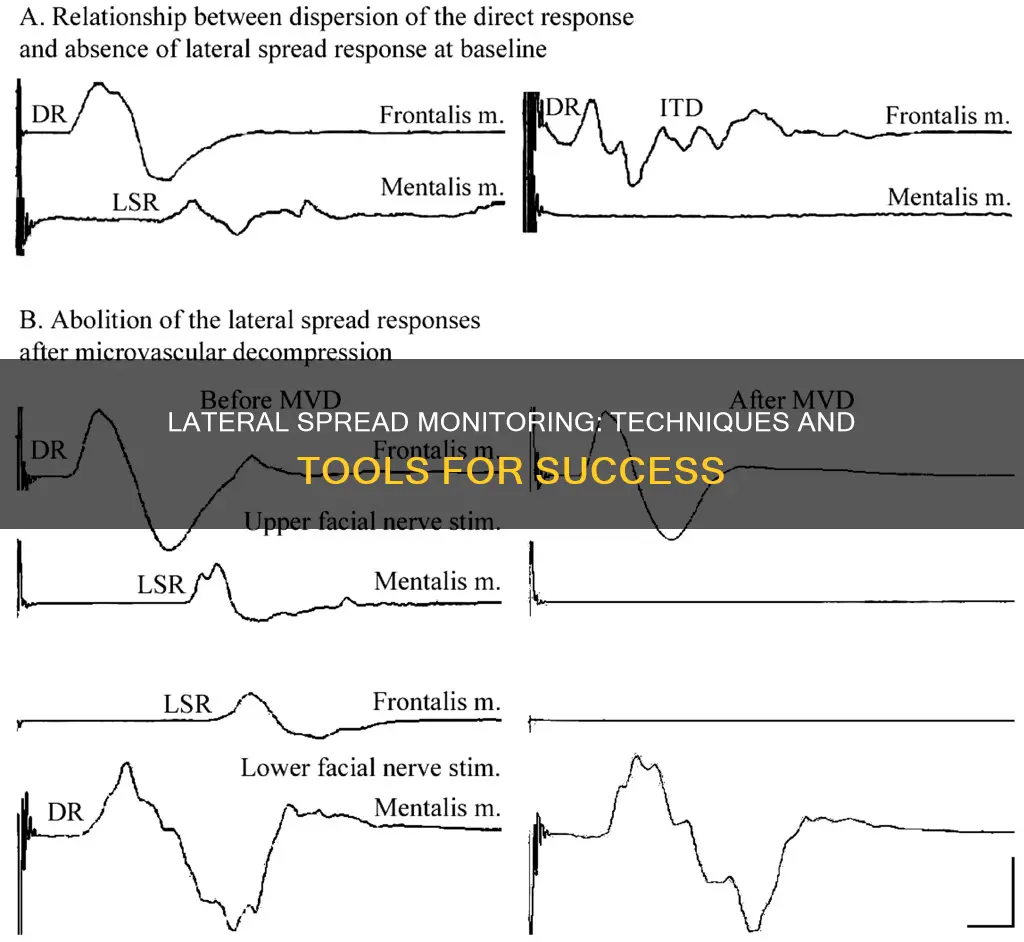
| Lateral spread response monitoring | An intraoperative tool used to ensure adequate decompression of the facial nerve during microvascular decompression surgery |
What You'll Learn

Detecting lateral movement
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
Real-time monitoring is crucial for detecting potential threats. This involves collecting, normalising, and correlating data across the network in real time, enabling the identification of suspicious activities that require further investigation. By aggregating alerts, security teams can observe the progression of a threat and identify compounding activities that indicate a genuine threat. Rules and frameworks, such as the MITRE ATT&CK framework, can be applied to ensure comprehensive coverage of potential exploitation areas.
Behavioral Analysis and Investigation
Behavioural analysis provides a unique perspective on user and entity behaviour by using machine learning to establish a baseline of normal behaviour and identify significant deviations. This helps in prioritising and addressing anomalous activities that may indicate malicious activity. User and Entity Behaviour Analysis (UEBA) solutions are effective in this context, providing contextual evidence to support investigations into suspicious activities. Combining real-time monitoring with behavioural analysis ensures a robust detection system that can adapt to different scenarios.
Map Lateral Movement Paths (LMPs)
Identifying potential LMPs within the organisation's network is essential. Review the infrastructure and hierarchy to spot vulnerable connections between devices, data, and systems. While removing these connections may not be feasible, monitoring and securing them becomes a priority.
Leverage Reporting Tools
Monitoring and reporting tools are crucial for detecting suspicious activities. However, it is important to be cautious about alert fatigue, and alerts should be aggregated for prioritisation.
Monitor Unknown Devices
With the increasing trend of "bring your own device" (BYOD) to work, it is important to monitor unknown devices registered on the network for any suspicious activities.
Monitor Logins and Credentials
Monitor logins, especially on devices using multiple credentials. Unusual login times, such as after hours, or multiple logins on a single device, may indicate lateral movement attempts. Additionally, monitor for abnormal administrative tasks and file sharing, as attackers often use native tools to avoid detection, creating anomalies that can be detected.
Identify Port Scans and Abnormal Network Protocols
Port scans are commonly used by hackers during reconnaissance, and they can be detected by intrusion detection systems. Abnormalities between the protocol used for a connection and the transmitted or received data may indicate the absence of encryption.
Preventing Lateral Movement
While detection is crucial, preventing lateral movement is ideal. Here are some additional strategies to prevent lateral movement:
- Install software updates and system patches regularly to eliminate vulnerabilities.
- Update endpoint security solutions to protect vulnerable endpoints.
- Enforce the principle of least privilege (PoLP) to restrict user access.
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add layers of security to user logins.
- Implement network segmentation to isolate sensitive parts of the network.
- Backup critical data to reduce the impact of potential ransomware attacks.
- Implement zero-trust security, assuming every user is a potential threat.
Monitoring Internet Usage: Netgear Router Settings Guide
You may want to see also

Monitoring unknown devices
Identifying Unknown Devices:
- Using a Router's Web Interface: Access your router's admin page by typing its IP address into a web browser. Log in with the admin credentials, which can be found in the manual or on the router itself. Look for sections like "Attached Devices", "Device List", or "DHCP Client List". Compare the list of devices, along with details such as device names, MAC addresses, and IP addresses, with the devices you know to identify any unknown devices.
- Using Terminal/CMD: On Windows, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and enter "arp -a" or "arp -an" to display the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) table, which shows IP addresses and corresponding MAC addresses of devices on the network. On Linux and macOS, use the "ifconfig" command to view all network settings.
- Using a Scanner App: Install a network scanner app, such as Auvik, Intruder, SolarWinds, NetScan Tools Pro, or NMap. These apps can help identify connected devices and provide details about them.
Removing Unknown Devices:
- Change Wi-Fi Password: Immediately change your Wi-Fi password to something strong and unique to prevent unauthorized access.
- Disable WPS: Disable features like Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) that allow easy device connections but compromise security.
- Enable MAC Address Filtering: Only allow recognized devices with approved MAC addresses to connect to your network.
- Update Router Firmware: Regularly update your router's firmware to benefit from the latest security features and fixes.
Securing Your Network:
- Regular Scans: Scan your home network at regular intervals to identify and remove unknown or unauthorized devices.
- Strong Passwords: Always use strong and unique passwords for your Wi-Fi network and consider changing them periodically.
- Update Default Wi-Fi SSID: Update your default Wi-Fi Service Set Identifier (SSID) to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Enable New Device Approval: Enable the "New Device Approval" feature on your network to maintain control over which devices can connect.
By following these steps, you can effectively monitor and manage unknown devices on your network, ensuring that your data remains secure and that only authorized users access your network.
Monitoring Staff Performance: Meeting Organizational Standards
You may want to see also

Preventing lateral movement
Lateral movement is a group of methods used by cybercriminals to explore an infected network to find vulnerabilities, escalate access privileges, and reach their ultimate target. This is done by moving sideways from device to application and so on, with the actual intent being to move upwards in terms of access or deeper in terms of data. Lateral movement was seen in 25% of all cyberattacks, according to a recent report.
- Map lateral movement paths (LMPs): Identify possible LMPs in your organization's network. Review the infrastructure and hierarchy to spot vulnerable connections between devices, data, and systems. While removing these connections may not be feasible, you can monitor and secure them.
- Leverage reporting tools: Utilize tools for monitoring and reporting to recognize suspicious activity. Be cautious of alert fatigue and aggregate alerts for better prioritization.
- Investigate and analyze user behavior: Analyze behavioral patterns through machine learning to help isolate and investigate anomalies. While some abnormal behavior may be benign, analysis and investigation may uncover unauthorized access attempts.
- Monitor unknown devices: With the increasing trend of "bring your own device" (BYOD) to work, it's important to monitor unknown devices for suspicious activity as they may be used by attackers to gain initial access.
- Investigate abnormal administrative tasks and file sharing: Attackers may use native tools to avoid detection, but this can create anomalies in file-sharing access that can indicate lateral movement.
- Monitor logins, especially on devices using multiple credentials: Be vigilant about users logging in at odd hours or multiple logins on a single device, as these may indicate lateral movement attempts.
- Identify port scans and abnormal network protocols: Detect port scans performed by hackers during their reconnaissance through intrusion detection systems. Additionally, watch for abnormalities between the protocol used for a connection and the data transmitted or received, as this may indicate a lack of encryption.
By implementing these strategies, security teams can strengthen their defenses against lateral movement and protect their organization's data and systems.
Understanding Holter Monitor Removal: Timing and Procedure
You may want to see also

Map lateral movement paths
Mapping lateral movement paths (LMPs) is a critical step in preventing lateral movement attacks and safeguarding your organization's network. Here are some detailed instructions on how to map LMPs:
- Identify possible LMPs: Begin by understanding your organization's network infrastructure and hierarchy. Look for vulnerable connections between devices, data, and systems. These connections can be potential pathways for lateral movement and should be identified as critical areas to monitor and secure.
- Review network architecture: Analyze the network architecture to identify potential lateral movement paths. Understand how different systems, devices, and data are interconnected. Look for any unnecessary or risky connections that could facilitate lateral movement and consider removing or securing them.
- Identify common LMPs: Familiarize yourself with common lateral movement paths used by attackers. This includes methods such as internal spear phishing, pass-the-hash attacks, pass-the-ticket attacks, remote services exploitation, and secure shell hijacking. Understanding these common paths can help you anticipate and secure potential vulnerabilities in your network.
- Conduct a vulnerability assessment: Perform a comprehensive vulnerability assessment of your network to identify potential entry points and paths that an attacker might exploit. This includes identifying systems with weak security measures, outdated software, or unprotected credentials that could be exploited for lateral movement.
- Utilize monitoring tools: Employ network monitoring tools to track and analyze traffic flow within your organization's network. Look for any unusual or suspicious activity, such as large data transfers, unusual login attempts, or connections to unknown devices. These tools can help you identify potential LMPs and detect ongoing attacks.
- Implement security measures: Once you have identified the LMPs, implement additional security measures to protect them. This includes measures such as multi-factor authentication, network segmentation, access controls, and regular security updates. By securing these paths, you make it harder for attackers to move laterally within your network.
- Regularly review and update: Lateral movement techniques are constantly evolving, so it is crucial to stay updated. Regularly review and update your LMPs identification and security measures. Conduct periodic security assessments to identify new vulnerabilities and adapt your security strategies accordingly.
By following these steps and maintaining a proactive security posture, you can effectively map LMPs and strengthen your organization's defense against lateral movement attacks.
Asus Monitors: Do They Support Gay-Straight Alliance?
You may want to see also

Monitor logins
Monitoring logins is a crucial aspect of detecting and preventing lateral movement in cybersecurity. Here are some detailed instructions on how to monitor logins to enhance the security of your organization's network:
Identify Potential Threats
Monitor for unusual login activity, especially during off-hours. Be vigilant for multiple logins from a single device or logins from unknown devices. These could indicate potential security breaches and warrant further investigation.
User Behaviour Analysis
Utilize machine learning algorithms to establish a baseline of normal user behaviour. This includes understanding regular login patterns, such as the typical time of logins, devices used, and user locations. By identifying deviations from this baseline, you can detect anomalous activity that may be indicative of a security threat.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing MFA adds extra layers of security to user logins. Even if an attacker compromises a user's credentials, MFA ensures that additional security measures are in place to prevent unauthorized access. This makes it harder for intruders to move laterally within your network.
Monitor Privileged Accounts
Pay close attention to logins for accounts with elevated privileges, such as administrator accounts. If you notice any suspicious activity or unauthorized access attempts, take immediate action. These accounts are often targets for lateral movement as they provide broader access to sensitive data and systems.
Regular Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits and reviews of login activities. Look for patterns or trends that could indicate potential security breaches. This proactive approach helps identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary security measures to protect your network.
Secure Login Procedures
Review and enhance login procedures to make them more secure. This includes enforcing strong password policies, regular password changes, and enabling two-factor authentication wherever possible. Additionally, consider implementing single sign-on (SSO) solutions to reduce the number of passwords users need to remember, minimizing the risk of password-related security issues.
By following these instructions and maintaining a vigilant monitoring system for logins, you can significantly enhance the security posture of your organization and deter lateral movement by potential intruders.
Esports Racing: Monitor Size for the Ultimate F1 Experience
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Lateral spread monitoring is a technique used to ensure adequate decompression of the facial nerve during microvascular decompression surgery.
Microvascular decompression is an effective treatment for hemifacial spasms.
Lateral spread response (LSR) monitoring is used as a prognostic indicator for the outcome of microvascular decompression surgery. LSR monitoring helps to ensure that the facial nerve is adequately decompressed during the procedure.
Lateral spread monitoring can help predict the clinical outcome after microvascular decompression surgery and guide surgeons to ensure adequate decompression of the facial nerve.
While lateral spread monitoring is a useful tool, it may not always be a reliable prognostic indicator for treatment outcome. In some cases, it may only serve as an intraoperative guide without providing definitive information on the clinical outcome.







