Monitoring vendor performance is essential for any business to ensure that vendors are meeting expectations and providing quality goods and services. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) such as quality, cost, delivery time, and customer satisfaction, organisations can identify issues and take corrective action to improve their bottom line and protect their reputation. This process involves supervision and management, including regular observation, addressing issues, conducting formal risk reviews, and adjusting performance targets. This paragraph will explore the key aspects of monitoring vendor performance and why it is crucial for business success.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Quality | Product quality, responsiveness, customer satisfaction, innovation |
| Reliability | On-time delivery, order accuracy, timeliness, lead time, responsiveness |
| Delivery | Delivery times, order accuracy, timeliness, lead time, responsiveness |
| Cost | Price, cost-effectiveness, cost variance, total cost of ownership, price volatility, cost savings |
| Compliance | Regulatory compliance, contractual compliance, financial stability, compliance with laws, quality control standards, certification requirements |
| Risk | Financial stability, compliance, cyber-security, risk identification and mitigation |
| Customer Satisfaction | Customer satisfaction, net promoter score |
What You'll Learn

Define what you want to measure
Before tracking vendor performance, it is crucial to decide on the criteria for assessment. This will vary depending on the organisation, the industry, and the type of products or services being sourced.
When defining what you want to measure, it is important to consider the unique needs and requirements of your organisation. For instance, if you are a manufacturing company, you may want to evaluate the quality of the products received from each vendor by performing quality control tests.
- Quality: Evaluate the quality of the products or services delivered by the vendor. This can be done by assessing defect rates or the supplier's conformance to specifications.
- Timeliness and Delivery: Monitor the vendor's ability to deliver products or services on time and within the agreed-upon lead time.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Assess the cost variance and total cost of ownership to determine the impact on your organisation's bottom line.
- Communication and Responsiveness: Measure response times and communication efficiency to ensure a mutually beneficial relationship.
- Compliance: Ensure the vendor complies with regulatory requirements, contractual terms, and industry guidelines.
- Continuous Improvement: Evaluate the vendor's ability to bring new ideas, technologies, or improvements to products or services over time.
- Customer Satisfaction: Collect and analyse feedback from internal stakeholders and end-users to gauge their satisfaction with the vendor's performance.
- Risk Management: Assess the vendor's efforts to identify and mitigate potential risks that could impact performance, including their plans for maintaining operations during disruptions.
Blind Spot Monitors: DIY Installation and Setup Guide
You may want to see also

Set targets and thresholds
Setting targets and thresholds is a crucial step in monitoring vendor performance. Here are some detailed instructions and considerations for this process:
Before establishing targets and thresholds, it is essential to define the criteria you will use to assess your vendors. These criteria will vary depending on your organisation, the industry, and the type of products or services being procured. Common criteria include quality, cost, delivery timeframes, customer satisfaction, timeliness, and responsiveness.
Once you have defined your criteria, you can set specific targets and thresholds for each. These will help you determine whether your vendors are meeting, exceeding, or falling short of your expectations. For example, you might set a target for on-time deliveries at 95% and a threshold at 90%, indicating that any lower value is unacceptable.
When setting targets and thresholds, it is important to make them measurable and objective. This could involve using data from existing systems, such as financial data or customer relationship management systems. You can also utilise surveys, interviews, focus groups, or even social media data to gather information and set baselines.
Consider the weight or priority of each criterion and how they collectively contribute to the overall evaluation of vendor performance. You might use a balanced scorecard method, which involves assigning weights to different metrics and evaluating vendors across multiple areas. This comprehensive approach ensures that all relevant factors are considered and provides a full view of vendor performance.
Remember that the targets and thresholds you set should be realistic and achievable. Involve your vendors in the process to ensure their buy-in and understanding. Clear and mutually agreed-upon targets will help hold vendors accountable and enable you to take swift action if performance deviates from expectations.
Regularly review and adjust your targets and thresholds as needed. This ensures that they remain relevant and aligned with your evolving organisational needs and goals. Continuous improvement is key to successful vendor performance management.
Understanding TFT LCD Color Monitors: How They Work
You may want to see also

Collect data
Collecting data is an essential step in monitoring vendor performance. Here are some ways to gather information on your vendors' performance:
Surveys, Interviews, and Focus Groups
One approach to collecting data is to conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups with relevant stakeholders. This can include internal stakeholders such as employees who interact with the vendors or external stakeholders like customers who have experienced the products or services provided. By gathering feedback and insights from these individuals, you can gain valuable qualitative and quantitative data about the vendors' performance.
Existing Systems and Data Sources
Another source of data is your existing systems, such as financial or customer relationship management (CRM) systems. These systems often contain valuable information about the vendors' performance, including financial data, customer interaction data, and operational metrics. For example, you can analyse financial data to assess cost-effectiveness, or review customer service tickets to evaluate responsiveness and issue resolution.
Social Media Data
Social media platforms can also provide insights into vendor performance. By monitoring social media, you can gather feedback and sentiments from customers who interact with the vendors or use their products and services. This can help identify areas where the vendor excels or needs improvement, especially regarding customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Vendor-Provided Data
Vendors themselves can be a source of data. They often have performance metrics and reports that they can share with you. This may include data on delivery times, order accuracy, product quality, and responsiveness to customer inquiries. By requesting and reviewing these data and reports, you can gain insights into the vendors' performance against the established key performance indicators (KPIs).
Audits and Assessments
Conducting regular audits and assessments of your vendors is another effective way to collect data. This can include financial audits, quality audits, or compliance audits, depending on the nature of your relationship and the industry. These audits provide an independent evaluation of the vendors' performance and can help identify areas of concern or non-compliance with regulations and contractual obligations.
Removing Acer Monitor Cover: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Analyse the data
Analysing the data is a crucial step in monitoring vendor performance. This process involves evaluating the collected data to identify trends, areas of improvement, and ensure that vendors are meeting expectations. Here are some key considerations for analysing vendor performance data:
Define Clear Performance Metrics:
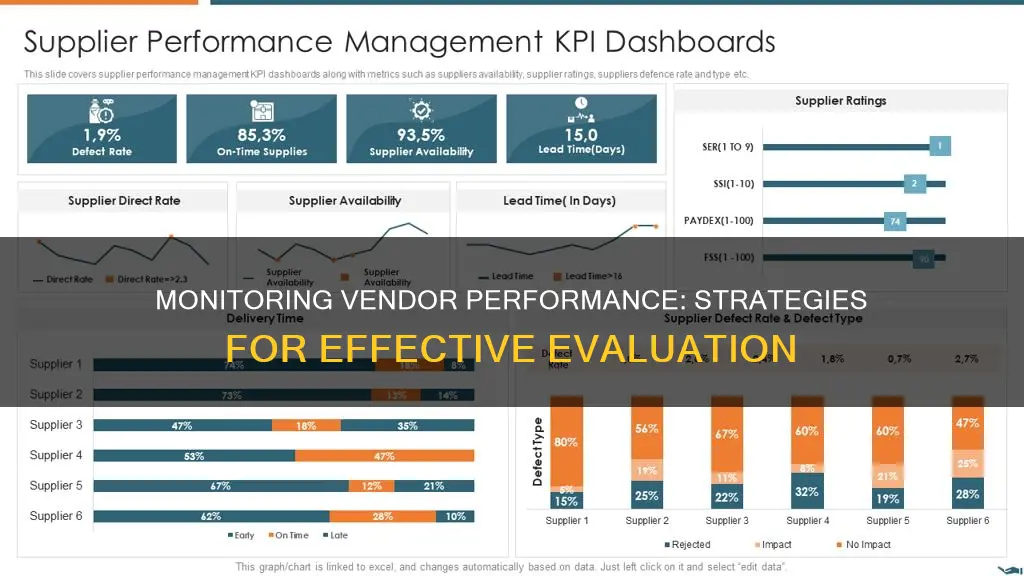
Begin by establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) that are relevant to your industry and specific to your organisation's needs. These KPIs could include metrics such as on-time delivery, order accuracy, quality of products or services, responsiveness to inquiries, financial stability, compliance with regulations, and customer satisfaction.
Utilise Technology and Automation:
Integrate technology and automation into your data analysis process. Vendor management software and analytics tools can help streamline data collection, analysis, and reporting. This enables you to centralise data, gain real-time insights, and make data-driven decisions.
Regular Performance Reviews:
Conduct regular reviews and assessments of vendor performance through meetings, reports, or scorecards. These reviews provide an opportunity to discuss performance, address any issues, and identify areas where the vendor can improve. Regular feedback is essential for maintaining a positive and productive relationship with your vendors.
Benchmarking and Comparison:
Compare the vendor's performance against industry standards and best practices. This benchmarking analysis will help you identify areas where your vendors excel and areas where they need to improve to meet industry expectations.
- Identify Trends and Patterns:
- Root Cause Analysis:
When analysing the data, focus on identifying the root causes of any issues or problems. This will enable you to address the underlying factors affecting the vendor's performance and implement effective solutions.
Data Visualisation and Reporting:
Use data visualisation tools, such as dashboards and charts, to present the analysed data in a clear and accessible format. Create reports that summarise the key findings, trends, and areas of improvement. Ensure that these reports are communicated to both the vendor and your organisation's stakeholders to drive collaborative action.
By following these steps and analysing the data effectively, you can make informed decisions about your vendor relationships, improve performance, and ultimately contribute to the success and competitiveness of your organisation.
Is Your iPad Being Monitored? Here's How to Find Out
You may want to see also

Monitor compliance
Monitoring vendor compliance is a critical aspect of vendor performance management. It involves evaluating whether vendors adhere to contractual agreements, regulatory requirements, and ethical standards. By doing so, organisations can proactively identify and mitigate potential risks associated with vendor non-compliance.
To effectively monitor vendor compliance, organisations should establish clear performance metrics and conduct regular evaluations through scorecards. This includes assessing vendors' performance against key performance indicators (KPIs) such as on-time delivery, order accuracy, quality of products or services, responsiveness to customer inquiries, and financial stability.
Additionally, organisations should foster open communication with vendors to address any compliance issues promptly. This collaborative approach helps to strengthen the relationship between the organisation and the vendor, leading to continuous improvement and innovation.
Integrating technology, such as vendor management software, can streamline the vendor compliance monitoring process. For example, organisations can use software to centralise vendor records, including certificates, licenses, and compliance-related documentation. This enables easy access to information and ensures that vendors meet industry, regulatory, and compliance requirements.
By regularly monitoring vendor compliance, organisations can identify areas where vendors may not be meeting their contractual obligations or industry standards. This allows for timely corrective actions and ensures that the organisation's expectations are met. Ultimately, effective monitoring of vendor compliance contributes to risk management and helps safeguard the organisation's operations and reputation.
CRT Monitor Sizing: Understanding the Measurement Techniques
You may want to see also