The Camera Raw filter is a powerful tool that offers access to the features of Adobe Camera Raw (ACR) in your Photoshop workflow. It allows you to make adjustments within ACR at any time during your workflow, rather than limiting its usage to the RAW processing stage only. To convert the Camera Raw filter to a layer, you can first convert the image or image layer to a Smart Object (Smart Filter) layer. This allows you to re-edit the Camera Raw settings just as you would when editing a raw image. You can then apply the Camera Raw filter as a Smart Filter.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| How to access the filter | Select Filter > Camera Raw Filter |
| How to convert to a layer | Convert the background to a smart object, then add the Camera Raw filter |
| How to apply to multiple layers | Group layers into a Smart Object/Smart Filter, then apply the Camera Raw filter |
| How to apply to a single layer | Select the layer and choose Camera Raw Filter from the Filter menu |
| How to apply to a video file | Convert the video file to a Smart Object, then add the Camera Raw filter |
What You'll Learn

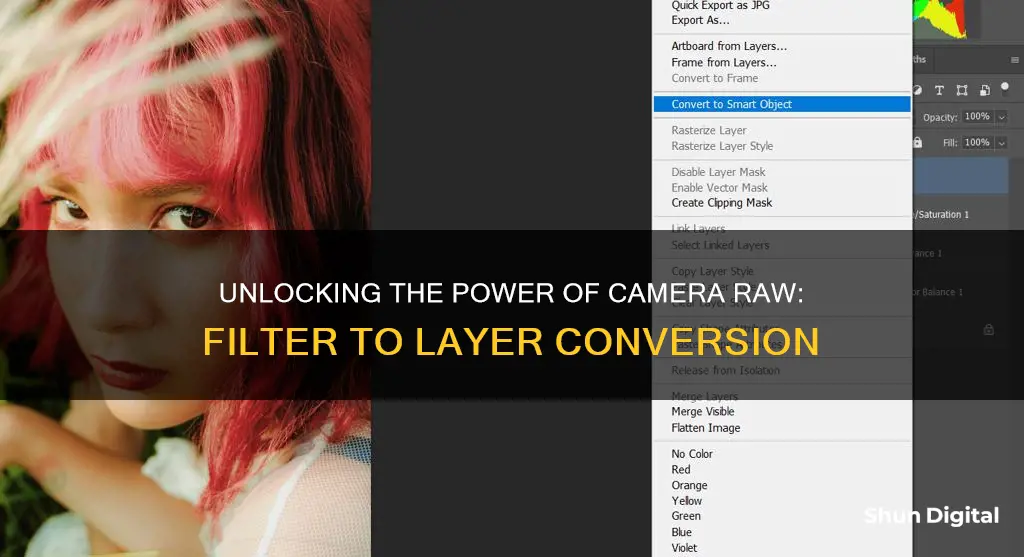
Convert to a smart object
Converting to a smart object is a simple process that can be done at any time during the editing process. It allows you to make adjustments to your image without having to start over again.
To convert to a smart object, right-click on the layer and select "Convert to Smart Object". This will allow you to make any adjustments you want within Adobe Camera Raw, and once you're done, simply click "OK".
Converting to a smart object gives you the flexibility to go back and tweak any adjustments you've made. It's especially useful if you tend to second-guess your decisions or want to try out different editing techniques.
It's important to note that when working with a smart object, you won't have the same versatility as when editing a RAW file in Adobe Camera Raw (ACR). You'll lose some functionality, such as the white balance adjustment and the Crop and Rotate tools. However, it's still a powerful tool that can enhance your editing capabilities and save you time in the long run.
Additionally, you can apply the Camera Raw filter to multiple layers by first grouping them together within a Smart Object/Smart Filter. This allows you to make adjustments to the grouped layers as if they were a single layer.
Ejecting the Casio EX-Z1000 Battery: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Apply the filter
Now that you have converted your background to a smart object, you can apply the Camera Raw filter. Go to the Filter menu and choose Camera Raw Filter (Command+Shift+A on Mac, or Control+Shift+A on PC).
You can also apply the Camera Raw filter to multiple layers at once. To do this, first group the layers together within a Smart Object/Smart Filter. Then, select the Camera Raw Filter, which will be applied to a composite of all the layers contained in the Smart Object.
If you want to apply the filter to a single-pixel image layer, simply select that layer and choose Camera Raw Filter from the Filter menu. If you want the filter effect on that layer to be reversible, choose 'Convert for Smart Filters' first.
The Camera Raw Filter can also be applied to video files. First, convert a video file to a Smart Object, then choose to add Camera Raw as a filter. This allows you to use almost all of the Camera Raw editing tools to improve the appearance of a video clip.
Lithium-Ion Camera Batteries: Powering Your Photography
You may want to see also

Fine-tune adjustments
- Stamp the layers: Before applying the Camera Raw filter, it is recommended to stamp all the layers by pressing "Ctrl/Cmd+Shift+Alt/Opt+E". This combines all your layers into a new layer, giving you a single layer to work with and avoiding any loss of previous edits.
- White balance adjustment: The Camera Raw filter allows you to adjust the white balance of your image. Use the White Balance tool under the Basic panel to specify an area in the image that you want to be neutral (white or gray), and the filter will adjust the colors accordingly.
- Exposure adjustments: You can fine-tune the exposure of your image by dragging the Exposure slider in the Basic panel. An adjustment of +1.00 is similar to opening the aperture by one stop, while an adjustment of -1.00 is like closing the aperture by one stop.
- Contrast adjustments: The Contrast slider in the Basic panel allows you to increase or decrease image contrast, mainly affecting the midtones. Increasing contrast will make the middle-to-dark areas darker and the middle-to-light areas lighter.
- Highlight and shadow recovery: The Highlights and Shadows sliders in the Basic panel can be used to recover highlight and shadow details, respectively. Drag the sliders to the left to darken highlights or brighten shadows, and to the right to brighten highlights or darken shadows.
- Clarity adjustments: The Clarity slider in the Basic panel can add depth to your image by increasing local contrast, especially in the midtones. Zoom in to 100% or more and increase the setting until you see halos near the edge details, then reduce the setting slightly.
- Vibrance and saturation adjustments: The Vibrance and Saturation sliders in the Basic panel allow you to adjust the color saturation of your image. Vibrance prevents skin tones from becoming oversaturated, while Saturation adjusts all colors equally.
- Histogram and RGB levels: Keep an eye on the histogram as you make adjustments. A histogram with non-zero values for each luminance value indicates an image with good contrast. Adjust your settings to spread out the pixel values evenly across the histogram.
- Color panel adjustments: The Color panel in Camera Raw allows you to fine-tune the white balance and make precise adjustments to specific colors. The Point Color tool, introduced in the October 2023 release, lets you select and refine individual colors across hue, saturation, and luminance.
- Curves adjustments: After making basic tonal adjustments in the Basic panel, you can fine-tune your image using the Curve drop-down in the Edit panel. The Parametric Curve, for example, helps you adjust values in specific tonal ranges.
- Targeted adjustment tool: The Targeted Adjustment tool in the Curve panel allows you to make tonal and color corrections by dragging directly on your image. This tool can adjust multiple sliders at once, so be sure to check which sliders are being affected.
Unleashing Creative Control: Understanding Camera Raw's Power
You may want to see also

Make quick edits
Making quick edits with the Camera Raw filter is easy and can be a game-changer for photographers of all skill levels. Here are some tips to make quick edits using the Camera Raw filter:
Fine-tune adjustments after RAW processing
If you've already made some edits in Photoshop and want to go back to make some fine-tune adjustments, you can use the Camera Raw filter without losing your previous work. Simply stamp the layers to a new layer and run the Camera Raw filter. This is perfect for quick edits like exposure, contrast, and vibrancy adjustments.
Make trickier adjustments
Some adjustments, like the Clarity tool in ACR, can be tricky to replicate in Photoshop. The Camera Raw filter makes it easier to make these types of adjustments and can save you a lot of time. For example, you can use the Highlights, Whites, Darks, and Blacks sliders in the Camera Raw filter to make quick, intuitive global contrast adjustments.
Apply local adjustments
The Camera Raw filter allows you to make targeted adjustments to specific areas of your image. You can use tools like the Camera Raw Radial filter to adjust the brightness of a particular area, like a shirt sleeve that's too bright. You can also use a layer mask to ensure that your adjustments only affect the parts of the image you want.
Add quick and easy vignettes
The Vignette tool in the Camera Raw filter is easy to use and can help you create subtle or extreme vignettes in just a few seconds. If any part of the vignette interferes with your subject, you can always mask it out later using Photoshop's masking options.
Make final tweaks
Once you've finished editing your image in Photoshop, you can run the Camera Raw filter to see if there are any small tweaks you can make to enhance your photo. These can include tiny shifts to the file's exposure, contrast, clarity, and vibrance.
Camera Battery Drain: Quick Fix Tips
You may want to see also

Use for black and white conversion
Converting a colour image to black and white can be done in a million different ways. Here are some methods to achieve this using the Camera Raw Filter in Photoshop.
Using the HSL/Grayscale Panel
Open the image in Photoshop. Go to the Filter pull-down menu and choose Convert for Smart Filters. Then, go to the Filter pull-down menu again and choose Camera Raw Filter. This will launch the image inside Camera Raw. Zoom in on the image for a better view. Go to the HSL/Grayscale panel and click on Convert to Grayscale. You can now use the Targeted Adjustment Tool to brighten or darken different areas of the image. You can also use the sliders to darken or brighten specific colours.
Using the Channel Mixer
This method is a bit more complicated but offers more control over the black and white conversion. First, duplicate the image so you have a copy to work with. Then, go to the Channels tab in the Layers Palette. You should see four sections: RGB, Red, Green, and Blue. Select the Red, Green, and Blue channels one by one to see how your image would look in black and white. Choose the channel that has the most pleasing effect. Activate the selection by going to Select > All, then copy the selected channel. Now, paste the copied channel into the other two channels. Click on the RGB channel and your image will now be in black and white.
Using the Black and White Adjustment Layer
Go to the Layers Palette and choose Black and White. Your image will be converted to black and white and you will see an array of colour sliders in the properties tab. Moving these sliders to the right will brighten any tones associated with that colour, and moving them to the left will darken those tones. This is a non-destructive method of editing, so you can always go back to the properties tab and alter the sliders.
Using the Gradient Map
This method is the most powerful and complicated black and white conversion tool. First, set your foreground and background colours to black and white. Then, go to the Layers Palette and choose Gradient Map. Make sure the gradient selected is black to white. Your image is now monochromatic and may have higher contrast. If your image looks like a negative, click the Reverse box in the Gradient Map's properties tab. You can further adjust the tonality of your image by double-clicking on the image of the gradient in the properties tab, which will open the Gradient Editor. Moving the white slider to the right will brighten the highlights, and moving the black slider to the left will deepen the shadows. You can also adjust the mid-tones by creating a new slider in the Gradient Editor.
Replacing Polaroid 600 Camera Battery: Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To convert a camera raw filter to a layer, first, make sure the photo layer is a smart layer. Then, you can create a camera raw filter as an adjustable layer on top.
The Camera Raw filter offers access to the features of ACR within your Photoshop workflow. It allows you to make adjustments within ACR at any time during your workflow, rather than limiting its usage to the RAW processing stage only.
Yes, there are some limitations to the Camera Raw filter. For example, you may lose some functionality of the white balance adjustment as you are not working from a RAW file. The Crop and Rotate tools are also not available when using the Camera Raw filter.
Yes, you can apply the Camera Raw filter to multiple layers. First, group the layers together within a Smart Object/Smart Filter. Then, apply the Camera Raw filter to the Smart Object.
Yes, you can apply the Camera Raw filter to video files. First, convert the video file to a Smart Object, then add the Camera Raw filter.