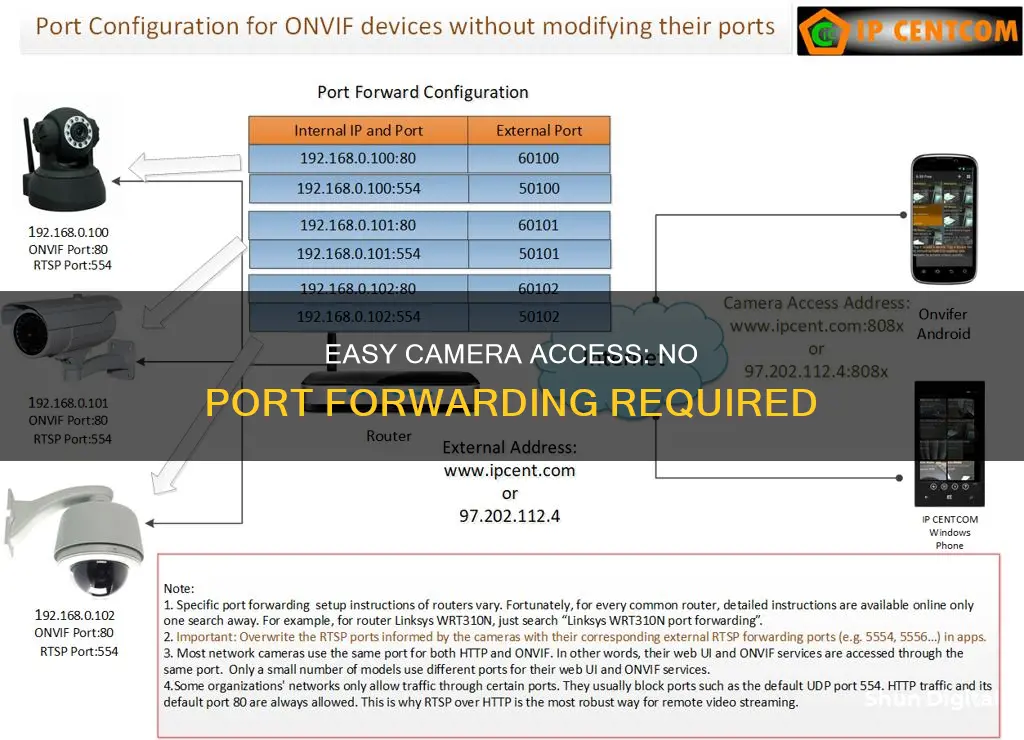
IP cameras are popular for home and business security, allowing users to remotely monitor their property. To access an IP camera remotely, users must first configure the device for remote access. This process is known as port forwarding and can be complex for those unfamiliar with networking concepts. Port forwarding is necessary because most IP cameras use a specific port to communicate with other devices on the network. When a device sends data across a network, it uses a specific port number, which can be thought of as a virtual door that allows data to be sent and received by the correct device. Routers and ISPs are typically configured to block incoming connections from the internet as a security measure, so to access an IP camera, the router must be configured to forward any incoming connections on the specific port used by the camera to the local IP address of the camera.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Method | VPN, P2P, UPnP, DHCP reservation, Static IP address, DDNS service, Port forwarding |
| Devices | Computer, smartphone, tablet |
| Software | Blue Iris, VPN Primer for Noobs, OpenVPN, ZeroTier, IP Cam Talk, CCTV Camera Pros, Reolink, LocalXpose, Dynamic DNS, DHCP, DDNS |
| Protocols | RTSP, HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, TCP, UDP |
| Ports | 7000, 554, 80, 443, 8080/TCP, 4444 |
| IP Address | 192.168.0.101, 192.168.0.2, 207.5.23.205, 182.37.154.136 |
What You'll Learn

Use a VPN
Using a VPN is a much safer method of accessing your cameras remotely than port forwarding. It is also recommended over port forwarding unless you want to get hacked and jeopardise the security and integrity of your network.
With a VPN, you can better restrict who can access the network from the outside. You can log who logged in, when they logged in, and from where. You can also ensure that the traffic from end to end is encrypted. With digital certificates or manual keys, you can limit access to specific devices.
Using a VPN, you don't have to mess around with port forwarding, which exposes your internal network to attack via the cameras. IP cameras have notoriously bad security and many can be exploited through their web interface via maliciously crafted URLs, bypassing any built-in security.
A reliable VPN can help you encrypt your data and transfer it securely to the other device. PureVPN, for example, uses AES-256 bits encryption standard, which is the same standard used by the US military.
However, when using a VPN with your IP camera application, you might face problems connecting to the IP camera remotely over the network. This problem usually occurs when the default IP camera transmission TCP port is blocked on your network. To solve this problem, you can use the Port Forwarding feature offered by some VPN services, which allows you to open the desired ports on your network to use them for your IP camera applications.
Apple Watch 4: Camera Functionality Explored
You may want to see also

Use a cloud server
Using a cloud server to access your cameras without port forwarding is possible, but it may not be the most secure method.
Cloud-based IP camera systems typically use P2P (peer-to-peer) technology, which allows you to access your cameras from anywhere in the world with an internet connection. This can be done through a web browser or a dedicated app provided by the camera manufacturer.
To set up remote access to your cameras via a cloud server, follow these general steps:
- Install the camera manufacturer's app on your smartphone or computer.
- Launch the app and create an account or log in if you already have an account.
- Add your camera device to the app by entering a unique ID number (UID) or scanning a QR code.
- Some apps may require you to enter the camera's IP address, which can be found in the camera's network settings.
- Once your camera is added to the app, you should be able to view the live feed from anywhere.
It is important to note that while cloud-based access is convenient, it may come with security risks. Some cloud services may require monthly fees to maintain a secure connection and protect your privacy.
Additionally, it is recommended to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) for a more secure remote connection. A VPN adds an extra layer of encryption, ensuring that your camera feed is only accessible to authorised users.
In summary, while using a cloud server to access your cameras without port forwarding is possible, prioritising security is crucial. Consider using a VPN for added protection and always research the security features offered by your camera manufacturer and cloud service provider.
Apple Watch Series 3: Camera-Equipped or Not?
You may want to see also

Use a static IP address
Using a static IP address is another way to set up remote viewing for your security camera without port forwarding. This method is possible if your Internet Service Provider (ISP) offers you a static IP address.
A static IP address is an unchanging, permanent IP address that is assigned to a device on a network. In this case, your ISP would assign a static IP address to your router, which would allow you to always access your camera remotely using that IP address.
If your ISP provides you with a static IP address, you can set up remote viewing for your security camera by following these steps:
- Find the IP address of your security camera. This can usually be found in the network status page of your camera software or your router configuration software.
- Check the WAN/External IP address of your router. This is the static IP address that your ISP has assigned to your router.
- Use the URL address, which consists of your WAN IP address and the port number, to access your security camera remotely. For example, if your WAN IP address is 182.37.154.136 and the HTTP port is 8001, the URL address would be "http://182.37.154.136:8001".
- Enter this URL address into your web browser, and you should be able to view your security camera online outside of your home network.
Using a static IP address from your ISP can be a convenient way to set up remote viewing for your security camera without having to worry about port forwarding or dynamic IP address changes. However, it is important to note that some ISPs may charge additional fees for providing a static IP address.
Wiring Swann Cameras Directly to Your TV: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Use a reverse proxy
A reverse proxy is a server that acts as an intermediary between a client and another server. In this case, the client is your device, and the other server is the one hosting your camera feed. The reverse proxy server takes requests from your device and forwards them to the camera server, then returns the camera server's response back to your device. This way, your device can access the camera feed without connecting directly to the camera server.
To set up a reverse proxy for your cameras, you can use a service like LocalXpose. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Download LocalXpose: Visit the LocalXpose website and download the software to your device.
- Install and Launch LocalXpose: Follow the installation instructions provided by LocalXpose. Once installed, launch the application.
- Configure Port Forwarding: In the LocalXpose application, you will need to configure port forwarding. This involves specifying the port number that your camera uses. You can usually find this information in your camera's manual or web-based configuration interface.
- Set Up a Reverse Proxy Rule: In LocalXpose, create a rule that forwards incoming connections on a specific port to your camera's local IP address and port. For example, if your camera is listening on port 8080/TCP, you would forward incoming connections on port 4444 to your camera's local IP address and port 8080.
- Generate a Public Address: Once you have set up the reverse proxy rule, LocalXpose will generate a public address that you can use to access your camera. This address will typically be in the format of "camera.loclx.io", where "camera" is the subdomain and "loclx.io" is the domain provided by LocalXpose.
- Access Your Camera Remotely: You can now use the public address provided by LocalXpose to access your camera feed from anywhere. Simply enter the address into a web browser, and you should be able to view your camera feed.
By using a reverse proxy like LocalXpose, you can access your cameras without having to worry about port forwarding configurations on your router. This method provides a simple and secure way to remotely view your cameras without exposing your network to potential security risks associated with direct port forwarding.
Exploring Apple Watch: Accessing the Camera Functionality
You may want to see also

Use a Dynamic DNS service
Dynamic Domain Name Systems (DDNS) allow you to access your security cameras remotely. This is especially useful if your Internet Service Provider (ISP) has assigned you a dynamic IP address.
Step 1: Get a Dynamic DNS Hostname
First, you will need to sign up for a DDNS service. There are several providers available, such as No-IP, that offer both free and paid versions. Once you have chosen a provider, create an account and obtain your hostname.
Step 2: Login to Your Camera Administration
Next, log in to your camera's administration settings using its local IP address. This can usually be found in the Network section of your camera's settings.
Step 3: Enable DDNS and Choose a Provider
In the "Network" section, enable the DDNS function and select a DDNS provider from the dropdown menu. It is recommended to choose the same provider that you signed up with in Step 1 for ease of use.
Step 4: Enter Your DDNS Credentials
Fill in the required fields, including the domain/DDNS host, your username, and password associated with your DDNS provider.
Step 5: Save Your Settings
Scroll down and save your settings. Your camera is now configured to work with your DDNS service.
Step 6: Set Up Port Forwarding (Optional)
If you wish to access your camera feed from outside your local network, you may need to set up port forwarding on your router. First, find the Media Port value of your camera in the "Network Advance" or "Port Settings" section. Then, log in to your router and forward this Media Port to the IP address of your camera.
Note that the specific steps for port forwarding may vary depending on your router model, so be sure to refer to your router's user manual for detailed instructions.
Step 7: Test Your Connection
Finally, test your connection by accessing your camera feed through a web browser. If you are using Internet Explorer, remember to add "http://" before the domain name. For other browsers, simply type in the DDNS hostname.
By following these steps, you should now be able to view your security cameras remotely without the need for port forwarding.
Smart TVs: Are They Watching You?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can access your IP camera remotely by connecting it to an app/client provided by the manufacturer. This allows you to stream your IP camera over the internet.
You can set up remote camera monitoring by downloading the manufacturer's app or client to your phone or computer. You will then need to enter a unique ID number (UID) to add the camera device.
Port forwarding is a process that enables users to access their security cameras over the internet. It is necessary because most IP cameras use a specific port to communicate with other devices on the network. To access an IP camera from outside your local network, it must be configured for port forwarding.







