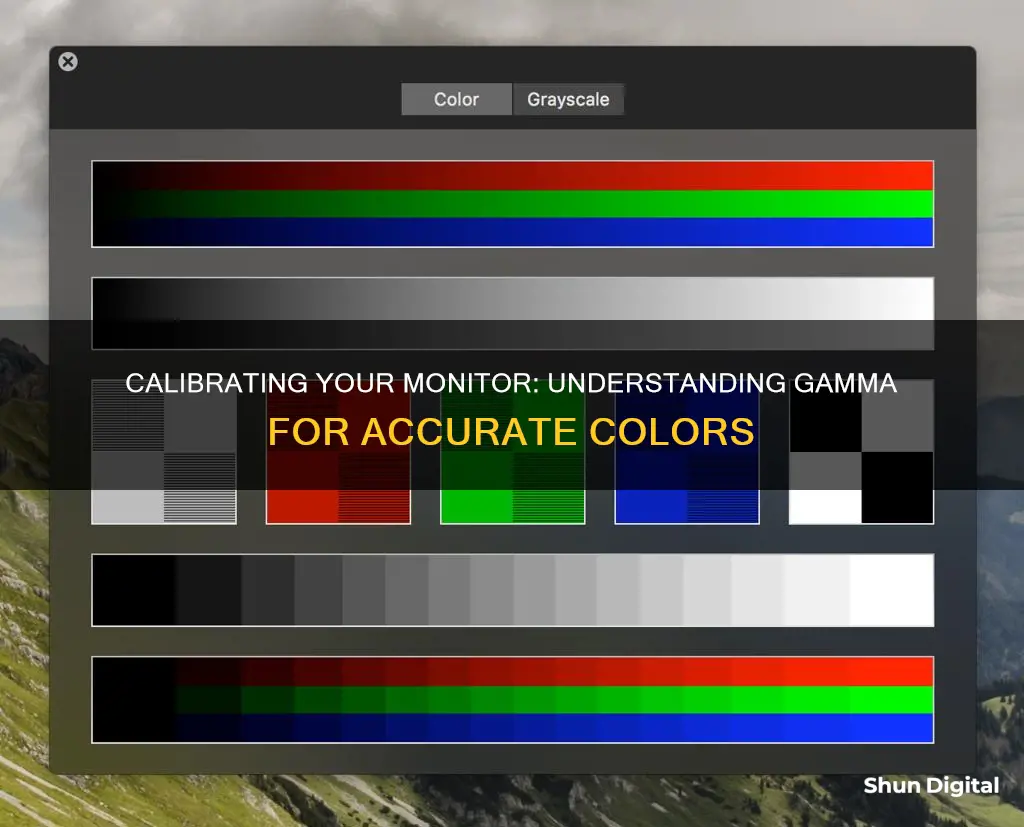
Gamma is an important feature of your monitor, affecting the appearance of dark areas, shadows, mid-tones, and highlights. It is a measure of the brightness of your monitor's pixels at every brightness level from 0-100%. A gamma that is too low or too high can result in a washed-out or dull image, so it is important to ensure your monitor is correctly calibrated. The standard gamma value for Windows is 2.2, while for Mac OS it is 1.8. You can check your monitor's gamma value by viewing a specific image and comparing the brightness of square outlines and the stripes around them. If the square frame appears dark, your gamma value is low, and if it appears bright, the gamma value is high.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| How to find out the gamma of your monitor | View a gamma image on your screen, then adjust the brightness and contrast until you find the display's gamma value. |
| Gamma value for Windows | 2.2 |
| Gamma value for Mac OS | 1.8 |
| Gamma value for movie and TV industry | 2.4 |
| Gamma value for digital movie theaters | 2.6 |
| How to adjust gamma settings | Use the OSD (on-screen display) on your monitor or use gamma correction software. |
| How to equalize gamma between Windows and Mac | Change the gamma value on the Mac OS and adjust the monitor gamma setting to 1.8 for images created on a Mac OS. |
| How to check display quality at different angles | View the gamma image and move up and down; if the bars change colour slightly, it's IPS or PLS, if they change colour a lot, it's TN. |
| Software to make gamma corrections | QuickGamma |
| Ideal gamma value | 1.0 |
What You'll Learn

How to check your monitor's gamma value
The gamma value of your monitor determines how smoothly it transitions from black to white. It is important because it affects the appearance of dark areas, like blacks and shadows, and can impact the overall image quality. While there are software tools available to check the gamma value, there is also a quick manual check that you can perform.
Step 1: First, ensure your monitor is set to its native resolution.
Step 2: Position yourself slightly back from your monitor.
Step 3: View the image with different gamma values on your screen. You can find such images online.
Step 4: Look directly at the image and half-close your eyes.
Step 5: Compare the square outlines and the stripes around them. Look for patterns that appear to have the same tone of grey or brightness.
Step 6: If the square frame appears dark, your monitor's gamma value is low. If the square frame appears bright, the gamma value is high.
For example, if you are looking at an image with a gamma value of 2.2 and the square frame appears dark, your monitor's gamma value is lower than 2.2. If the square frame appears bright, the gamma value is higher than 2.2.
This method will give you a rough idea of your monitor's gamma value. For a more accurate reading, you can use specialised software or hardware tools.
Connecting Your Xbox to the New MSI Monitor
You may want to see also

The impact of gamma on colour reproduction
Gamma is a non-linear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma is important because it affects the appearance of dark areas, like blacks and shadows and mid-tones, as well as highlights. It defines the relationship between a pixel's numerical value and its actual luminance. Without gamma, shades captured by digital cameras wouldn't appear as they did to our eyes (on a standard monitor).
The human perception of brightness (lightness) follows an approximate power function, with greater sensitivity to relative differences between darker tones than between lighter tones. Gamma encoding of images is used to optimise the usage of bits when encoding an image or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and colour. If images are not gamma-encoded, they allocate too many bits or too much bandwidth to highlights that humans cannot differentiate, and too few bits or too little bandwidth to shadow values that humans are sensitive to.
The standard gamma value for the Mac OS is 1.8, while the standard gamma value for Windows is 2.2. The standard gamma value in a Windows environment is 2.2 and many LCD monitors can be adjusted to a gamma value of 2.2. However, due to the individual tendencies of LCD monitors (or the LCD panels installed in them), it's hard to graph a smooth gamma curve of 2.2. Traditionally, LCD panels have featured S-shaped gamma curves, with ups and downs here and there and curves that diverge by RGB colour. This phenomenon is particularly marked for dark and light tones, often appearing to the eye of the user as tone jumps, colour deviations, and colour breakdown.
Monitors with poor gamma can either crush detail at various points or wash it out, making the entire picture appear flat and dull. Proper gamma leads to more depth and realism and a more three-dimensional image.
The image below (courtesy of BenQ) shows an image with the 2.2 gamma standard compared to that same image with low gamma and with high gamma.
! [Gamma 2.2/the standard](https://i.imgur.com/mJ8bY0z.png)
! [Gamma 1.0/low gamma](https://i.imgur.com/mJ8bY0z.png)
! [Gamma 2.6/high gamma](https://i.imgur.com/mJ8bY0z.png)
In most computer display systems, images are encoded with a gamma of about 0.45 and decoded with the reciprocal gamma of 2.2. A notable exception, until the release of Mac OS X 10.6 (Snow Leopard) in September 2009, were Macintosh computers, which encoded with a gamma of 0.55 and decoded with a gamma of 1.8.
How to find out the gamma of your monitor
Monitors actually have gamma values in the range 2.0 to 2.6. If your monitor is usually used in a dim environment, we often use a gamma value that is 10% - 20% lower than the actual display gamma to give the images more contrast. Some systems, such as Macs, NeXTs, and SGIs, already do gamma correction, so they may have display gammas of 1.0 or 1.8 or so.
To find the gamma of your monitor, follow these steps:
- Darken the room and set the monitor brightness and contrast to maximum.
- While viewing a black screen, lower the brightness gradually until the "background" (i.e. the scanlines that you see across what should be a black screen) is no longer noticeable (when it just fades from view).
- Now, while viewing the above image, lower the contrast until the alternating white and black bars on the left edges of each column are equal in width. This is trying to get a 50% grey by using half white and half black. If this is not possible, choose a contrast setting that is about in the middle of the available range.
- While viewing the image from a distance, or with squinted eyes, one of the numbered "swatches" will best match the grey value approximated by the white and black bars. The number in this "swatch" is your display's actual gamma value.
Fixing TCP Port Monitor 1722 Not Found Error
You may want to see also

Gamma correction methods
Gamma correction is a method used to adjust image brightness and darkness levels to align with
Lace Monitor Buying: Where to Purchase Your New Pet
You may want to see also

The difference between gamma in Windows and Mac OS
The gamma of a monitor refers to the luminance of each pixel at a given brightness level, from 0-100%. Gamma affects the appearance of dark areas, like blacks and shadows, mid-tones, and highlights. Lower gamma makes shadows look brighter and can result in a flatter, washed-out image, while higher gamma can make it harder to see details in shadows.
The standard gamma for the sRGB colour space is 2.2, which generally gives Windows accurate colour results. The standard gamma for Mac OS is 1.8. These differences are due to the design concepts and histories of the two operating systems. Windows adopted a gamma value corresponding to television (2.2), while Mac OS adopted a gamma value corresponding to commercial printers (1.8).
To check the gamma value of an LCD monitor, you can use image patterns and visually compare the square outlines and the stripes around them to find patterns that appear to have the same tone of gray (brightness). Based on a gamma value of 2.2, if the square frame appears dark, the LCD monitor's gamma value is low, and if it appears bright, the gamma value is high.
To change the gamma settings on a Windows 10 or 11 PC, go to Settings > Display > Advanced display settings > Display adapter properties for Display 1 > Color management > Calibrate display. Use the slider on the left to find the right gamma setting for your display by adjusting it until the dots in the middle are less visible.
To set the display gamma on a Mac, you can use the built-in ColorSync Utility or open the Color Calibrator Assistant in Expert Mode by going to Apple > System Preferences > Displays > Color (hold the ALT key and click Calibrate). Then, click Continue until you get to Target Gamma.
Monitoring App Usage: Android's Built-in Tools for Control
You may want to see also

Gamma and its link to visual response
Gamma is a term that refers to the brightness of intermediate tones (greys) on a digital display. It is often associated with a number, such as 2.2 or 2.4, which represents the extent of the curve from black to white or vice versa. Gamma can be described as how smoothly black transitions to white on a screen, and it plays a crucial role in determining image quality and visual perception.
The standard gamma value for the sRGB colour space, which includes most computer displays, is 2.2. This value is also the standard for Windows operating systems. A gamma of 2.2 delivers a balanced or 'neutral' tone between highlights and shadows, making it easier to distinguish the greys in between. A gamma value higher than 2.2 can make it harder to see details in shadows, while a lower gamma value can result in flatter, washed-out images where shadows appear brighter.
The standard gamma value for Mac OS, on the other hand, has traditionally been 1.8, corresponding to commercial printers. However, with the release of Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard in 2009, Apple switched to a gamma value of 2.2, bringing it in line with the Windows standard. This change was made due to the increasing use of colour spaces like sRGB and Adobe RGB, which are commonly used for wide-gamut printing.
Gamma values also play a significant role in the movie and TV industries. The Rec. 709 standard, for example, specifies a gamma value of 2.4, which enhances contrast and colour saturation. More recently, the DCI-P3 standard, endorsed by many digital movie theatres, has adopted a gamma value of 2.6, resulting in darker and more saturated images as intended by the directors.
The importance of gamma in visual response is further highlighted by the issue of gamma correction. Gamma correction is necessary to compensate for the unique colour handling characteristics of different devices, such as monitors, printers, and scanners. Without proper gamma correction, colours may appear unnatural or deviated when displayed on a device with different gamma characteristics.
To ensure accurate colour reproduction and visual response, it is essential to maintain a smooth gamma curve. An uneven gamma curve can lead to artefacts in perceptual grayscale and RGB ramps, making it challenging to distinguish greys and affecting colour accuracy and contrast.
To adjust gamma settings on a monitor, users can usually access the On-Screen Display (OSD) and select from pre-calibrated gamma curves, typically ranging from 1.6 to 2.6. Additionally, specialised calibration software and external calibrators can be used to fine-tune gamma settings for professional colour accuracy.
IBM Employee Internet Usage: Monitored or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can find out the gamma of your monitor by viewing a gamma image. This involves downloading an image with gamma values and viewing it on your monitor. You then need to visually compare the square outlines and the stripes around them, looking for patterns that appear to have the same tone of grey or brightness. The pattern where the square frame and the striped pattern appear closest in brightness represents the rough gamma value of your monitor.
Gamma refers to the brightness of a monitor's pixels at every brightness level, from 0-100%. It is often associated with a number, such as 2.2 or 2.4, which represents the extent of the curve from black to white or vice versa. Gamma affects the appearance of dark areas and highlights on a monitor, impacting the overall image quality.
There are a few ways to adjust the gamma settings on your monitor. One way is to use the on-screen display (OSD) on your monitor, which should have a Custom Mode in the Colour Mode option. Here, you can select different gamma curves. Another way is to use calibration software, such as BenQ's Palette Master Element, which allows you to select the desired gamma curve.