Monitoring supply chain performance is a critical business method, and with good reason. With low-cost country sourcing, outsourcing, customisation, and globalisation, supply chains are becoming increasingly complex. To improve performance, it's crucial to first understand how your supply chain is currently performing. This means establishing a comprehensive and systematic supply chain performance measurement system. While the appropriate metrics will vary depending on the industry, company, and scale of the business, a well-structured, hierarchical framework is universally necessary to organise and manage these metrics effectively.
There are several models and frameworks available to help with this, such as the SCOR model and the Balanced Scorecard. The former helps companies measure supply chain performance based on reliability, responsiveness, agility, cost, and assets. The latter helps businesses manage their future growth, plans, and objectives by measuring the requirements to set goals.
Other important supply chain performance measurement strategies include maintaining healthy supplier relationships, optimising inventory for reduced costs, and outsourcing supply chain operations.
What You'll Learn

Monitor various factors
Monitoring supply chain performance is crucial to ensure that the supply chain is aligned with the overall strategy and to identify areas that require improvement. To effectively monitor supply chain performance, it is essential to track various factors and metrics that provide insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain. Here are some key factors to monitor:
Balanced Scorecard:
The balanced scorecard is a popular framework used to measure supply chain performance. It helps organisations track and manage their future growth, plans, and objectives by setting goals and measuring performance against them. The balanced scorecard provides insights into core operations, including customer interactions, financial metrics, and internal business perspectives. It also enables organisations to identify areas where training or product development is necessary to maintain a competitive advantage.
Customer Service Levels:
Customer service levels are a critical aspect of supply chain performance. The order fill rate, which is the fraction of customer demands that are met from stock, is an important metric to monitor. Proactive customer service, strong logistics with broad reporting and analytics, and valuing customer feedback are key to maintaining high customer service levels.
Supplier Relationships:
Maintaining healthy relationships with suppliers is essential for supply chain performance. Two-way communication, trust, and treating suppliers as partners contribute to higher success rates, reduced risks, and enhanced collaboration and innovation. It is important to select suppliers strategically and collaborate closely with them to ensure a stable supply of goods and services.
Inventory Optimisation:
Optimising inventory levels is crucial for efficient supply chain management. By recording and monitoring inventory data, organisations can improve supply chain performance and reduce costs associated with excess inventory. Integrating tracking technologies, such as RFID chips and GPS-enabled forklifts, can help streamline the warehousing process and improve inventory management.
Logistics and Shipping:
Logistics is a critical area to monitor, as it is prone to disruptions and cost overruns. Adopting technologies like sensors and GPS tracking can enable real-time data analysis and allow for course corrections and route changes during shipments. Integrating these technologies with IoT sensors and shipment tracking tools can further enhance visibility and reduce costs.
Performance Metrics:
Organisations should define key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with their specific supply chain goals. These KPIs should be easy to understand, quantitative (based on real data), and focused on important aspects of the supply chain. Examples of KPIs include perfect order (percentage of complete orders with no re-orders or missing items), delivery lead time, and inventory carry rate.
Ford Bronco: Blind Spot Monitoring Feature Explained
You may want to see also

Consolidate your system
To monitor supply chain performance, it is important to consolidate your system by employing a well-structured, hierarchical framework to organise and manage your metrics. This framework should include both external and internal measures, with metrics that monitor the performance of an entire major functional area considered strategic, and those that monitor sub-functions of sub-functions considered operational.
A cohesive framework is necessary to avoid inadequate management support and the waste of resources that can result from developing conflicting metrics. A hierarchical performance measurement system offers several benefits, including providing a unified framework for aggregating performance metrics and facilitating the alignment of collective activities with a company's mission and objectives.
To achieve this consolidation, you can utilise models such as the SCOR model and the Balanced Scorecard, which is used to help businesses manage their future growth, plans, and objectives by measuring the requirements to set goals. This scorecard can be simple or complex, depending on demand, and provides insights into core operations by tracking customer interaction, financial status, internal business perspective, and innovative and learning perspectives.
Additionally, you can implement Industry 4.0 technology, such as IoT sensors, to gain visibility into your processes and production line maintenance needs. This technology enables you to monitor the health status of your production equipment and conduct predictive analysis to optimise maintenance and avoid unplanned downtime.
By consolidating your system through the use of hierarchical frameworks, performance measurement models, and technology, you can effectively monitor and improve your supply chain performance.
Setting Up Front Monitor Speakers: Mixer Connection Guide
You may want to see also

Benchmark your performance
Benchmarking your supply chain performance is a critical aspect of your business. It allows you to identify areas of improvement and ensure that your supply chain is aligned with your overall business strategy. Here are some detailed instructions on how to effectively benchmark your supply chain performance:
Understand the Importance of Benchmarking:
Benchmarking is the process of comparing your supply chain performance against established standards or best practices in the industry. It helps you identify gaps, set performance targets, and develop strategies for improvement. By benchmarking, you can gain valuable insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of your supply chain operations.
Define the Scope of Benchmarking:
Determine the specific areas of your supply chain that you want to benchmark. This could include metrics such as on-time delivery, inventory management, supplier performance, logistics efficiency, or customer service levels. Clearly defining the scope will help you focus your efforts and ensure a comprehensive evaluation of your supply chain performance.
Collect and Analyse Data:
Gather relevant data for the selected metrics across your supply chain. Utilise technology and tools, such as Industry 4.0 solutions, to collect accurate and timely data. Analyse the data to identify trends, patterns, and areas where your supply chain excels or falls behind. Compare your metrics with industry benchmarks and best-in-class organisations to identify opportunities for improvement.
Set Performance Targets:
Based on your data analysis and industry benchmarks, set realistic and measurable performance targets. These targets should be aligned with your overall business goals and considered achievable within a defined timeframe. Involve key stakeholders, such as supply chain managers and executives, in setting these targets to ensure buy-in and accountability.
Develop Improvement Strategies:
Brainstorm and implement strategies to meet your performance targets. This could include process optimisation, technology enhancements, staff training, or collaboration with suppliers and logistics providers. Encourage a culture of continuous improvement, where your team is actively involved in identifying bottlenecks and proposing innovative solutions.
Monitor and Review Performance:
Establish a robust performance measurement system to regularly monitor and review your supply chain performance against the set targets. Utilise tools such as balanced scorecards or hierarchical performance measurement frameworks to track your progress. Conduct periodic reviews to evaluate the effectiveness of your improvement strategies and make adjustments as necessary.
Foster Collaboration:
Engage and collaborate with your suppliers, logistics partners, and customers throughout the benchmarking process. Their insights and feedback are invaluable in identifying areas for improvement and co-creating effective solutions. Strong relationships and open communication will help align expectations and ensure a seamless supply chain.
Standardise and Document Processes:
Standardise the processes and best practices that contribute to successful supply chain performance. This ensures consistency, reduces variability, and enables continuous improvement. Document and share these standardised processes across your organisation and with relevant supply chain partners.
Continuously Benchmark and Improve:
Benchmarking is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. Regularly review and compare your supply chain performance against industry benchmarks and best practices. Stay updated with the latest advancements and innovations in supply chain management to identify new opportunities for enhancement.
By following these instructions and adapting them to your specific context, you can effectively benchmark your supply chain performance. Remember that benchmarking is a dynamic process that requires flexibility, adaptability, and a strong commitment to continuous improvement.
Monitoring PSU Performance: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Communicate results
Communicating the results of supply chain performance monitoring is a critical step in ensuring that all relevant stakeholders are informed and aligned with the company's overall strategy and objectives. Here are some key considerations for effective communication of supply chain performance results:
Define the Audience:
Understand who needs to receive the information. This may include senior leadership, department heads, operational teams, suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders. Each audience may have different information needs, so tailor your communication accordingly.
Set the Frequency:
Determine how often you will communicate the performance results. This could be on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on the nature of your business and the speed at which data becomes available. Regular updates help keep everyone informed and allow for course corrections if needed.
Choose the Right Metrics:
Select the most relevant metrics that provide a comprehensive view of supply chain performance. This includes metrics such as on-time delivery, order fill rate, inventory turns, lead times, forecasting accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Ensure that the metrics are easy to understand, quantifiable, and aligned with the company's strategic goals.
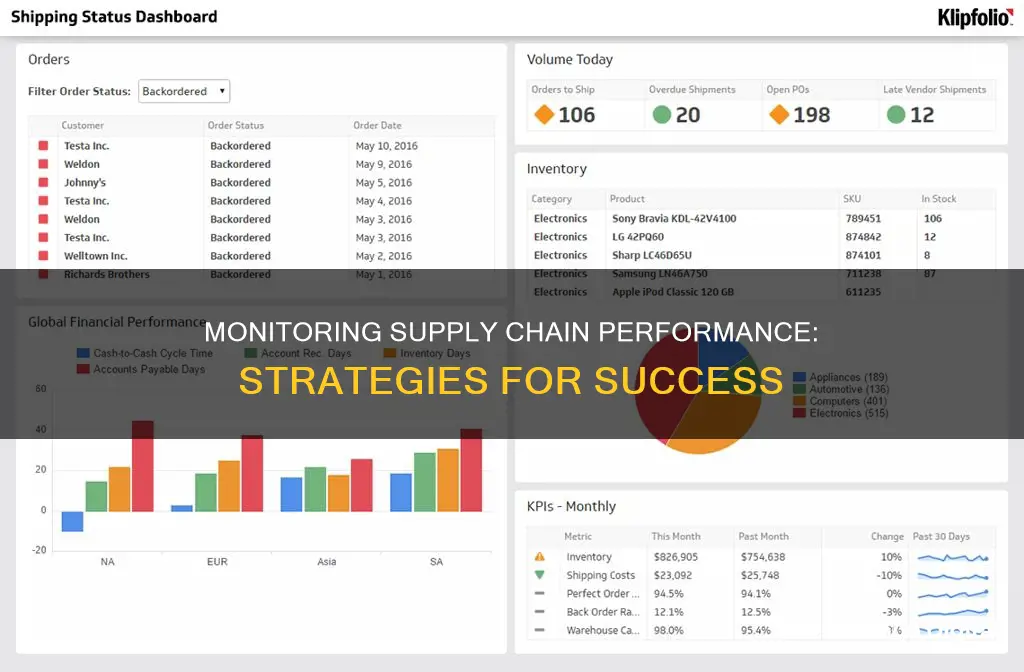
Use Visuals and Reports:
Create visual representations of the data, such as graphs, charts, and dashboards, to make complex information more accessible and engaging. Develop standard reports that highlight key performance indicators and distribute them to relevant stakeholders. Ensure that the reports are concise, clear, and actionable.
Hold Regular Meetings:
Schedule regular meetings to discuss supply chain performance results. These meetings provide a forum for interpreting the data, identifying areas for improvement, and making strategic decisions. Ensure that relevant stakeholders are invited and encouraged to participate in the discussions.
Foster a Culture of Transparency:
Encourage open communication and information sharing across the supply chain. Create a safe environment where stakeholders can voice their concerns, provide feedback, and suggest improvements. Transparency builds trust and promotes collaboration, leading to more effective supply chain management.
Utilize Technology:
Leverage technology platforms and data visualization tools to communicate performance results. Use dashboards and data analytics tools to provide real-time updates and enable stakeholders to drill down into specific areas of interest. Ensure that the technology is user-friendly and accessible to all relevant users.
Provide Context and Insights:
When communicating results, provide context by comparing current performance to historical data, industry benchmarks, or competitors' performance. Offer insights and analysis to help stakeholders understand the implications of the results and identify areas for improvement.
Solicit Feedback:
Encourage stakeholders to provide feedback on the performance results and the communication process itself. This feedback loop helps to refine and improve the way you monitor and communicate supply chain performance over time.
Link Performance to Strategic Goals:
Finally, tie the supply chain performance results to the company's strategic goals and objectives. Demonstrate how the metrics and key performance indicators align with the overall business strategy. This helps stakeholders understand the broader impact of supply chain performance and their role in driving organizational success.
Performance Monitoring Strategies of Big Businesses
You may want to see also

Monitor supplier performance
Monitoring supplier performance is a critical aspect of supply chain management. Here are some strategies and metrics to consider:
Strategic Selection of Suppliers
The choice of suppliers is one of the most challenging and crucial tasks for managers. During the selection process, managers must consider various factors, including strategic, operational, tangible, and intangible measures. Collaborating with suppliers is essential, as it helps to establish a strong relationship and improve monitoring capabilities.
Supplier On-Time Delivery
Measuring supplier on-time delivery performance is calculated based on the agreed-upon delivery time. This metric can be stated as a percentage (on-time or late) or in terms of hours late or early. Late deliveries can negatively impact manufacturing schedules and increase operating costs, so it is crucial to monitor this metric closely.
Maintaining Healthy Supplier Relationships
Healthy supplier relationships are characterised by two-way communication and trust between the customer and the seller. Building trust through honest communication, listening to concerns, and involving suppliers in your processes can turn them into vested partners. This leads to higher success rates, reduced risks, and enhanced collaboration and innovation.
Balanced Scorecard
The balanced scorecard is a tool that helps businesses manage their future growth, plans, and objectives by measuring the requirements to set goals. It can be simple or complex, depending on the company's needs, and it provides valuable insights into core operations. The balanced scorecard uses an Executive Information System (EIS) to monitor supply chain performance, including customer interaction, financial status, and internal business perspectives.
Economic Value Analysis (EVA)
Economic Value Analysis (EVA) measures the return on capital or economic value addition of an organisation. It assesses the performance of high-level executives in supply chain management, which is crucial since organisations invest significant capital in these individuals. EVA is widely used as a logistics scoreboard approach to measuring supply chain performance.
Removing BMW X5's On-Board Monitor: Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also







