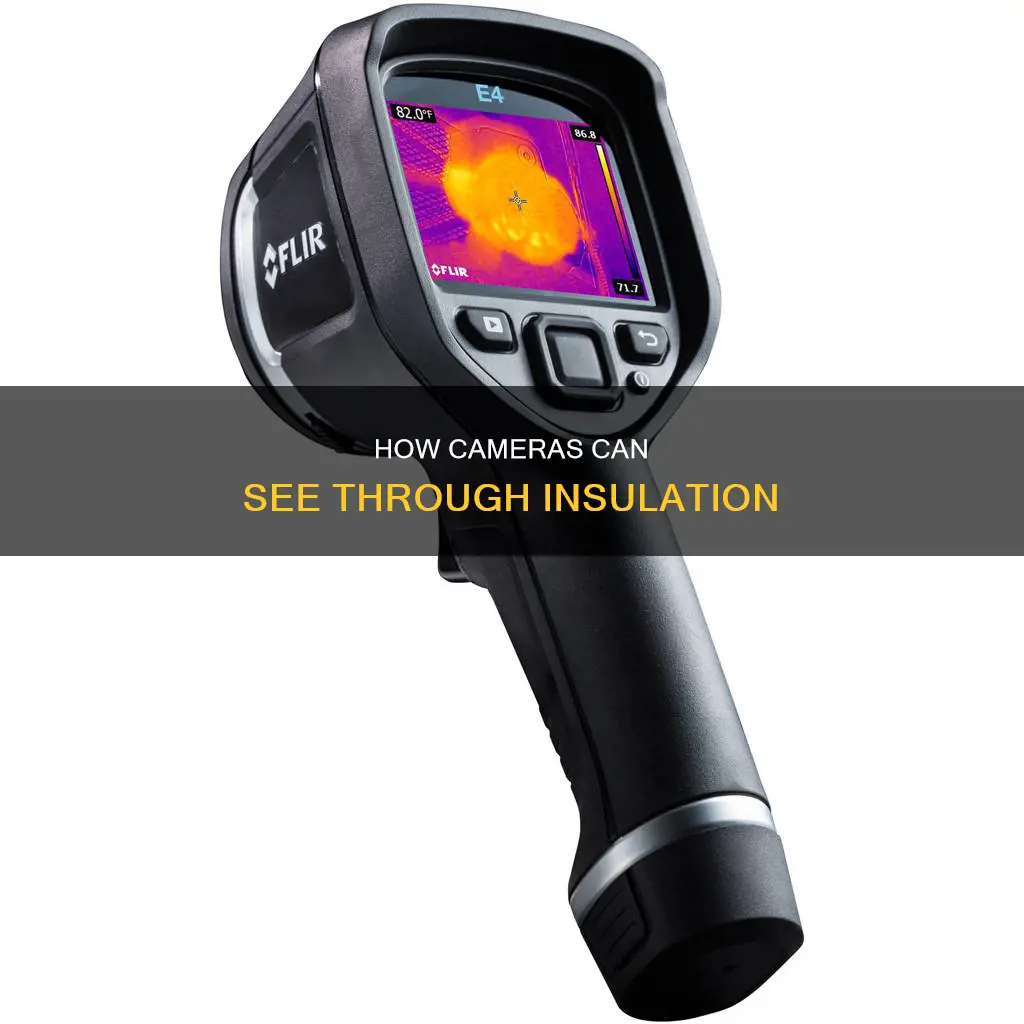
Thermal imaging cameras are an invaluable tool for identifying heat patterns and temperature differences. They can be used to detect issues such as water leaks, missing insulation, electrical hotspots, and air leaks. While thermal cameras cannot see through walls, they can detect temperature differences on the surface of walls, which can indicate missing insulation. To detect missing insulation, a temperature difference of at least 15-20 degrees is ideal. This can be achieved by heating or cooling a house depending on the external temperature. Thermal cameras are, therefore, a useful tool for identifying missing insulation but do not literally see through insulation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Can IR cameras see through insulation? | No, but they can detect temperature differences on the surface of the insulation. |
| How do IR cameras work? | IR cameras detect the invisible world of infrared waves or "heat" that is radiated by the environment. |
| What can IR cameras see? | IR cameras can see hidden water leaks, approaching animals, electrical hotspots, missing insulation, and human footsteps. |
| How do you prepare for an IR camera inspection? | To prepare for an IR camera inspection, ensure there is a temperature difference of at least 15-20 degrees between the inside and outside of the house. |
What You'll Learn
- IR cameras can identify insulation defects.
- They can't see through walls, but can detect heat signatures from internal elements
- They can identify temperature differences of 15-20°C
- They can detect water leaks, electrical hotspots, and human footsteps
- They are useful for industrial inspections and building diagnostics

IR cameras can identify insulation defects.
Infrared (IR) cameras are an indispensable tool for home inspectors. They can identify insulation defects by capturing and interpreting infrared radiation emitted by objects, providing a visual representation of temperature differences. This allows inspectors to identify areas where heat transfer is occurring, revealing potential insulation gaps that may have otherwise gone unnoticed.
Infrared cameras are especially useful when looking for air leaks and insulation defects during an energy audit. By purposely controlling the temperature and air pressure inside a house, inspectors can force air inside through cracks and holes. Using an infrared camera, the sources of these air leaks can be quickly located and visually documented.
Infrared cameras detect the subtle heat signatures that transmit from internal elements through barriers. For example, if there is a hot or cold pipe within a wall, an infrared camera will likely pick it up. The thermal camera picks up on these heat patterns, and skilled thermographers then interpret the imaging to identify thermal irregularities that reveal leaks, blockages, breaks in insulation, or other issues.
Infrared cameras are also useful for building diagnostics, such as finding missing insulation, air leaks, and moisture damage. By simply scanning the walls, ceilings, and other surfaces, inspectors can quickly identify areas that require further investigation. Common areas prone to missing insulation include interior walls and ceilings, attic and roof spaces, doors and windows, and electrical outlets.
It's important to note that infrared cameras have limitations. They cannot directly "see" insulation or determine its R-value. Instead, they detect temperature variations on the surface of objects, which can indicate missing or inadequate insulation. Additionally, factors such as wall coverings or exterior cladding may affect the camera's accuracy.
Cameras' Role in Television: On-Screen and Behind-the-Scenes
You may want to see also

They can't see through walls, but can detect heat signatures from internal elements
Thermal imaging cameras are an invaluable tool for inspectors, engineers, and maintenance teams. They can be used to detect heat patterns behind walls, inside equipment, and beneath surfaces. While thermal cameras cannot see through walls or concrete, they can detect the subtle heat signatures that transmit from internal elements through barriers.
Thermal cameras do not see through solid objects. Instead, they detect the unique infrared radiation signature that all objects emit in proportion to their temperature. This allows thermal cameras to detect heat sources located behind barriers. Skilled thermographers can use this imaging to locate and analyse issues such as leaks, blockages, breaks in insulation, or other problems.
Infrared radiation sits just beyond the spectrum of light visible to the human eye. Thermal cameras read these infrared signatures and express the differences in heat through a gradient colour scheme. Hotter areas are displayed as brighter colours, while cooler areas appear as darker colours.
Thermal cameras can be used to detect heat patterns from pipes, wires, ducts, and structural components through concrete. The heat from these internal elements radiates through the concrete to the surface, and the thermal camera picks up these heat patterns.
To effectively use a thermal camera to detect issues within a building, it is important to set up testing conditions with a large temperature difference between the interior and exterior. This can be achieved by controlling the temperature and air pressure inside the building. By purposely creating a temperature difference, insulation defects can be more easily viewed by the camera.
Accessing ADT Cameras: Server Viewing Guide
You may want to see also

They can identify temperature differences of 15-20°C
How to Identify Temperature Differences of 15-20°C with a Thermal Imaging Camera
Thermal imaging cameras are an invaluable tool for identifying temperature differences of 15-20°C. Here are some detailed instructions to help you achieve this:
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Thermal Imaging
Thermal imaging cameras visualise heat patterns and detect temperature differences by capturing infrared radiation emitted by objects. The amount of radiation emitted increases with temperature, allowing the camera to identify variations.
Step 2: Prepare the Environment
To identify temperature differences of 15-20°C, you need to create a significant temperature difference between the interior and exterior of the building. This can be done by heating or cooling the interior and waiting for at least 15 minutes to establish a stable temperature.
Step 3: Use the Right Equipment
Ensure you have a high-quality thermal imaging camera capable of detecting subtle temperature changes. The camera should have a sufficient temperature range and sensitivity to capture the desired temperature differences.
Step 4: Inspect the Building
Start your inspection by scanning areas likely to have insulation issues, such as electrical receptacles, basement rim joists, plumbing penetrations, and attic edges. Look for hot or cold spots on walls or ceilings, which indicate missing or inadequate insulation.
Step 5: Analyse the Data
Review the thermal images to identify areas with temperature differences of 15-20°C or more. These spots may indicate missing or faulty insulation. Compare the thermal images with digital photos of the same areas for further analysis and documentation.
Step 6: Verify and Address Issues
If you identify potential problem areas, verify the insulation in those spots. Check if the insulation was moved or if its thickness is inadequate. Make any necessary repairs or call a contractor for more complex issues.
By following these steps, you can effectively use a thermal imaging camera to identify temperature differences of 15-20°C and improve the energy efficiency of your home or building.
How Camera Filters Can Capture the Invisible UV Rays
You may want to see also

They can detect water leaks, electrical hotspots, and human footsteps
Infrared (IR) cameras are becoming an increasingly useful tool for inspectors and homeowners alike. They can be used to detect water leaks, electrical hotspots, and human footsteps, all of which can be difficult to identify with the naked eye.
In the case of water leaks, IR cameras can detect moisture behind walls. This is particularly useful for identifying leaks before mould has a chance to grow and spread, saving time and money. The Evaporative Cooling effect is often the most powerful indicator of moisture in insulation and other interior wall components.
IR cameras can also be used to identify electrical anomalies and hotspots. Electrical circuits with current flowing through them generate heat, so when inspecting an electrical component, it's important to determine whether the heat is a result of normal heating or abnormal overheating. The thermal pattern is key to detecting electrical system anomalies, and abnormal heating is often caused by abnormal electrical resistance on a contact surface, which can be due to insulation breakdown.
In addition, IR cameras can be used for real-time tracking of humans and their footsteps. This technology employs multiple-human tracking from a single camera, capturing the top-view of the target area and tracking people as moving blobs. By predicting the location and orientation of their next footsteps, the system can display virtual footsteps in front of the person in real-time.
Overall, IR cameras are a valuable tool for detecting water leaks, electrical hotspots, and human footsteps, providing detailed information that may not be immediately apparent to the naked eye.
Smart TV Camera: A Hacker's Window to Your Home
You may want to see also

They are useful for industrial inspections and building diagnostics
Infrared (IR) cameras are becoming indispensable tools for inspectors in the industrial and building sectors. They can visualise heat patterns behind walls, inside equipment, and beneath surfaces, allowing inspectors to identify issues such as leaks, blockages, and breaks in insulation.
In the industrial sector, IR cameras are used to rapidly survey facilities for temperature standard compliance, equipment function optimisation, and the prevention of downtime and breakages. This helps to reduce operating expenses through increased energy efficiency. IR cameras can be used to scan mechanical parts, motors, pipes, tanks, and ducts for temperature changes that may indicate wear, blockages, leaks, or contamination. They can also be used to check raw material quality, verify furnace/reactor conditions, and reduce cycle times.
IR cameras are also useful for facility inspections, where they can scan piping insulation, equipment seals, cold storage, server rooms, and other areas for maintenance or energy audits. They can be used to detect energy inefficiencies, such as missing insulation, air leaks, and moisture damage. For example, by walking around a house with a thermal imager, you can easily detect areas of missing insulation by looking for temperature differences.
In the building sector, IR cameras are used for building diagnostics, helping to find missing insulation, air leaks, moisture damage, and other building envelope deficiencies by visualising energy waste. They can identify temperature anomalies, helping to detect water leaks, electrical problems, and HVAC system inefficiencies. This allows for targeted repairs and preventive maintenance, improving building safety and comfort while reducing costs.
Overall, IR cameras are a valuable tool for industrial inspections and building diagnostics, providing unique insights that can lead to increased energy efficiency, reduced costs, and improved safety.
Activating Your LG Smart TV's Camera: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, IR cameras cannot see through insulation. However, they can detect temperature differences on the surface of the insulation, which can indicate missing or inadequate insulation.
IR cameras detect infrared radiation or heat in the environment and convert it into a visual image. They can identify temperature differences that may indicate defects, such as missing insulation or air leaks.
IR cameras allow inspectors to quickly and accurately identify defects that may not be apparent to the naked eye. They are especially useful for locating missing insulation, air leaks, water leaks, and electrical issues without causing damage to the building.
Yes, IR cameras have limitations when it comes to certain materials, such as glass, metal, and highly reflective surfaces. These materials can reflect infrared radiation, making it difficult to see through them. Additionally, IR cameras require a temperature difference between the interior and exterior of a building to function effectively.







