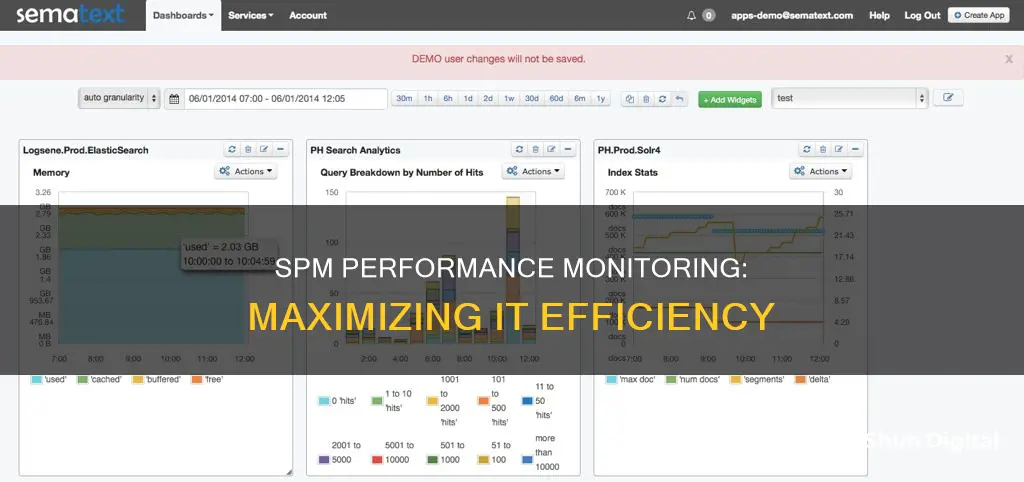
SPM is a broad term that can stand for several things, including System Performance Monitor, Service Performance Monitoring, Sales Performance Management, and Supplier Performance Management.
In this response, I will introduce the topic of SPM in the context of system performance monitoring and sales performance management.
System Performance Monitor (SPM) is an application that identifies, collects, monitors, and reports on the overall operational health of a computer system. It enables end users, administrators, and organizations to evaluate system performance by collecting and reporting key performance indicators and metrics, such as CPU usage, memory, hard disk, and network activity. SPM provides insights and aids in decision-making for system administrators.
Sales Performance Management (SPM), on the other hand, is a process that helps sales organizations track, manage, and improve the work of their sales teams. It involves activities such as forecasting, training program implementation, monitoring sales activities, quota management, and incentive planning. SPM guides sales representatives toward achieving company goals and measures their performance against targets, sales velocity, and sales cycle length.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | System Performance Monitor (SPM) is a type of application that identifies, collects, monitors and reports on the overall operational health of a computer system. |
| Purpose | SPM enables end users, administrators and organizations to gauge and evaluate the performance of a given system. |
| Performance Metrics | SPM collects and reports key performance indicators and metrics into the operational state of a system, including the use of the CPU, memory, hard disk and network. |
| Suggestions | SPM provides suggestions and guidelines for improving performance and tuning/optimizing the system automatically. |
| User | SPM is a key tool for any system administrator as it provides system-wide insight and aids in decision-making. |
| Example | Based on past trends provided by the SPM, a system administrator can schedule a system upgrade if a system has an over-utilized CPU/memory. |
| Deployment | SPM can be deployed as a native SPM application/component within an operating system, displaying factual and graphical stats for system performance. |
| Sales Performance Management | SPM helps sales organizations track, manage, and improve the work of their sales teams, including forecasting, training programs, monitoring activities, quota management, and incentive planning. |
| Supplier Performance Management | SPM is a process that assesses, monitors, and manages the performance of a company's suppliers, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of materials while maintaining strong relationships with suppliers. |
What You'll Learn

System Performance Monitor (SPM)
SPM applications can display factual and graphical statistics for system performance, allowing users to easily understand the current state of their computer systems. This information can be used to identify potential issues and optimize performance. For example, if a system is showing signs of over-utilization of CPU or memory resources, administrators can use SPM data to schedule system upgrades accordingly. SPM tools can also provide recommendations for improving performance and optimizing system settings.
SPM plays a crucial role in maintaining the operational efficiency and effectiveness of computer systems. By regularly monitoring and evaluating system performance, administrators can identify areas where improvements can be made. This proactive approach helps to ensure that computer systems are running optimally and can prevent potential issues from becoming larger problems. SPM tools can also assist in capacity planning and resource allocation, ensuring that computer systems have the necessary resources to handle current and future workloads.
In addition to system administrators, SPM tools can also benefit end users by providing insights into their system's performance. This can help users understand how their computer is performing and identify any potential issues that may impact their work. SPM applications can also provide recommendations for optimizing their system's performance, such as suggesting software updates or hardware upgrades.
Furthermore, SPM can play a crucial role in service performance monitoring. By aggregating span data and producing Request, Error, and Duration (RED) metrics, SPM tools can help identify interesting traces, such as high request rates, slow responses, or errors. This information can be used to monitor and troubleshoot services, ensuring optimal performance and identifying potential issues before they impact users.
Monitor Lizard in Your Home? Here's How to Get Rid of Them
You may want to see also

Service Performance Monitoring (SPM)
SPM is an important feature for post-deployment sanity checks, monitoring and root-causing when alerted of an issue, and long-term trend analysis of QPS, errors, and latencies. It provides a service-level and operation-level aggregation of Request rates, Error rates, and Durations, also known as RED metrics.
SPM is crucial for maintaining high-quality standards, ensuring timely delivery, and optimising cost-effectiveness. By regularly monitoring and managing service performance, businesses can identify and address risks related to supply disruptions or quality issues, maintain competitive pricing, and foster strong relationships with their suppliers.
The three critical phases of SPM include establishing KPIs, monitoring and assessing performance, and continuous improvement. Firstly, clear expectations and metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) are set, aligned with strategic goals, and agreed upon with suppliers. This phase may also involve contract negotiations and finalising service-level agreements (SLAs).
The second phase involves continuously monitoring and assessing the actual performance of suppliers against the predefined metrics and targets. This includes collecting data on various aspects, such as quality, delivery timeliness, cost management, and compliance. Regular reviews and audits are conducted to evaluate supplier performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure contract compliance.
The final phase focuses on taking action based on the evaluation results, providing feedback to suppliers, discussing improvement areas, and collaboratively working on development plans. It may also involve adjusting KPIs and targets to reflect changes in business strategies or market conditions, with the goal of fostering continuous improvement and strengthening supplier relationships.
SPM plays a crucial role in various aspects of procurement, including supplier onboarding, supply chain management, and overall risk management. By focusing on SPM, businesses can control costs, support compliance, and foster long-lasting relationships with suppliers.
Scaling Virtual Machine Monitor Size: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Supplier Performance Management (SPM)
SPM encompasses the tools and practices used to evaluate supplier performance, with the goal of understanding vendor relationships to effectively manage supplier risk, lower procurement costs, and encourage positive relationships. It helps businesses identify and mitigate risks associated with supply disruptions and quality issues, maintain competitive pricing, and foster strong relationships with suppliers.
The process of SPM can be divided into three phases: establishing key performance indicators (KPIs), monitoring and assessing performance, and continuous improvement. During the first phase, clear expectations and metrics are defined, performance targets are set, and service level agreements (SLAs) are agreed upon with suppliers. The second phase involves the continuous monitoring and assessment of supplier performance against predefined metrics, including quality, delivery timeliness, cost management, and compliance. The final phase focuses on taking action based on evaluation results, providing feedback to suppliers, and collaboratively working on development plans to enhance performance.
Effective SPM helps businesses avoid quality issues, supply chain disruptions, increased costs, compliance and legal risks, missed opportunities, and damaged relationships with suppliers. By implementing SPM, businesses can identify areas for improvement, ensure timely delivery, optimize cost-effectiveness, and maintain high-quality standards.
To achieve successful SPM, it is important to have a clear strategy, decide on a framework for evaluating supplier performance, prioritize vendors based on their strategic importance, and select relevant metrics and KPIs to track. Communicating regularly with suppliers, dealing with disruptions productively, and holding up your end of the bargain are also crucial aspects of SPM.
Angelcare Monitors: Which One Should You Buy?
You may want to see also

Sales Performance Management (SPM)
SPM is important because it supports the sales team's overall strategy. It streamlines and automates simpler tasks so that sales reps can focus on selling, and leaders can focus on improving business strategies. SPM can be used to optimise a salesperson's daily workflow, helping them meet customers and boosting sales opportunities. It can also help identify why some sales reps are closing deals and others are not.
SPM can help sales organisations to:
- Fine-tune sales forecasts: Accurate forecasts are achieved through regular data analysis. Understanding past sales performance trends and patterns allows for quicker and easier forecasting and budgeting.
- Align sales strategies with KPIs: Analysing key metrics such as conversion rates, customer satisfaction, and churn rate gives leaders a clearer view of sales performance. This allows them to develop strategies to improve overall sales efficiency and effectiveness.
- Optimise sales processes: Data can highlight which steps in the sales process are the most time-consuming or least productive. It can also reveal knowledge gaps that can be addressed with coaching, and which workflow functions can be automated for higher productivity.
A sales performance management strategy has several key components, including:
- A sales plan: This helps reps understand company objectives and gives them a roadmap for meeting them, including target customers, potential obstacles, and revenue goals.
- Sales territory planning: Matching reps with the right territories and customers, and providing data-driven strategies for closing more deals.
- Sales compensation and incentives: Implementing commission structures and bonuses to motivate reps and meet goals.
- Quota management: Setting, tracking, and achieving specific sales goals over certain periods, keeping reps motivated and rewarding those who reach their goals.
- Sales training and coaching: Providing ongoing support, call coaching, and continuing education on sales techniques and best practices.
- Sales insights and strategies: Focusing on what is sold, and how much can be sold, including pipeline management, price setting, and go-to-market strategies.
SPM software can help sales organisations become more efficient, productive, and effective at selling and meeting sales targets. Features such as automated plans and workflows, real-time reporting and dashboards, and intelligent territory assignments can streamline processes and provide valuable insights.
Removing Annoying Dots from Your ASUS Monitor
You may want to see also

SPM condition monitoring
- Establishing KPIs: This involves setting clear expectations and defining metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate supplier performance. It includes establishing performance targets, aligning them with strategic goals, and agreeing upon them with suppliers.
- Monitoring and assessing performance: During this phase, supplier performance is continuously monitored and assessed against predefined metrics and targets. This involves collecting data on various aspects, such as quality, delivery timeliness, cost management, and compliance. Regular reviews and audits are conducted to evaluate performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure contract compliance.
- Continuous improvement: This phase focuses on taking action based on evaluation results. It includes providing feedback to suppliers, discussing areas of improvement, and collaboratively working on development plans to enhance performance. It may also involve adjusting KPIs and targets to reflect changes in business strategy or market conditions.
Uncover Hidden Internet Monitors: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
SPM performance monitoring can refer to either Service Performance Monitoring, System Performance Monitoring, or Supplier Performance Monitoring.
Service Performance Monitoring is a feature of Jaeger that helps identify interesting traces such as high QPS, slow or erroneous requests.
System Performance Monitoring is a type of application that identifies, collects, monitors, and reports on the overall operational health of a computer system.
Supplier Performance Monitoring is a business practice that focuses on assessing, monitoring, and managing the performance of a company's suppliers.
SPM performance monitoring can help to identify and address issues, improve efficiency, and optimise costs.
Some challenges of implementing SPM performance monitoring include collecting and analysing data, ensuring supplier buy-in, and locating and allocating the necessary resources.
The key steps to implementing SPM performance monitoring include establishing performance metrics, collecting and analysing data, conducting regular performance reviews, providing feedback, and collaborating to improve.