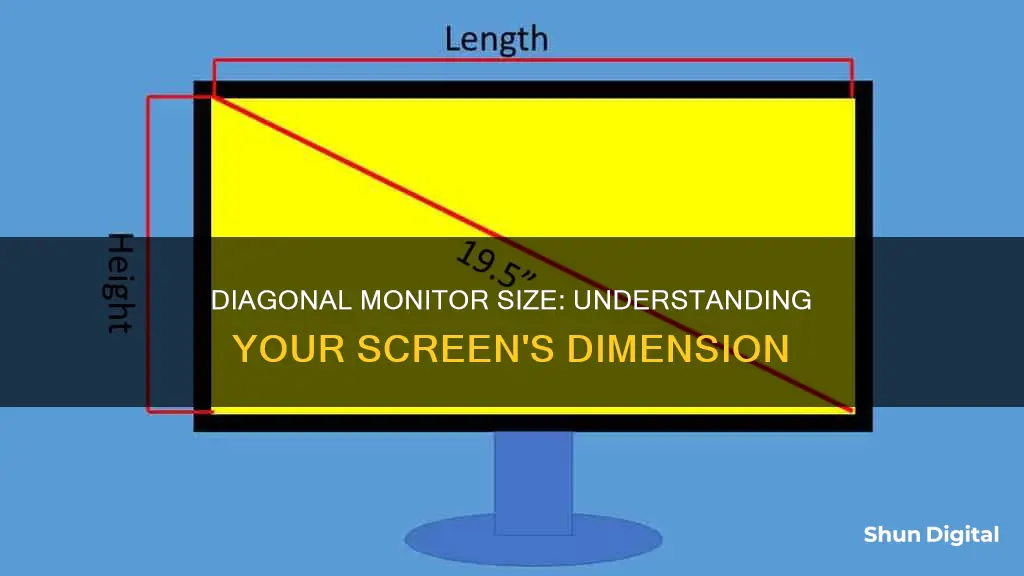
If you're looking to determine the size of your monitor, you'll need to measure its screen diagonally from one corner to the opposite corner. This is the standard way of measuring monitor size, and it provides an indication of the display area available for viewing content. The size is typically measured in inches, and common monitor sizes range from around 19 inches to over 40 inches diagonally. You can use a tape measure or ruler to obtain the diagonal measurement, and then round it to the nearest inch to get your monitor's size.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What it refers to | The physical dimensions of a monitor screen |
| How it's measured | Diagonally from one corner to the opposite corner |
| Units | Inches |
| Range | 19 inches to over 40 inches |
| Factors to consider when choosing | Workspace limitations, viewing distance, and intended use |
| Common sizes | 21.5 inches, 24 inches, 27 inches, and 32 inches |
| Impact on computing experience | Affects content viewability, multitasking, immersion, and entertainment enjoyment |
| Relation to resolution | Independent; larger monitors often support higher resolutions, but it varies |
| Customization | Display scaling settings can adjust content size |
What You'll Learn

How to measure your diagonal monitor size
To measure the diagonal size of your monitor, you can use a measuring tape or a simple mathematical equation.
Using a Measuring Tape
- Use a measuring tape of sufficient length.
- Place one end of the measuring tape at the top-left corner of the screen and extend it diagonally to the bottom-right corner. Alternatively, you can start from the top-right corner and extend it to the bottom-left corner.
- Ensure that you only measure the screen and not the bezel or casing around it.
- The diagonal measurement you obtain is the screen size.
Using Simple Math
- Measure the width and height of your screen in inches.
- Square the width and height measurements and add them together.
- Calculate the square root of this sum to obtain the diagonal measurement, which is the screen size.
For example, let's say you have a Dell XPS 13 laptop with a screen width of 11.57 inches and a height of 6.51 inches. By squaring these values, adding them together, and then calculating the square root, you can find the diagonal screen size. In this case, it would be approximately 13.27 inches.
Additionally, you can use online calculators, such as the Omni Calculator, to estimate the diagonal size based on the width or height of your screen.
Disassembling Your ASUS Monitor: Removing the Arm Base
You may want to see also

The importance of screen size for productivity
When it comes to productivity, screen size can play a significant role. A larger monitor provides more screen real estate, making it easier to work with multiple windows or applications simultaneously. This is especially beneficial for tasks that require multitasking, such as graphic design or programming. Additionally, a bigger screen enhances the viewing experience, allowing users to see intricate details clearly and facilitating effective viewing, editing, and use of productivity apps such as email, calendar, documents, and presentations.
The impact of screen size on productivity is evident in various scenarios. For instance, in a study by Apple, users experienced a significant increase in productivity when performing tasks like cutting and pasting cells from Excel spreadsheets on a larger monitor. While the methodology of the study has been questioned, it highlights the potential benefits of bigger screens. Similarly, in a study on intranet usability, employees were able to perform tasks faster and more efficiently on intranets with better usability, which included factors such as screen size and design.
However, it's important to note that simply having a larger screen does not guarantee improved productivity. Other factors come into play, such as screen resolution, ergonomic setup, and individual workflow efficiency. For example, a smaller, high-resolution monitor or multiple smaller monitors may suit some users' work styles better, reducing the need for excessive eye movement and window rearrangement. Additionally, skilled performance, where users become highly proficient at specific tasks through repetition, may not always require a larger screen.
When choosing a monitor size, it's crucial to consider factors such as workspace limitations, viewing distance, and intended use. Assess the available desk space and your typical viewing distance to determine the optimal screen size. For example, a 27-inch or larger monitor is often ideal for graphic design work, while mobile professionals may prefer smaller screens for portability and power efficiency.
In conclusion, screen size is an important factor in enhancing productivity. A larger screen can improve multitasking capabilities and provide a more immersive viewing experience. However, it should be complemented by other considerations, such as resolution, ergonomics, and task-specific requirements, to maximize productivity.
Luma's Monitoring Features: Keeping Tabs on Device Usage
You may want to see also

How does screen size impact gaming?
The size of a monitor is typically measured by its diagonal, from one corner to the opposite corner. While a larger monitor can enhance your gaming experience by offering a more immersive view, the screen size itself does not directly impact the frame rate or performance. Instead, it is the screen resolution—the number of pixels—that affects gaming performance. A higher resolution means more pixels for the graphics card to process, which can result in a lower frame rate. However, a larger monitor can often support higher resolutions, which may demand more processing power from the graphics card.
When choosing a monitor for gaming, it is essential to consider factors such as resolution, refresh rate, and response time. A higher refresh rate and a lower response time will provide a smoother gaming experience with less lag. Additionally, certain games or graphic design tasks may benefit from a larger display, allowing you to see more detail and enhancing your situational awareness.
In summary, while a larger monitor size can improve your gaming experience by providing a more immersive view, the screen size itself does not directly impact gaming performance. It is the resolution and other hardware specifications that play a more significant role in determining the frame rate and overall gaming performance.
Adjusting Grandblue: Monitor Fitting Guide
You may want to see also

How to calculate the optimal viewing distance
The optimal viewing distance for a monitor depends on several factors, including the size and resolution of the monitor, the user's eyesight, and their field of vision. Here are some guidelines and calculations to help you determine the ideal viewing distance for your monitor:
Understanding Monitor Size and Viewing Distance:
Firstly, it's important to understand how monitor size is measured. The size of a monitor typically refers to the physical dimensions of the screen, measured diagonally from one corner to the opposite corner, usually in inches. Common monitor sizes range from around 19 inches to over 40 inches diagonally.
Factors Affecting Optimal Viewing Distance:
When determining the optimal viewing distance, consider the following factors:
- Resolution and Pixel Density: Higher resolution monitors with higher pixel densities can be viewed at shorter distances without noticing individual pixels.
- Field of Vision (FOV): Humans have an average field of vision of about 140 degrees. The viewing distance should be such that the entire screen fits within this field of vision.
- Eye Resolution: The human eye with 20/20 vision can detect details as small as 1/60th of a degree of arc. If you sit too far beyond this point, pixels may start to blend together, reducing image sharpness.
- Workspace Constraints: Consider the physical constraints of your room and the size of your desk. You should have enough space to maintain the desired viewing distance without feeling cramped.
- Individual Preferences: Your preferred viewing distance may vary depending on the type of work you do. For example, tasks requiring close attention to detail may require a shorter viewing distance.
Calculating Optimal Viewing Distance:
There are formulas and online calculators available to determine the optimal viewing distance for a specific monitor. Here's a general guideline:
- For a 27-inch monitor with a QHD (2560 x 1440) resolution, the recommended viewing distance is about 80 cm to 1 meter (3 feet).
- For a 32-inch QHD monitor, the ideal distance increases slightly to 80 cm to 96 cm, with a maximum of 1.3 meters (4.5 feet).
- Keep in mind that these figures are based on recommendations from the SMPTE (Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers) and THX, an authoritative cinematic entertainment company.
- Additionally, consider your eyesight. If your vision is not 20/20, you may need to adjust the viewing distance accordingly, typically by sitting closer or opting for a larger display.
Practical Tips:
- Pay attention to your posture and viewing position. You may find that you adjust your distance based on the task at hand, moving closer for tasks requiring focus and attention.
- Use the "Squint and Head Swivel Test". If you need to lean in and squint to see details, you're too far. If you constantly swivel your head to focus, you're too close. The ideal distance is when the entire screen fits comfortably within your field of vision.
- Remember, there is an absolute "too far" for any screen size and resolution. Beyond a certain distance (usually 7 meters or more), even an 8K display will appear similar to a lower-resolution image.
Asus Portable Monitors: Compatible Partners for MacBook Pro 13?
You may want to see also

The difference between physical and logical image size
When it comes to monitors and displays, the difference between physical and logical image size is important to understand. Let's break down what each term means and how they differ from each other:
Physical Image Size
Physical image size refers to the actual, tangible dimensions of a monitor or display. It represents the number of physical pixels present on the screen. These physical pixels are the smallest unit of the display, and colours are created by adjusting the intensity of the three subpixels (red, green, and blue) that comprise them. When examining a Full HD screen resolution of 1920x1080, for instance, there are 1920 rows of physical pixels on the horizontal axis and 1080 columns of pixels on the vertical axis.
Logical Image Size
Logical image size, on the other hand, pertains to the amount of logical pixels displayed on a screen. Logical pixels, also known as device-independent pixels (DIP), virtual pixels, or CSS pixels, are the units that front-end developers and designers work with in their respective tools. They are considered "logical" because they merely store information about a colour represented at a specific location, regardless of the physical characteristics of the display.
The Relationship Between Physical and Logical Pixels
The correlation between physical and logical pixels is defined by the device pixel ratio (DPR). When the DPR increases, the size also increases on both the horizontal and vertical axes, as this relationship is quadratic. For example, if the DPR is 1, one logical pixel will contain just one physical pixel. However, if the DPR is 2, a single logical pixel will encompass four physical pixels.
Practical Application
Understanding the distinction between physical and logical image size is crucial in web design and user experience (UX) research. By considering the DPR and viewport size, designers and developers can create scalable designs that adapt to various monitor and display configurations. This ensures that their work is rendered consistently across different devices, preventing size conflicts.
Customizing Your ASUS Monitor: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Measure the distance from one corner of the screen to the diagonally opposite corner. This is the standard way to measure monitor size.
The method of measuring screen size diagonally was inherited from the first generation of CRT televisions, which had circular faces. The external diameter of the bulb was used to describe their size. This method continued even when cathode ray tubes were manufactured as rounded rectangles. It has the advantage of being a single number specifying the size.
You can use a tape measure or ruler. Place the tape measure or ruler at one corner of the screen and extend it to the diagonally opposite corner. Make sure to measure only the screen itself and not the bezel or frame around it.