Adobe Premiere Pro is a video editing software that allows users to view, edit, share, and search for metadata using the Metadata panel. Metadata is a set of descriptive information about a file, including basic properties such as date, duration, and file type. The Metadata panel in Premiere Pro shows both clip-instance metadata and XMP file metadata for a selected asset. Clip metadata provides information about a clip in Premiere Pro and is saved in the Premiere Pro project, while file metadata is specific to the actual file and is saved to the source file or a corresponding sidecar file.
To access the Metadata panel in Premiere Pro, go to Window > Metadata or use the keyboard shortcut Alt+Shift+8. The Metalogging workspace is also useful for entering metadata after importing, capturing, or digitizing media, and can be enabled by going to Window > Workspace > Metalogging.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| What is metadata? | Descriptive information about a file |
| File types with metadata | Video and audio files |
| Basic metadata information | File name, type, size, path, date, and duration |
| Additional metadata information | Location, director, copyright, etc. |
| How to open the Metadata panel | Window > Metadata (or keyboard shortcut Alt+Shift+8) |
| How to enable the Metalogging workspace | Window > Workspace > Metalogging |
| Difference between Clip and File metadata | Clip metadata is saved in the Premiere Pro project file; File metadata is saved to the source file or a corresponding sidecar file |
| XMP metadata | Extensible Metadata Platform; a standard format for storing and displaying information across applications and platforms |
| XMP metadata storage | Within a source file; for file formats that don't support XMP, it's stored in an XMP sidecar file |
| Customising metadata schemas | Click Metadata Display in the panel drop-down menu |
| Filtering metadata information | Use the search bar in Premiere's Project panel or browse and filter metadata in columns in the Project panel |
What You'll Learn
- Use the Metadata panel in Premiere Pro to view, edit, share and search for metadata
- Basic metadata properties include date, duration, and file type
- Add details to basic metadata properties such as location, director, and copyright
- Use XMP metadata to streamline your workflow and organise your files
- Use the Metalogging workspace for entering metadata after importing, capturing or digitising media

Use the Metadata panel in Premiere Pro to view, edit, share and search for metadata
Adobe Premiere Pro has a Metadata panel that allows you to view, edit, share, and search for metadata. This is a powerful tool to streamline your workflow and keep your files organised.
Viewing and Editing Metadata
Metadata is a set of descriptive information about a file. Video and audio files automatically include basic metadata properties, such as date, duration, and file type. You can also add extra details such as location, director, and copyright information.
To view and edit metadata, go to Window > Metadata. Here, you can edit text and adjust values as needed. If you have selected multiple items, the panel will display matching entries for properties that are the same across all items, and "Multiple Values" for properties that differ.
Sharing Metadata
The Metadata panel allows you to share information about assets across Adobe video and audio applications. Unlike conventional clip properties, which are limited to a single application, metadata properties are embedded in source files, so the data automatically appears in other applications. This makes it easier to track and manage video assets as they move through your production workflow.
Searching for Metadata
To search for specific metadata, enter the text you want to find in the search box at the top of the Metadata panel. The list of metadata will collapse to only show properties that contain your search term. You can then navigate through the search results using the Previous and Next buttons, or by pressing Tab.
Customising the Metadata Panel
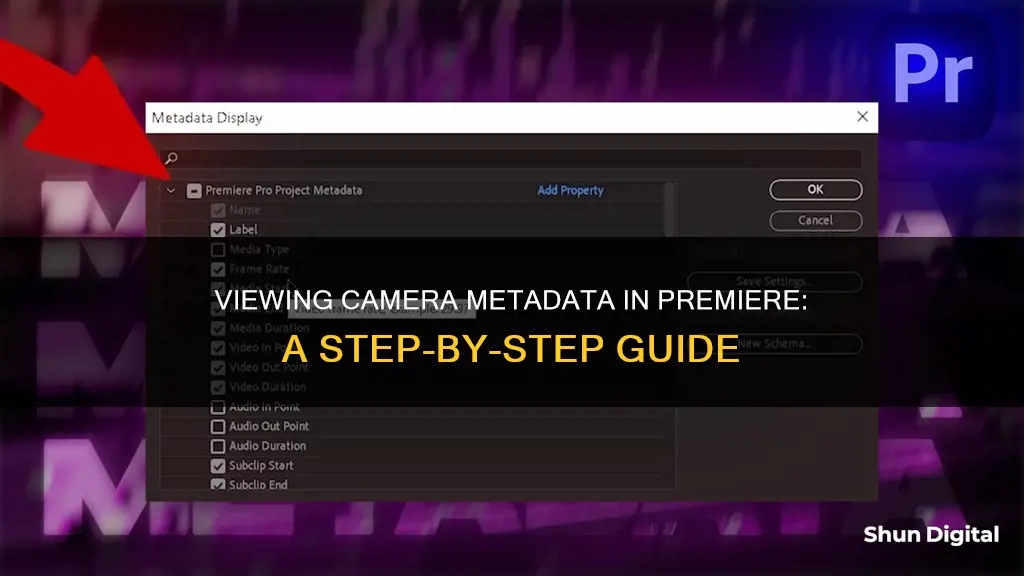
You can customise the Metadata panel to optimise it for your workflow. You can choose to show or hide entire schemas or individual properties, displaying only the information you need. To do this, go to the options menu for the Metadata panel and select Metadata Display.
Saving, Switching, and Deleting Metadata Sets
If you use multiple workflows, you can save, switch between, and delete different sets of displayed metadata. Go to the options menu for the Metadata panel and select Metadata Display. From here, you can save a customised set of displayed metadata, display a previously saved set, or delete a set.
Creating Schemas and Properties
If you have a unique, customised workflow that the default metadata options don't address, you can create your own schemas and properties. Go to the options menu for the Metadata panel, select Metadata Display, and then click New Schema. Enter a name for your schema, and then click Add Property to the right of the schema name. Enter a property name and select a type.
Viewing Clip Data
You can show or hide clip information in the Metadata panel. Premiere Pro saves clip information in the schema named Premiere Project Metadata. To view clip data, go to Window > Metadata, and then click the triangle next to Premiere Project Metadata to view all the clip information fields.
Linking Clip Data to XMP Metadata
In the Metadata panel, the Clip property value fields are internal to Premiere Pro. However, you can link some clip metadata fields with XMP metadata fields, allowing applications outside Premiere Pro to access the clip-based metadata. To do this, click the link option box next to the relevant property value field in the Clip section.
Source Clips, Clip Instances, Subclips, and Duplicate Clips
XMP file metadata refers to information about a source file that is stored in that source file. Clip metadata, on the other hand, is information about a clip that is stored in a Premiere Pro project file. In Premiere Pro, multiple clips can point to the same source file. For example, a group of subclips with different In and Out points can point to the same source file.
Use the XMP metadata fields to store data that applies to the source file and all associated clip instances. Use the clip metadata fields to store data specific to each unique clip. Link clip metadata fields to XMP metadata fields if you want the clip metadata copied to the source file. However, do not link a clip metadata field to an XMP metadata field for more than one clip pointing to the same source file.
OLED TV Camera: Fact or Fiction?
You may want to see also

Basic metadata properties include date, duration, and file type
When working with video and audio files, it's important to understand the basic metadata properties that are automatically included. These properties provide essential details about a file and serve as a foundation for further organisation and editing. Basic metadata properties include date, duration, and file type.
Date metadata is crucial for organising and sorting your media assets. It allows you to determine when a file was created or modified, helping you keep track of the timeline of your project. This is especially useful when working with footage from multiple cameras or sources, as you can easily identify when each clip was captured. However, it's important to note that some cameras or file formats may not include date metadata, requiring you to rely on other methods to sort your clips.
Duration is another fundamental aspect of basic metadata. It provides you with the length of each video or audio clip, enabling you to quickly assess the content and plan your edits accordingly. This information is vital for creating a smooth and seamless final product, ensuring that your clips align and flow together effectively.
Additionally, file type metadata is automatically included in your video and audio files. This property identifies the format or extension of the file, such as MOV, MP4, or WAV. Understanding the file type is essential for compatibility purposes, ensuring that you can open and work with the files in the appropriate software applications. It also helps in determining the appropriate codecs and settings for your project.
While these basic metadata properties are automatically included, you have the ability to add further details to enhance your workflow. This can include information such as location, director, or copyright details. By utilising Adobe Premiere Pro's Metadata panel, you can view, edit, and manage this metadata effectively. The panel allows you to access both clip-instance metadata, which is specific to Premiere Pro, and XMP file metadata, which is embedded in the source files and accessible by other applications.
In conclusion, understanding and utilising basic metadata properties such as date, duration, and file type is a crucial step in the video editing process. They provide essential information about your media assets and serve as a foundation for further organisation and customisation. By leveraging the tools within Adobe Premiere Pro, you can efficiently manage your metadata and streamline your video editing workflow.
The Benefits of City-Wide Camera Surveillance
You may want to see also

Add details to basic metadata properties such as location, director, and copyright
Adobe Premiere Pro's default Metalogging workspace is the best way to work with metadata. This workspace is designed to be used directly after you import your footage. To enable the Metalogging workspace, choose Window > Workspace > Metalogging. Alternatively, you can open just the Metadata panel by selecting Window > Metadata (or use the keyboard shortcut Alt+Shift+8).
Once you have the Metadata panel open, you can add details to basic metadata properties such as location, director, and copyright. To do this, follow these steps:
- Select the desired files or clips that you want to add metadata to.
- In the Metadata panel, edit the text or adjust the values as needed. For example, if you are adding the location, you would type in the location name.
- If you have selected multiple items, the panel will display properties with matching or differing values. If a property matches for all items, the matching entry will appear. If a property differs, "
" will appear. To apply matching values, click the text box and type. - To search for a specific schema or property, hover your pointer over it in the Metadata panel. A tooltip will appear with details for most items.
- To save your customized set of displayed metadata, click "Save Settings" in the options menu for the Metadata panel. Enter a name and click OK.
By adding this information to your video and audio assets, you can quickly and easily find it later with a simple keyword search.
Apple's Watchful Eye: Camera Surveillance Concerns
You may want to see also

Use XMP metadata to streamline your workflow and organise your files
Adobe's Extensible Metadata Platform (XMP) is a file-labelling technology that allows users to embed metadata into files during the content creation process. XMP is built on XML, which facilitates the exchange of metadata across a variety of applications and publishing workflows.
XMP is a powerful solution enabler, providing a standard way of tagging files with metadata across products from Adobe and other vendors. It is freely available to developers as an open-source technology, meaning that the user community benefits from the innovations contributed by developers worldwide.
By using XMP metadata, you can streamline your workflow and organise your files. Metadata is a set of descriptive information about a file, including basic properties such as date, duration, and file type. With XMP, you can add further details such as location, director, and copyright information.
The Metadata panel in Adobe applications allows you to share this information about assets across Adobe video and audio applications. Unlike conventional clip properties, which are limited to a single application, metadata properties are embedded in source files, so the data automatically appears in other applications. This enables you to quickly track and manage video assets as they move through your production workflow.
Additionally, XMP metadata fields can be used to store data that applies to the source file and all clip instances that point to it. Clip metadata fields, on the other hand, are used to store data specific to each unique clip. By linking clip metadata fields to XMP metadata fields, applications outside of Adobe Premiere Pro can access the clip-based metadata through the XMP fields.
Overall, XMP provides a flexible and powerful way to manage your files and streamline your workflow by embedding meaningful information that can be easily understood by your team, software applications, and hardware devices.
Activating Your Camera on Ome TV: A Quick Guide
You may want to see also

Use the Metalogging workspace for entering metadata after importing, capturing or digitising media
The Metalogging workspace in Premiere Pro is designed to be used directly after you import your footage. It is for entering metadata after importing, capturing, or digitizing media. To enable the Metalogging workspace, choose Window > Workspace > Metalogging. This layout will make logging your media much easier.
The Project panel and the Metadata panels are maximized to make entering metadata easier. The Metalogging workspace offers two types of metadata: clip-instance metadata, exclusive to Premiere Pro, and XMP file metadata.
Clip metadata provides information about your clip in Premiere Pro, and the information is saved in the Premiere Pro project. File metadata is specific to your actual file and is saved to the source file or a corresponding sidecar file.
If you create subclips or import duplicate clips, your Clip metadata will only correspond with your clip in Premiere. Premiere Pro is equipped to convert clip data into XMP metadata so you can use it in other Adobe programs.
XMP file metadata is a standard format for storing and displaying information across applications and platforms. It is a set of descriptive information about a file. Video and audio files automatically include basic metadata properties, such as date, duration, and file type. You can add details with properties such as location, director, and copyright.
With the Metadata panel, you can share this information about assets throughout Adobe video and audio applications. This sharing of metadata lets you quickly track and manage video assets as they move through your production workflow.
The Science Behind Pinhole Cameras and Image Formation
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To view camera metadata in Premiere, open the Metadata panel by selecting Window > Metadata (or use the keyboard shortcut Alt+Shift+8). Here, you'll be able to see both clip-instance metadata and XMP file metadata for your selected asset.
Clip metadata provides information about your clip in Premiere Pro and is saved in the Premiere Pro project file. File metadata is specific to the actual file and is saved to the source file or a corresponding sidecar file.
Not all cameras record all metadata, and Adobe may not have parsed the metadata for you to view it in Premiere. If the metadata is not available in Premiere, try using the manufacturer's respective software (such as Canon XF or Sony Catalyst Browse) to view the metadata.







