Microphone latency is a common issue that can be incredibly distracting for performers and frustrating for audio engineers. It occurs when there is a delay between the production of a sound and its audible transmission through a microphone. This can be due to signal processing, hardware constraints, software setups, and network latency. To resolve this issue, you can modify buffer sizes and sample rates, update firmware and audio drivers, use low-latency monitoring, optimise system resources, examine hardware connections, disable audio enhancements, and use direct monitoring. Additionally, you can try using an external sound card or mixer, as well as adjusting settings in your operating system's sound properties.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Cause of delay | Driver delay, HW and software buffering, signal processing, hardware constraints, software setups, network latency, etc. |
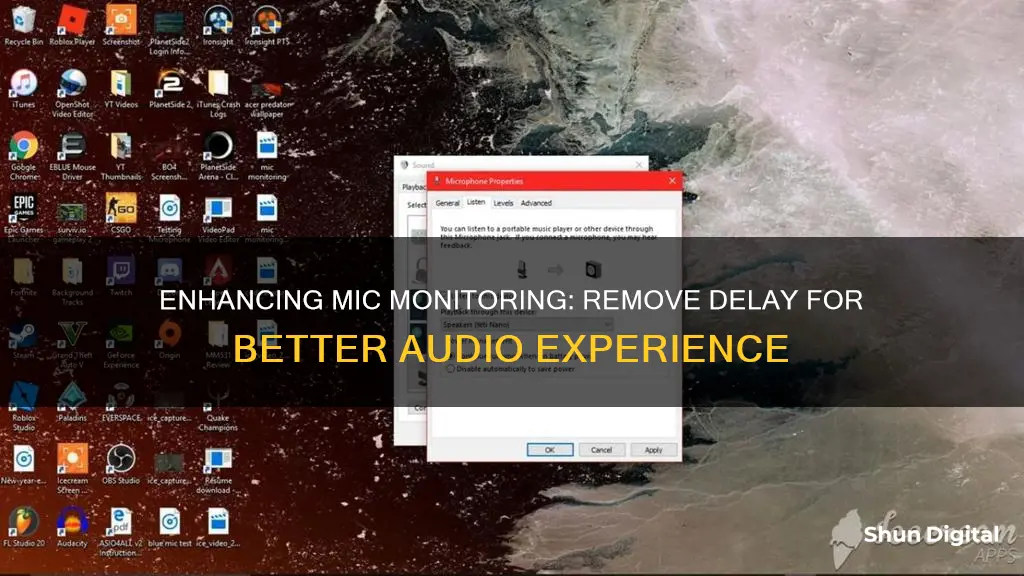
| Fix for Windows | Uncheck "Listen to this device" for the mic in Recording Devices, then in Playback Devices, go to the Level tab for the speakers, unmute the microphone there and increase the level to the desired level |
| Fix for Dell PC with RealTek High Definition Audio | 1. Right-click the speaker icon in the taskbar and click on "Recording devices" 2. Click on Microphone -> Properties -> Listen 3. Uncheck "Listen to this device" 4. Right-click on the speaker icon in the taskbar and click on "Playback devices" 5. Click on Speakers -> Properties -> Levels 6. Unmute BOTH "Microphone" and "Rear Pink In" and turn up the volume level for both |
| General fixes | Modify buffer size and sample rate, update firmware and audio drivers, use low-latency monitoring, optimize system resources, examine hardware connections, disable audio enhancements, use direct monitoring, upgrade hardware |
What You'll Learn

Modify buffer size and sample rate
Modifying the buffer size and sample rate can significantly reduce the delay in mic monitoring. Here's a detailed guide to help you with the process:
Buffer size refers to the number of samples or the amount of time it takes for your computer to process incoming audio signals. It is measured in samples, and a higher buffer size results in increased latency or delay. Therefore, lowering the buffer size will reduce the processing time, leading to decreased latency. For instance, if you set the buffer size to 256 samples and the sample rate to 48 kHz, the latency will be approximately 5.3 ms. On the other hand, changing the settings to a buffer size of 512 and a sample rate of 48 kHz will result in around 10.6 ms of latency.
However, it's important to note that reducing the buffer size will require your computer to utilise more resources for data processing. Hence, it's a balancing act where you need to choose the smallest buffer size that your computer can manage without encountering errors.
Sample rate, measured in frequency, determines how many samples your audio interface will capture per second. It also defines the highest frequency that can be accurately captured. A higher sample rate enables the capture of higher frequencies. For example, a sample rate of 48 kHz captures 48,000 samples per second, resulting in a theoretical upper limit of 24,000 Hz.
For live performances, musicians often use a buffer size of 256 or 128 and a sample rate of 44.1 kHz. This setup provides a balance between latency and audio quality while allowing the computer to run more intensive plugins without issues.
Additionally, the quality of your audio interface can impact the overall latency. Some interfaces introduce higher internal latency during analogue-to-digital and digital-to-analogue conversions, requiring you to lower the buffer size to achieve the desired overall latency.
To optimise your system for live performance, it's crucial to ensure sufficient CPU headroom. This can be achieved by setting larger buffer sizes or using lower sample rates, which reduce the workload on your computer, allowing it to run at lower temperatures.
In summary, to reduce the delay in mic monitoring, experiment with different buffer sizes and sample rates, keeping in mind the trade-off between latency and computer resource utilisation. Additionally, consider the quality of your audio interface and its impact on overall latency.
Understanding Monitor LCDs: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Update firmware and audio drivers
Firmware is a set of instructions permanently embedded in a device's hardware that controls how it operates. It is installed directly onto components such as memory chips or graphics cards in electronic devices. To improve the performance of your microphone, you may need to update the firmware on your device.
Firstly, identify the device model and manufacturer. You can usually find this information on the device itself or in the user manual. Once you have this information, visit the manufacturer's official website or support page and look for a section dedicated to firmware updates or downloads for your specific device model. Here, you should be able to find the latest firmware version available.
Next, download the appropriate firmware update for your device. Be sure to download it to a location that is easily accessible, and remember the file name and where it is saved.
After downloading the firmware update, connect your device to your computer using a USB cable or follow the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer. Then, locate the firmware update file you downloaded and follow the on-screen instructions to install the update. Ensure you read and follow all the steps provided to avoid any potential issues.
During the firmware update, your device may restart multiple times or display progress indicators. It is important to allow the update to complete without interruption to avoid issues such as corrupted firmware or even permanent damage to your device.
Once the update is complete, verify that the firmware update was successful. Check the device settings or refer to the manufacturer's instructions to confirm that the updated firmware version is now installed on your device.
Now, let's discuss updating audio drivers. Audio drivers assist in ensuring audio-related devices, such as headphones, microphones, audio interfaces, and onboard sound cards, communicate properly with your computer. While some audio devices are designed to work automatically on Windows and Mac by using the drivers included in the OS, others require a custom audio driver provided by the manufacturer.
To update your audio drivers on a Windows PC, open the Control Panel and select 'Device Manager'. Locate 'Sound, video and game controllers', then click the dropdown to view all available audio device drivers. If you are using onboard audio without an audio interface or a third-party graphics card, Windows Update typically updates the audio driver automatically. However, if you need to update manually, right-click on the device driver and select 'Update Driver'. In the window that appears, select 'Search automatically for updated driver software' and follow the prompts.
If Windows doesn't find a new driver, you can try looking for one on the device manufacturer's website and follow their instructions for installation. Alternatively, you can uninstall the current driver and then reinstall it through Windows Update, which may provide an updated version.
Setting Up Studio Monitors: Interface Connection Guide
You may want to see also

Use low-latency monitoring
If you're experiencing mic monitoring delay, one solution is to use low-latency monitoring. This can be achieved by adjusting your audio settings and using specific software or hardware.
Firstly, ensure that you have selected the correct microphone for your setup. If you're using a cardioid studio mic, you will need a pre-amp to boost the volume of your vocals before sending the signal to your computer for recording. This will help prevent distortion and ensure a clean, clear sound.
Next, adjust your Windows sound settings. Right-click on the speaker icon in the bottom right corner of your screen, click 'Sounds', then the 'Recording' tab, and select 'Microphone'. Click 'Properties', then the 'Listen' tab, and uncheck 'Listen to this device'. This will disable mic monitoring, which can cause delays.
Now, you can minimise the delay by using low-latency monitoring. If you're using Logic Pro, set the sample rate of your project to a higher value, which will result in less input monitoring latency. Also, adjust the I/O buffer size to the lowest setting to reduce latency. Keep in mind that smaller buffer sizes require more processing power, so you may need to increase the buffer size if you encounter system overload alerts.
Additionally, you can enable Low Latency Mode in Logic Pro to minimise plug-in latency. This mode ensures that all delays remain under the Limit slider value in the Plug-in Latency section of the General Audio settings.
If you're using OBS, you may need to install an ASIO driver to reduce latency. This has been known to significantly improve latency issues, especially for Windows users.
Finally, consider using hardware monitoring if possible. For example, if you have a Focusrite interface, you can use it for hardware monitoring with <1ms latency, which is effectively latency-free to human ears.
Monitoring Data Usage: Netgear Routers and Devices
You may want to see also

Optimise system resources
To optimise system resources and reduce audio latency, it is important to reduce CPU usage and free up system resources. This can be achieved by closing any unnecessary background processes, applications, and browser tabs. High CPU usage can cause performance issues and audio latency, especially when resource-intensive tasks such as audio processing and recording are being performed.
Additionally, it is worth noting that decreasing the buffer size in a digital audio workstation can help reduce audio latency. However, this may result in higher CPU and system resource usage, so a balance needs to be struck. Lower buffer sizes require more processing power, and if the computer cannot handle the requirements, errors or artefacts may be introduced.
To safely decrease the buffer size, ease up on the processing requirements of the computer by closing any unnecessary programs or applications. This will help free up processing power and may reduce latency.
Another way to optimise system resources is to use an external sound mixing board with effects, also known as "direct monitoring". This bypasses the computer's software monitoring, which often introduces latency. By using an external mixer, both the playback and your final voice enter the computer together, resulting in synchronisation.
Finally, if you are using a desktop or laptop computer, consider plugging your microphone directly into the integrated sound card on the motherboard. This may solve your lag issues without the need for additional equipment.
Finding the Perfect Monitor Scaling for Your Setup
You may want to see also

Examine hardware connections
To remove the delay on mic monitoring, it is important to examine hardware connections. This involves checking that all hardware components are securely and correctly connected, including microphone cables, audio interfaces, and recording devices. Poor or loose connections can lead to latency issues, interference, or signal deterioration.
- Check Cable Connections: Ensure that all cables are firmly plugged into the correct ports. This includes the cable connecting your microphone to the audio interface or computer, as well as any other cables in your setup, such as USB or audio cables.
- Try Different Ports: If you're using a USB connection, try plugging the cable into different USB ports on your computer. Sometimes, the convenient USB ports on the front of desktop computers can be laggy due to the thin wires connecting them to the motherboard. It's recommended to use USB ports that are soldered directly onto the motherboard, as they often provide faster transfer speeds and reduce latency.
- Use Direct Connections: If possible, avoid using Bluetooth or wireless connections for your microphone and audio devices. Instead, opt for direct connections using the appropriate cables. Wireless connections can introduce additional latency, especially if the Bluetooth receiver is an outdated USB dongle.
- Use Traditional Audio Ports: Consider using traditional audio ports on your computer, such as an XLR-to-3.5mm cable connection. This bypasses the need for a USB or Bluetooth connection and may help reduce latency.
- Check Hardware Compatibility: Ensure that your microphone, audio interface, and recording device are compatible with each other and your computer. Sometimes, hardware restrictions or limitations can cause latency issues.
- Optimize Cable Routing: Pay attention to how you route your cables. Try to avoid coiling or tangling cables, as this can cause interference and affect signal quality. Proper cable management can help reduce potential sources of latency.
- Use High-Quality Cables: Invest in high-quality cables that are specifically designed for audio applications. Poor quality cables can degrade the signal and introduce unwanted noise or latency.
- Maintain Hardware: Regularly clean and maintain your hardware connections. Over time, connectors and ports can become dirty or oxidized, affecting the signal quality. Use appropriate cleaning tools and methods to ensure optimal connections.
- Troubleshoot Hardware: If issues persist, try swapping out different components to narrow down the source of the problem. For example, try using a different microphone or audio interface to see if the issue is specific to a particular piece of hardware.
- Consider Hardware Upgrades: If you've tried all the above steps and latency issues remain, consider upgrading your hardware. Newer models of audio interfaces, sound cards, and recording devices often offer improved performance and lower latency specifications.
By carefully examining and optimizing your hardware connections, you can significantly reduce latency issues and improve your audio monitoring experience.
Connecting Your Xbox to the New MSI Monitor
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Go to the 'Recording Devices' in the Sound settings, click on 'Microphone', then 'Properties', and 'Listen'. Uncheck the 'Listen to this device' box. Then, go to 'Playback Devices', click on 'Speakers', then 'Properties' and 'Levels'. Unmute the microphone and increase the volume to the desired level.
You may need to install an ASIO driver.
Ensure your microphone is set as the input device and your speakers/headphones are set as the output device. Modify buffer size and sample rate settings in digital audio workstations and recording software. Engage low-latency monitoring in these programs. Close any other programs using audio. Reduce the number of digital audio hardware devices.