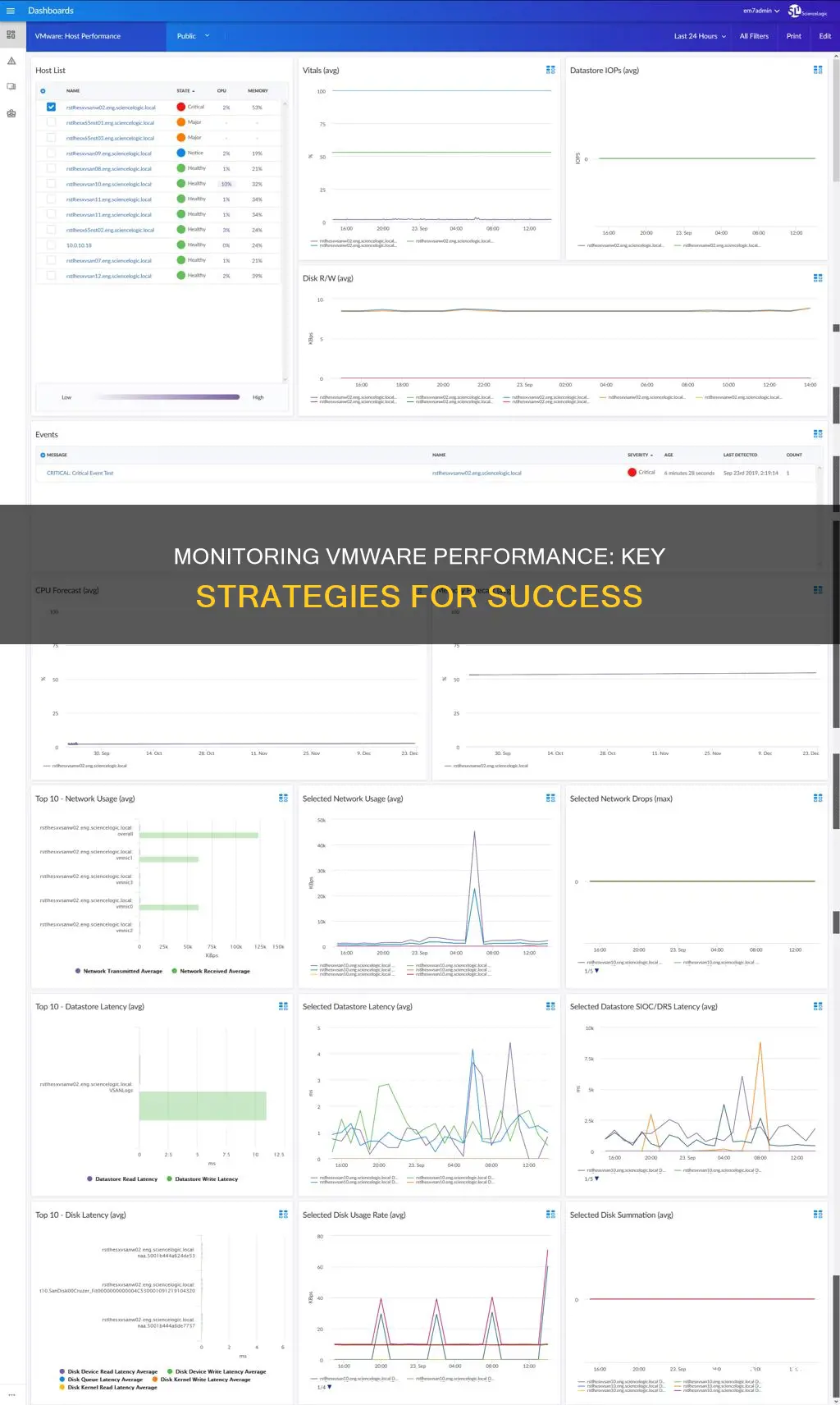
Monitoring VMware performance is essential to ensure optimal performance of VMware servers and to detect performance bottlenecks. VMware vSphere is a virtualization platform that allows users to provision and manage one or more virtual machines (VMs) on individual physical servers. With vSphere, organisations can optimise costs, centrally manage their infrastructure, and set up fault-tolerant virtual environments. VMware provides several built-in tools and utilities to monitor performance, including performance charts, command-line utilities, and prebuilt alarms. Third-party tools are also available that offer additional insights and features for VMware monitoring. By effectively monitoring VMware performance, administrators can identify and resolve issues, optimise resource allocation, and ensure a smooth and efficient virtual environment.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Tools | vSphere client performance charts, ESXTOP command line utility, vRealize Operations (vROPs) product suite, vCenter Events, vSphere Monitoring and Performance, vSphere Monitoring Tools, vSphere Performance Monitoring Tools, VMware vFabric tc Server Monitoring, VMware Horizon Monitoring, VMware Performance Monitor, VMware Performance Monitoring Tools, VMware vSphere Monitoring Tools, VMware ESX & ESXi Performance Monitoring, VMware Horizon Monitoring, VMware Monitoring Tools, VMware Monitoring Tool, VMware vSphere Performance Monitoring Tools |
| Performance data | CPU, Memory, Storage, Compute, Network, Storage Resource Usage, CPU Usage, Memory Usage, Network Throughput, Disk I/O and Capacity, Storage Capacity, Hardware Health, Disk Latency, Queue Latency, Disk Throughput, Disk Space, Data Store Performance, VM Performance, VM Health, VM Utilization, VM Space, VM Network Usage, VM Memory Utilization, VM Cluster Performance, VM Hardware Health, VM Network Performance, VM Resource Utilization, VM Space Split, VM Uptime, VM Virtual Machine File System, VM Virtual Machine Disk Files, VM Virtual Disks, VM Virtual Desktop and Remote Workstations, VM Virtual Environments, VM Virtual Machine Performance, VM Virtual Environments, VM Virtual Machine Performance, VM Virtual Environments, VM Virtual Machine Performance, VM Virtual Environments, VM Virtual Machine Performance |
What You'll Learn

Monitor CPU and disk utilisation
CPU and disk utilisation can be monitored using the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface. This allows you to monitor the overall CPU and memory usage of the vCenter Server Appliance. To do this, log in to the interface as root, click on 'Monitor', and then the 'CPU & Memory' tab. From the date range drop-down menu, select the time period for which you want to generate a CPU utilisation trending graph and a memory utilisation trending graph. Point to the graphs to see the CPU and memory use for a particular date and time.
The CPU Usage chart displays the CPU usage of the 10 virtual machines on the host with the most CPU usage. This can be found in the Virtual Machines view of the host Performance tab. The amount of CPU actively being used by each virtual machine on the host is shown, with 100% representing all CPUs. For example, if a virtual machine has one virtual CPU that is running on a host with four CPUs and the CPU usage is 100%, the virtual machine is using one CPU resource.
Temporary spikes in CPU usage are not necessarily a concern, but consistently high CPU usage might indicate a problem. You can use the CPU performance charts to monitor CPU usage for hosts, clusters, resource pools, virtual machines, and vApps. A high CPU usage value can lead to increased ready time and processor queuing of the virtual machines on the host. If the virtual machine CPU usage is above 90% and the CPU ready value is above 20%, application performance is impacted.
To enhance CPU performance, you can verify that VMware Tools is installed on every virtual machine on the host, set the CPU reservations for all high-priority virtual machines, compare the CPU usage value of a virtual machine with the CPU usage of other virtual machines on the host or in the resource pool, determine whether the high ready time for the virtual machine resulted from its CPU usage time reaching the CPU limit setting, increase the CPU limit on the virtual machine, increase the CPU shares to give the virtual machine more opportunities to run, increase the amount of memory allocated to the virtual machine, reduce the number of virtual CPUs on a virtual machine to only the number required to execute the workload, add the host to a DRS cluster, increase the number of hosts and migrate one or more virtual machines onto the new host, upgrade the physical CPUs on the host if necessary, and use the newest version of hypervisor software, enabling CPU-saving features.
VMware vSphere 7 offers several built-in tools and utilities to monitor performance, including vSphere client performance charts, where you can view the compute, network, or storage resource usage for your VMs, hosts, and clusters. The built-in charts in the vSphere 7 UI can be viewed and accessed via a web browser, and you can see performance metrics in different types of charts depending on the selected object and metric type. Line charts show metrics for a single inventory object, bar charts show metrics for objects where each bar is a metric for an object, pie charts show metrics for a single object with each slice representing a category or child object, and stacked charts display metrics for child objects.
Different overviews and advanced performance charts exist for data centres, clusters, hosts, resource pools, vApps, and virtual machine objects. Overview performance charts are also available for datastores and datastore clusters, but not for network objects. All charts are organised into views, which allow you to see related data together on one screen. The charts can be exported to a file or spreadsheet.
Ankle Monitors: Who Pays the Price for Surveillance?
You may want to see also

Monitor memory utilisation
Memory is often a leading resource constraint in virtual environments where multiple VMs share a limited capacity. To monitor memory utilisation in VMware, you can use the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface to monitor the overall memory use of the vCenter Server Appliance. This allows you to generate a memory utilisation trending graph over a specific time period.
There are several memory metrics you can use to analyse memory usage in VMware. These include:
- Guest physical memory—This refers to the virtual hardware memory presented to a virtual machine for its guest operating system. You can measure this using the Memory Granted metric for a virtual machine or Memory Shared for a host.
- Machine memory—This is the memory available at the application level of a VM. You can measure this using the Memory Consumed metric for a virtual machine or Memory Shared Common for a host.
- Memory ballooning—This is a memory reclamation technique used by ESXi hosts when they are short on memory. The host sends a request to the balloon driver installed on the VM to "inflate" and gather unused memory. While this can assist when hosts are low on memory, if done too often, it can degrade VM performance.
- Memory swapping—If memory ballooning is insufficient, hosts may begin using swap memory to meet VM memory demands, which will result in severe degradation in application performance.
The Performance tab of the vSphere Client also displays a Memory Usage chart for the 10 virtual machines on the host with the most memory usage. This allows you to monitor memory utilisation for these VMs and ensure that they have sufficient memory allocated.
Old Monitors: Why People Still Buy Them
You may want to see also

Monitor hardware health
Monitoring hardware health is crucial to ensure the optimal performance of your VMware environment. VMware provides various tools and methods to help you monitor the health of your hardware components. Here are the steps and features you can use to monitor hardware health:
Using vSphere Client:
The vSphere Client offers a comprehensive view of your hardware health status. Follow these steps:
- Select a host in the vSphere Client.
- Click on the "Monitor" tab, and then select "Hardware Health" or "Hardware Status".
- Choose the type of information you want to view. This can include sensor data, storage sensors, system event logs, alerts, and warnings.
- The sensors will be displayed in a tree view. If the status of a component is blank, it indicates that the health monitoring service cannot determine its status.
VMware Host Client:
If you are using the VMware Host Client, you can monitor the health status of the ESXi host hardware. Here's how:
- Log in to the VMware Host Client.
- Click on "Monitor" and then select "Hardware".
- Choose the type of information you want to view and use the filter controls to narrow down the list if needed.
- You can also sort the list by clicking on a column heading.
Performance Monitoring Tools:
VMware vSphere provides built-in tools to monitor performance, including hardware health. These tools offer insights into resource usage, such as compute, network, and storage utilisation for your VMs, hosts, and clusters. For example:
- VSphere client performance charts: These charts allow you to visualise resource usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- ESXTOP command-line utility: This utility provides deeper insights into system performance.
- Prebuilt alarms: vSphere includes prebuilt alarms that notify you of issues, such as low resource availability.
By utilising these features and tools, you can effectively monitor the hardware health of your VMware environment, ensuring optimal performance and identifying potential issues before they become critical.
Finding the Model Number of Your MYL Monitor
You may want to see also

Monitor network performance
Network performance monitoring is crucial to ensure healthy connectivity in a vSphere environment, which comprises a network of physically connected servers running ESXi hosts and logically connected virtual machines. By collecting usage and error metrics, administrators can identify and address issues that may impact key tasks such as VM provisioning and migration.
To monitor network performance, VMware provides various tools and utilities, including the vCenter Server performance charts and the vSphere client performance charts. These tools offer insights into network throughput, incoming and outgoing traffic, and utilisation rates.
VCenter Server Performance Charts
Using the vCenter Server performance charts, administrators can select an ESXi host from the inventory and navigate to Monitor > Performance > Advanced. From there, they can choose "Network" as the chart metric, set the timespan to real-time, and select the appropriate counters, such as data receive rate, data transmit rate, and usage. This provides an understanding of the network traffic generated by VMs and ESXi hosts.
VSphere Client Performance Charts
The vSphere client performance charts offer a comprehensive view of network performance. By selecting a VM in the inventory pane and navigating to Monitor > Performance > Overview, administrators can access performance metrics in the form of line charts, bar charts, pie charts, and stacked charts. These charts display compute, network, or storage resource usage for VMs, hosts, and clusters.
Other Considerations
In addition to utilising the performance charts, administrators should monitor network throughput at the host and VM level. This includes tracking the average rate of data received and transmitted, as well as the total network usage. Deviations from the baseline, such as spikes or drops, may indicate underlying issues with hardware or VM configurations.
Furthermore, it is essential to verify the installation of VMware Tools on each virtual machine and, if possible, use vmxnet3 NIC drivers for optimised performance. To reduce network traffic, virtual machines on the same host that communicate with each other should be connected to the same vSwitch.
Additionally, administrators should ensure efficient handling of different traffic streams by assigning each physical NIC to a port group and a vSwitch. This includes traffic generated by virtual machines, iSCSI protocols, and vMotion tasks.
To address dropped network packets, which indicate a bottleneck, administrators can adjust virtual machine shares or check the size of network packets and data transfer rates. Larger network packets generally result in faster network speed, while smaller packets require more CPU processing and lead to slower speeds.
Monitoring GPU Usage: A Comprehensive Guide to Tracking Performance
You may want to see also

Monitor data store performance
Monitoring data store performance is crucial to ensure optimal resource allocation and prevent performance degradation in your VMware environment. Here are some detailed instructions on how to monitor data store performance:
Basic Data Store Metrics:
Monitor the free space, used space, capacity, snapshots, swap file space, disk file space, and log file size of your data stores. This information is available in the datastore dashboard, which includes tabs for summary, storage, latency, outages, inventory, and log reports. Regularly refresh storage-related information, including free space, capacity, and VM usage, to ensure you have up-to-date data.
Metrics of VMs Occupying Data Stores:
Keep track of the space occupied by each virtual machine (VM) in the data store. Monitor the space allocated to each VM, the available space, the average read and write times, the read and write rates, and the log file details. This information will help you identify VMs with high resource consumption and adjust allocation accordingly.
Forecast Data Store Space Metrics:
Utilize AI-based predictions to forecast data store space metrics such as disk file space, snapshot space, and occupied space. These predictions can help you plan ahead and take proactive measures to avoid issues. For example, you can predict a full disk and clear disk files in advance, ensuring smooth VM operations.
Monitor Snapshots:
Snapshots can impact the performance of associated data stores. Monitor the age, size, and number of snapshots to manage your space requirements effectively. Consolidate snapshot files when they are no longer needed to free up space in the data store.
Utilize Performance Charts:
VMware vSphere provides performance charts that offer insights into resource usage for VMs, hosts, and clusters. You can view compute, network, or storage resource usage through these charts. Additionally, advanced performance charts provide more granular views and allow you to create custom charts to monitor specific data points.
By following these instructions and regularly monitoring data store performance, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, identify potential bottlenecks, and ensure optimal performance in your VMware environment.
Monitoring Rust Game Servers: Tracking RAM Usage
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Some tools to monitor VMware performance include SolarWinds Virtualization Manager, VMware vSphere 7, and VMware vCenter.
Important metrics to monitor include CPU and memory usage, disk latency, and network throughput.
You can monitor CPU and memory usage by tracking the percentage of CPU and memory being used by virtual machines and hosts.
Performance issues can be identified by setting up alerts for specific metrics, such as high CPU usage or low memory.
To improve VMware performance, you can optimize resource allocation, increase hardware capacity, or use a third-party monitoring tool for more detailed insights.







