Monitoring page file usage can be done in several ways, depending on the operating system and the level of detail required. For Windows users, the Performance Monitor application can track page file usage by adding the Paging File counter and selecting % Usage and/or % Usage Peak. Alternatively, third-party programs like MemInfo can be used to monitor page file usage in real time, with customizable settings and alerts for specific usage percentages. For more advanced insights, tools like Server & Application Monitor (SAM) or Network Performance Monitor (NPM) can be leveraged to monitor virtual memory usage, which is considered a volume.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Windows paging file | Pagefile.sys |
| Other names | Swap or virtual memory file |
| Function | Used by Windows when it runs out of physical memory (RAM) |
| How to check usage | Performance Monitor application |
| Performance Monitor access | Type 'perform' into the Run window (Windows Key + R) |
| Additional steps | Include memory in the live graph's tracking by pressing Ctrl + N or clicking the green plus icon |
| Final step | Select Paging from the list of counters in the left pane, then click Add |
| Alternative method | Download MemInfo, a third-party application |
What You'll Learn

Use the Performance Monitor application
To monitor page file usage using the Performance Monitor application, follow these steps:
- Open the Windows start menu and go to Administrative Tools.
- Open Performance Monitor.
- Expand Monitoring Tools and click on Performance Monitor.
- Right-click on the graph and select "Add Counters..." from the context menu.
- In the Add Counters dialog, select "Paging File" from the list of available counters.
- Click on the down arrow icon next to "Paging File" and select "% Usage" to add it to the Added counters list.
- Click "OK" to close the Add Counters dialog.
Additionally, you can press Ctrl + N or click the green plus icon to include memory in the live graph's tracking.
Performance Monitor will now display the percentage usage of your paging file, allowing you to monitor your system's page file usage over time.
Note that on Windows Web Server 2008, the "page file usage" in Task Manager has been replaced with "commit (mb)", which represents the amount of reserved virtual memory. To get the actual amount of PageFile usage, use Performance Monitor and add the "% Usage" counter.
Monitoring GPU Usage: A Comprehensive Guide to Tracking Performance
You may want to see also

Add counters to the live graph's tracking
To add counters to the live graphs tracking, you can follow these steps:
- Open the Performance Monitor application on your computer. This application tracks various aspects of your computer's performance, including CPU and page file usage.
- Include memory in the live graph's tracking. You can do this by pressing Ctrl + N on your keyboard or by clicking the green plus icon.
- Select "Paging" from the list of counters in the left pane, then click "Add". This will add the paging file counter to the live graph.
- Customise the graph:
- To get the actual amount of PageFile usage, open Performance Monitor (perfmon.exe) and go to Add Counters -> Paging File -> Usage. This will display the usage as a percentage.
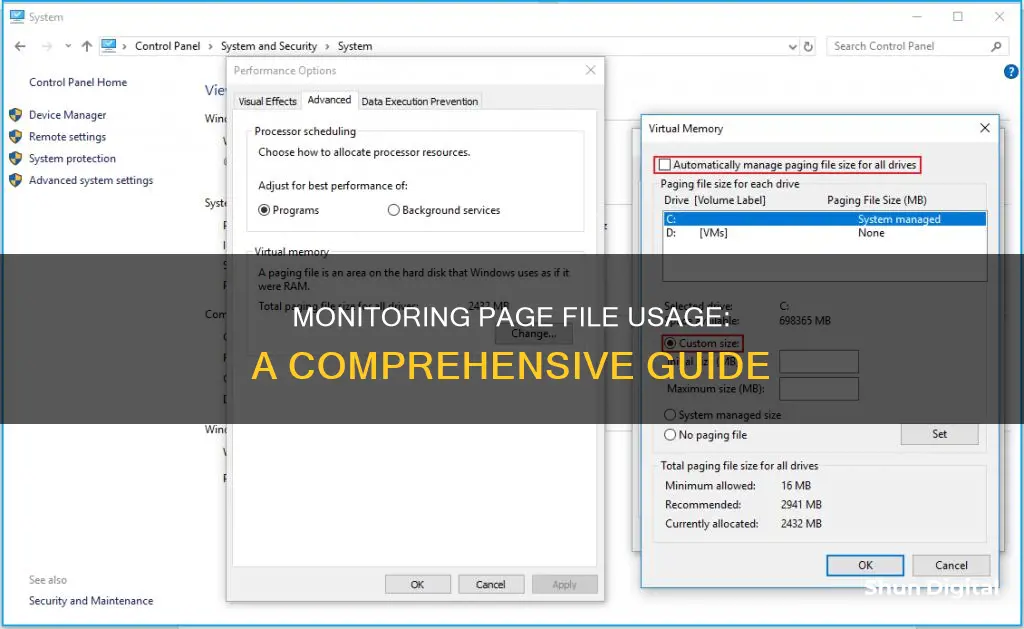
- To calculate the exact amount of used paging file in MB, press Win+Break keys to open System Properties, then navigate to Advanced -> Performance -> Advanced -> Virtual Memory -> Total Paging File Size (size will be in MB).
For more detailed analysis, consider using tools like Prometheus and Grafana. These tools allow you to create custom dashboards and queries to monitor specific metrics and gain deeper insights into your system's performance.
By following these steps, you can add counters to the live graphs tracking, providing you with valuable information about your computer's page file usage and overall performance.
Monitoring Electricity Usage: Room-by-Room Power Insights
You may want to see also

Select 'Paging' from the list of counters
Once you have accessed the Performance Monitor on your Windows computer, you can track your page file usage by following these steps:
- Press Ctrl + N on your keyboard or click the green plus icon.
- Select Paging from the list of counters in the left pane, then click Add.
- Now, you can view the percentage of page file usage by looking at the % Usage and/or % Usage Peak.
- To calculate the exact amount of page file usage, you can refer to the steps outlined in the following answer.
It is important to note that the Performance Monitor provides a snapshot of a particular point in time, so for a more comprehensive understanding of your page file usage, you can refer to your server statistics in your Tilaa dashboard.
Monitoring Bandwidth Usage on Your iPad: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Use the MemInfo utility
MemInfo is a utility that allows you to monitor your memory and page file usage in real-time. It is highly customizable and can be downloaded and used without installation.
MemInfo displays the current Windows memory usage in the taskbar, including both physical memory and the page file. You can adapt the settings to display the page file instead of physical memory, or switch to free memory and the actual percentage. Right-clicking on MemInfo in the taskbar will display more details about memory usage, such as the top 5 processes, physical memory usage, page file usage, and memory fragmentation.
You can also set up alerts within MemInfo if your usage crosses a certain percentage. This can be done in the Settings window, where you can also change the font and display options, as well as choose from a number of themes.
If you have more GB of RAM, under Settings, make sure to select "Optimize GB values" to ensure the display is shown correctly.
Monitoring Home Wi-Fi Data Usage: Tips for Beginners
You may want to see also

Monitor virtual memory
Virtual memory is a process that allows a system to use disk space as additional RAM, enabling the handling of larger workloads even when physical memory is limited. This process involves two mechanisms: swapping and paging. Swapping moves entire processes from RAM to disk when the physical RAM is full, while paging moves only specific pages of memory, allowing more granular control over memory usage.
High swap usage can severely impact performance, indicating that the system is running low on physical memory and potentially leading to process terminations by the Out Of Memory (OOM) Killer. Therefore, monitoring memory usage is crucial for maintaining system efficiency and preventing performance bottlenecks.
Windows
To monitor virtual memory usage on Windows, you can use the Performance Monitor application, which keeps track of your computer's performance, including CPU and page file usage. Here are the steps to access Performance Monitor:
- Type 'perform' into the Run window (Windows Key + R).
- Include the memory in the live graph's tracking by pressing Ctrl + N on your keyboard or clicking the green plus icon.
- Select 'Paging' from the list of counters in the left pane, then click 'Add'.
- To get the actual amount of Pagefile usage, open Performance Monitor (perfmon), and add counters by clicking the "+" icon -> Paging File -> % Usage and/or % Usage Peak.
Other Windows applications that can be used to monitor virtual memory include VMMap and Resource Monitor.
Linux
On Linux, monitoring virtual memory is straightforward and can be done using commands like free, top, and vmstat. Here are the essential commands for monitoring Linux memory usage:
- Physical memory: Use the free and top commands to get a snapshot of memory usage, including total, used, and memory allocation.
- Virtual memory usage: Use the free -t command to get detailed information about swap memory usage, which is critical for understanding how much virtual memory is in use.
- Monitoring virtual memory paging rate: Use the vmstat command to monitor the rate at which memory pages are moved from physical memory to disk. Specifically, look at the si (pages swapped in) and so (pages swapped out) columns.
Monitoring Bandwidth Usage: Per IP Address in Mikrotik
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
To check page file usage on Windows, open the Start menu and go to Administrative Tools. Open Performance Monitor, then Monitoring Tools, and click on Performance Monitor. Right-click on the graph and select Add Counters. From the Available counters list, select Paging File, then % Usage, and click Add.
A page file is an optional, hidden system file on a hard disk. It is a physical extension of RAM and allows the system to remove infrequently accessed modified pages from physical memory, allowing the system to use physical memory more efficiently for more frequently accessed pages.
Page file usage refers to the amount of reserved virtual memory. The commit charge is the total committed or "promised" memory of all committed virtual memory in the system.







