Adobe Camera Raw is a powerful tool for photographers, offering a range of editing options for RAW, TIFF, and JPEG files. While it can be challenging to open RAW files in Photoshop CS3, it is possible by downloading the Adobe Camera Raw Plug-In 4.6. This plug-in allows photographers to access and edit their RAW photos in Photoshop CS3, revealing incredible details in their images. With the plug-in, users can explore the redesigned user interface, new functions in the Image Controls menu, and enhanced synchronization with Lightroom. The plug-in installation process involves replacing the existing Camera Raw.8bi plug-in and copying the new one into the specified folder. This guide will explore the steps to install and utilize the Adobe Camera Raw Plug-In for Photoshop CS3, unlocking the potential for stunning photo editing.
What You'll Learn

Open and edit RAW, TIFF and JPEG files
Adobe Camera Raw is a powerful tool for editing and processing RAW, TIFF, and JPEG image files. It offers a range of features and adjustments that can enhance your photos and improve their visual appeal. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to open and edit these file formats using Camera Raw:
Opening RAW, TIFF, and JPEG Files in Camera Raw:
- Locating the File: Start by finding the image file you want to edit on your computer. It can be a RAW, TIFF, or JPEG file.
- Opening in Photoshop: Go to the File menu in Photoshop and choose "Open." Browse and select the desired image file.
- Selecting Camera Raw: In the Format pop-up menu at the bottom of the Open dialog box, choose "Camera Raw" as the format. Then, click "Open."
- Confirming File Type: Photoshop will open your image in Camera Raw. You can confirm that the image is a JPEG or TIFF file by checking the file name at the top of the window.
Editing RAW, TIFF, and JPEG Files in Camera Raw:
Once your image is open in Camera Raw, you can begin editing. Here are the steps to follow:
- Basic Adjustments: The first tab, labeled "B," contains basic controls such as White Balance, Exposure, Brightness, Contrast, and Saturation. Make adjustments to these settings as needed.
- Recovery and Fill Light: Two new sliders, Recovery and Fill Light, allow you to extract details from highlights and open up the shadows, respectively.
- Vibrance Slider: Below the "Convert to Grayscale" checkbox is the Vibrance slider, which enhances saturation.
- Tone Curve Adjustments: Click on the "T" tab to access the Tone Curve menu. Here, you can choose between Parametric and Point Curve editing options for fine-tuning highlights, lights, darks, and shadows.
- HSL / Grayscale Adjustments: The "H" tab opens the HSL (Hue, Saturation, and Luminance) and Grayscale adjustment pages. You can either apply grayscale conversion or make adjustments to the individual color channels.
- Split Toning: The "S" tab is for split toning, which is used for black-and-white images to impart different hues to highlights and shadows.
- Detail and Lens Correction: The "D" and "L" tabs provide adjustments for sharpening, noise reduction, chromatic aberration, and lens vignetting.
- Camera Calibration and Presets: The "Camera Calibration" tab allows you to enter ICC profiles for your camera or select the default ACR setting. The "Presets" page lets you store and manage your preferred settings.
- Batch Processing: Camera Raw also supports batch processing, allowing you to apply settings to multiple images simultaneously.
Saving Your Work:
After making your adjustments, you can save your image in various formats:
- Save Image: Click the "Save Image" button in the lower-left corner of the Camera Raw dialog box. This will process and save your image in the selected format.
- Save Options: Specify the location to save the file, the desired filename, and the file format. You can choose from formats such as PSD, TIFF, JPEG, or DNG.
Setting Preferences:
You can also set preferences for how Camera Raw handles JPEG and TIFF files:
- Automatically Open JPEGs and TIFFs in Camera Raw: Go to Photoshop (PC: Edit) > Preferences > Camera Raw. In the JPEG and TIFF Handling section, choose "Automatically Open All Supported JPEGs" and "Automatically Open All Supported TIFFs."
- Camera Raw Database or Sidecar XMP Files: In the Camera Raw Preferences dialog box, choose where to store your image settings. You can either use a Camera Raw database file or sidecar XMP files in the same folder as the image file.
How to Prepare Your Polaroid Camera for Instant Shots
You may want to see also

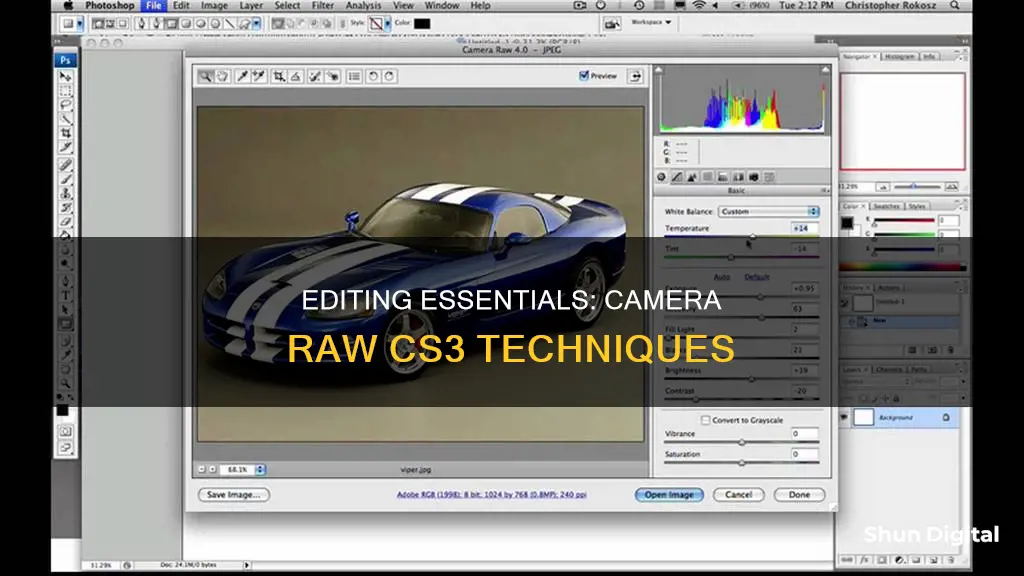
Use the histogram and image control tabs
The histogram is an exceptional tool for analysing and understanding the contrast in an image. It is a bar chart that graphs the distribution of tones in an image, with black on the left edge and white on the right. Each vertical bar represents the number of pixels for each tone.
In Camera Raw, the histogram display shows a separate histogram for each of the three colour channels: red, green, and blue. This can make it easier to correct certain colour issues and lets you know if you've overexposed individual colour channels.
The histogram in the Camera Raw dialog box shows the tonal range of the image at the current settings. As you make adjustments, the histogram updates automatically. You can also use the clipping displays to identify areas that have been over- or underexposed.
Below the histogram are the image control tabs, which include the Basic tab. This tab includes sliders for adjusting the white balance, exposure, brightness, contrast, and saturation. The sliders are now in two separate sections, with the Saturation slider below a checkbox for Convert to Grayscale. There are also two new sliders: Recovery, which enables detail to be extracted from highlights, and Fill Light, for opening up shadows.
Rechargeable Camera Batteries: Charged or Not When Bought?
You may want to see also

Convert to greyscale
Converting an image to greyscale in Camera Raw CS3 is a simple process. First, open the image in Camera Raw. You will notice a redesigned user interface with some new functions in the Image Controls menu on the right side of the workspace.
The "Convert to Grayscale" checkbox is located in the Basic Controls tab (denoted by the letter "B") in the Image Controls menu. This tab includes other adjustments such as White Balance, Exposure, Brightness, Contrast, and Saturation. The "Convert to Grayscale" checkbox is a new function in CS3, and it is located below the Saturation slider.
By checking the "Convert to Grayscale" box, you can create a greyscale version of your image. This process is based on the data contained in the red, green, and blue colour channels. It is a non-destructive way to preview a black-and-white version of your image and allows for further adjustments in subsequent tabs.
Additionally, there is a second "Convert to Grayscale" checkbox in the HSL / Grayscale adjustment page (accessed by clicking on the "H" tab). Checking this box will open a menu with sliders for adjusting tones in the greyscale image. This provides an eight-channel mixer for fine-tuning the greyscale tones.
Wireless Surveillance Cameras: How Long Do Batteries Really Last?
You may want to see also

Adjusting tone curve and HSL
Adjusting the tone curve and HSL in Camera Raw CS3 allows you to fine-tune the exposure, contrast, and colour of your images. Here's a detailed guide on how to do it:
Tone Curve Adjustments:
Firstly, make sure you've made your basic adjustments to the image, such as changes to exposure, contrast, brightness, and saturation. Then, you can use the Tone Curve adjustments to fine-tune your image.
In the Curve panel, you can select from different curve options:
- Point Curve: This is the standard curve tool that allows you to create extra control points and make targeted adjustments. It offers more freedom and precision but can be trickier to use.
- Parametric Curve: This curve splits your tones into sections: highlights, lights, darks, and shadows. It provides sliders for each section, making it easier to understand and preventing you from making drastic adjustments.
- Red/Green/Blue Channel Curve: These curves focus on adjusting specific colour channels. For example, adjusting the blue channel can make the midtones bluer or more yellow.
When using the Point Curve and Parametric Curve, the horizontal axis represents the original tone values, with black on the left and lighter values towards the right. The vertical axis represents the changed tone values, with black at the bottom and white at the top.
To adjust the tone curve:
- Click on the curve at the position on the horizontal axis that represents the colour tone range you want to adjust.
- Drag upwards to lighten the colours or downwards to darken them.
- For colour channel adjustments, dragging upwards increases the selected colour channel, while dragging downwards increases its complementary colour.
HSL Adjustments:
The HSL (Hue, Saturation, and Luminance) adjustments allow you to fine-tune the colours in your image. You can access this by clicking on the "H" tab in the Camera Raw interface.
To adjust the HSL:
- Ensure the "Convert to Grayscale" box is unchecked.
- Use the slider controls to adjust the Hue, Saturation, and Luminance parameters for each colour channel (Reds, Oranges, Yellows, Greens, Aquas, Blues, Purples, and Magentas).
- You can also use the "Auto" and "Default" hyperlinks to experiment with different settings.
Remember that the changes you make in the Tone Curve and HSL adjustments will be reflected in the histogram and the image preview. Always keep an eye on the histogram to ensure you're not clipping your shadows or highlights, which can lead to a loss of image detail.
Charging Reolink Cameras: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Copy and paste Camera Raw settings
Copying and pasting Camera Raw settings is a quick and efficient way to apply the same adjustments to multiple images. This method is especially useful when you have a batch of photos taken under the same lighting conditions and you want to apply the same corrections to all of them.
To copy and paste Camera Raw settings, you can use Adobe Bridge or keyboard shortcuts. Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Open your images in Adobe Bridge.
- Select the image that has the desired adjustments and choose "Edit > Develop Settings > Copy Camera Raw Settings" from the menu. Alternatively, you can use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Alt + C" on Windows or "Cmd + Option + C" on macOS.
- Select one or multiple images that you want to paste the adjustments to.
- Choose "Edit > Develop Settings > Paste Camera Raw Settings" from the menu, or use the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Alt + V" on Windows or "Cmd + Option + V" on macOS.
- The "Paste Camera Raw Settings" dialog box will open, allowing you to choose which specific adjustments you want to apply. You can select or deselect individual settings or choose a category from the "Subset" menu to apply or remove a group of settings.
- Click "OK" to apply the selected adjustments to the target images.
By following these steps, you can easily copy and paste Camera Raw settings, saving time and effort in your editing workflow.
Toucan Camera Battery Life: How Long Does It Last?
You may want to see also







