The Windows Reliability Monitor is a built-in Windows application that assists in identifying software issues in the Windows operating system that may affect system performance and reliability. It is a useful tool for troubleshooting and offers an easy interface to view and rate the system's dependability history, including what changed and when, alongside any application or OS crashes. There are several ways to access the Reliability Monitor, including through the Control Panel, the Windows Run Box, the Windows Search Box, and the Performance Monitor tool.
What You'll Learn

Accessing Reliability Monitor through the Windows search box
There are several ways to access the Reliability Monitor on Windows. One way is through the Windows search box. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Go to the Start Menu and click on the Search box, usually located in the bottom left corner of the screen.
- In the Search box, type "reliab" (without quotation marks). You can also simply type "reliability".
- From the search results, select "View reliability history". This will open the Reliability Monitor.
Alternatively, you can access the Reliability Monitor by opening the Control Panel, selecting "Security and Maintenance", and then clicking on "View reliability history" under the "Maintenance" or "Report problems" section.
Another option is to use the Windows Run Box (accessed by pressing Windows Key + R) and typing the command "perfmon /rel", followed by the Enter key.
The Reliability Monitor is a useful tool for identifying and troubleshooting software issues, tracking system stability, and monitoring critical performance metrics. It can help you resolve random issues and improve your PC's performance.
Asus ROG Monitors: Premium Price, Premium Experience?
You may want to see also

Using the Windows Control Panel
The Windows Reliability Monitor is a Windows application that helps you identify software issues in the Windows operating system that may affect system performance and reliability. It is different from the Performance Monitor, which shows how your hardware is performing. Reliability Monitor can be accessed through the Windows Control Panel. Here is a step-by-step guide to accessing the Reliability Monitor using the Windows Control Panel:
- Open the Control Panel: Press the Start button and type "Control Panel". Click on the top result that appears.
- Search for "Security and Maintenance": In the Control Panel, search for "Security and Maintenance" and click on the top result.
- Click "View reliability history": In the "Security and Maintenance" section, click on "View reliability history" under the "Maintenance" section.
- Wait for the report to generate: Depending on your system specifications and history, it may take a little time for the report to be generated. Typically, it shouldn't take more than a minute.
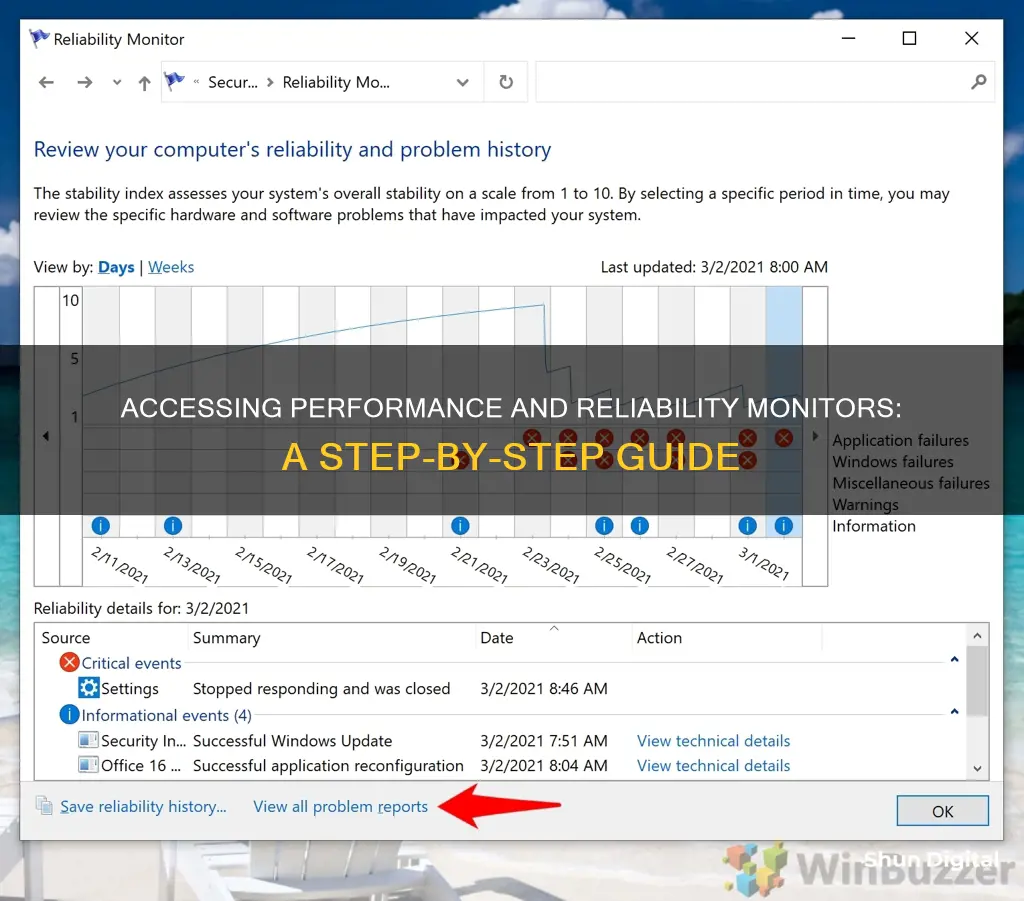
- Sort your computer reliability by Days or Weeks: Above the chart, you can choose to view your computer reliability by days or weeks. The "Days" or "Weeks" heading will allow you to view your system's reliability score over daily or weekly increments.
- View technical details: To get more information about a specific issue, click on its respective day or week in the graph. Then, click on "View technical details" in the bottom panel to see additional details about the event.
- Read the error description: The details of the event will provide more information to assist in troubleshooting or seeking further assistance.
- View all problem reports: You can also view a list of all problem reports by clicking on the "View all problem reports" button.
By following these steps, you can access and utilise the Windows Reliability Monitor through the Control Panel to identify and address software issues affecting your system's performance and reliability.
Understanding ASUS CPU Temp Monitoring: What's Really Going On?
You may want to see also

Using the Windows Run Box
The Windows Run Box can be used to access the Reliability Monitor, which is a Windows application that assists in identifying software issues in the Windows operating system that may affect system performance and reliability.
To access the Reliability Monitor using the Windows Run Box, follow these steps:
- Press the Windows Key + R on your keyboard to open the Run Box.
- Once the Run Box is open, type the following command: perfmon /rel.
- Press the Enter key.
This method of accessing the Reliability Monitor is one of several ways to launch the tool. The Reliability Monitor was originally intended to be used by system administrators running Windows Server 2008, which may explain why it is relatively unknown and underutilized.
The Reliability Monitor is a useful tool for identifying software issues and tracking system stability. It provides a quick view of how stable the system has been and allows users to see details on a day-by-day basis about events that impact reliability. It records failures, such as memory, hard disk, application, and operating system failures, as well as key events regarding system configuration, such as the installation of new applications and updates.
By using the Windows Run Box and typing in the command "perfmon /rel", users can quickly access the Reliability Monitor and take advantage of its features to identify and troubleshoot software issues affecting their Windows system's performance and reliability.
Connecting AV Cables to Your Monitor: A Simple Guide
You may want to see also

Using the Windows Start Menu
To access the Reliability Monitor on Windows, you can use the Start Menu in a few different ways.
Firstly, you can use the Windows search box from the Start Menu. Simply type "reliab" (without the quotation marks) and click on "View reliability history". This will take you to the Reliability Monitor.
Another option is to use the Windows Run Box. Press the Windows Key + R to open the Run Box, then type the command "perfmon /rel" and press Enter. This will bring up the Reliability Monitor.
Additionally, you can access the Reliability Monitor through the Control Panel. Go to "Control Panel > Security and Maintenance > Maintenance > 'View reliability history'". This will take you to the Reliability Monitor interface, where you can view your system's stability history and other relevant information.
The Reliability Monitor is a useful tool that assists in identifying software issues in the Windows operating system, which may impact system performance and reliability. It provides a quick view of how stable your system has been and tracks events to help pinpoint causes of reduced reliability.
Monitoring Internet Usage: BigPond's Guide to Online Activity
You may want to see also

Using the Performance Monitor tool
Performance Monitor is a system monitoring program that was introduced in Windows NT 3.1. It can be used to monitor various activities on a computer, such as CPU or memory usage, and can help determine the cause of problems on a local or remote computer. The program can also define thresholds for alerts and automatic actions, generate reports, and view past performance data.
Performance Monitor can be opened in Windows in several ways:
- Press Win+F, type 'perfmon' in the Search bar and hit Enter.
- Press Win+R, type 'perfmon' in the Run box and hit Enter.
- Open Command Prompt or PowerShell, type 'perfmon.exe' and hit Enter.
- Open System Configuration Tool > Tools tab > Select the Performance Monitor > Click Launch button.
- Open Computer Management > On the left, select Performance > Expand Monitoring Tools > Click on Performance Monitor.
When you first open Performance Monitor, you will see an overview and system summary. From the left pane, select 'Performance Monitor' under 'Monitoring Tools'. The graph you see here is the processor time over the last 100 seconds. The horizontal axis displays time, and the vertical axis displays the percentage of time your processor consumes working on active programs.
You can also analyse many other counters, such as:
- % Interrupt Time: The time required by your processor to receive and service hardware requests or interrupts. If this time exceeds 30%, there might be some hardware-related risk.
- % Committed Bytes In Use: This counter shows the percentage of your RAM currently in use. This counter should fluctuate as different programs are opened and closed. However, if it keeps increasing, there might be a memory leak.
- Available Bytes: This counter shows the amount of physical memory (in bytes) available for immediate allocation to a process or system. If there are less than 5% of available bytes, you may need to add more memory.
To add new counters under Performance Monitor:
- Click on the green plus-shaped icon on top of the graph.
- The 'Add Counters' window will open.
- Now, select the name of your computer (usually the local computer) in the 'Select counters from the computer' drop-down menu.
- Expand the category of counters you want, e.g. Processor.
- Select one or more counters from the list. To add multiple counters, select the first counter, then press and hold the Ctrl key while selecting the other counters.
- Click on the 'Add' button to add the counters. The added counters will be shown on the right.
- Click 'OK' to confirm.
- The new counters will start to appear in the graph with different colours.
- The details of each counter will be shown at the bottom, such as which colours correspond to it, its scale, instance, object, etc.
- Use the checkbox against each counter to show or hide it from the graph.
Once you have added all the desired counters, you can customise them:
- Double-click on any counter below the graph.
- To select multiple counters, press and hold the Ctrl key while selecting the counters. Then right-click and select 'Properties' from the list.
- The 'Performance Monitor Properties' window will open; from there, switch to the 'Data' tab.
- Here you can select the colour, scale, width and style of the counter.
- Click 'Apply', followed by 'OK'.
Note that when you restart Performance Monitor, all these set counters and configurations will be lost by default. To save these configurations, right-click on the graph and select 'Save settings as' from the menu. Type the desired file name and click 'Save'. The file will be saved as an .htm file.
You can also change the graph type by clicking the downward arrow beside the third icon above the graph. You can choose from a line, histogram bar or report. You can also press Ctrl + G to switch between the graph types.
Performance Monitor also includes Data Collector Sets, which is where you can create custom sets containing performance counters and alerts based on specific criteria.
To create a custom Data Collector Set:
- Expand 'Data Collector Sets' in the left pane of the Performance Monitor window.
- Right-click on 'User Defined', then select 'New' and click on 'Data Collector Set'.
- Type a name for the set and select 'Create manually (Advanced)'. Click 'Next'.
- Select the type of data you want to include. Click 'Next'.
- Click on 'Add' and select the performance counters you would like to log (e.g. memory, processor usage, etc.).
- Once the selection is complete, click 'OK'.
- Select the Sample interval and the Units and click 'Next'.
- Now select the location you want to save the data.
- Click 'Finish'.
You will see the new entry in the right pane. Right-click on it and select 'Start'. Once you are done, right-click on it again and select 'Stop'. The data log file will be created and saved in the specified location. Click on the file to view it in the Performance Monitor.
Finding the Right MSI Monitor Size for You
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
There are several ways to access the Reliability Monitor. You can:
- Go to Control Panel > Security and Maintenance > Maintenance > 'View reliability history'.
- Type "perfmon /rel" into Command Prompt.
- Open the Performance Monitor tool and select "Reliability Monitor..." from the "Action" menu-tab.
- Open the Performance Monitor tool, right-click the "Monitoring Tools" tab, and then choose "View system reliability..." from the context menu.
- Click on the 'Search' icon on the taskbar and type "Reliability". Click "View Reliability History" and then "Open".
The Reliability Monitor is a Windows application that helps identify software issues in the Windows operating system that may affect system performance and reliability.
The Reliability Monitor provides a quick view of how stable the system has been and tracks events that will help identify what causes reductions in reliability. It records failures, including memory, hard disk, application, and operating system failures, as well as key events such as the installation of new applications and system updates.
The Reliability Monitor uses a graphical interface to show and rate the system's dependability history, including exactly what changed and when, alongside any application or OS crashes. It can also show information related to updates, software installations or uninstalls, and hardware issues.
The Performance Monitor is a general-purpose tool that is more limited in scope and capability than the Reliability Monitor. The Reliability Monitor is a specialized part of the Performance Monitor and is much easier to use.







