When it comes to choosing a monitor, there are a few things to consider, including backlighting, lifespan, eco-friendliness, picture quality, viewing angles, and pricing. LCD (liquid crystal display) and LED (light-emitting diode) monitors differ in these areas, and it's important to understand these differences to make an informed decision. One such difference is in the brightness of the screens, which is measured in nits. So, do LED monitors have more nits than LCD monitors?
What You'll Learn
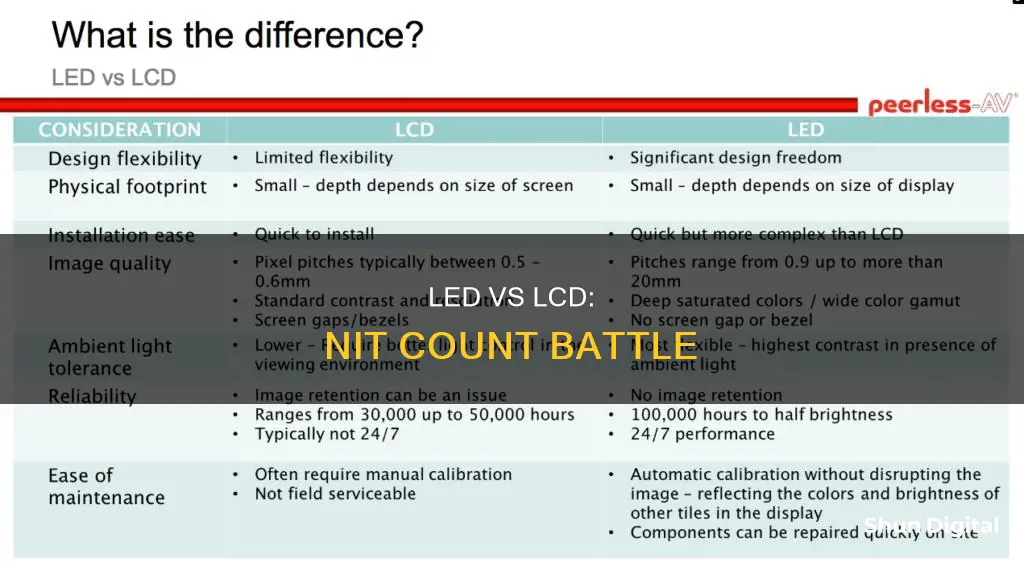
- LED monitors have a higher brightness of up to 600 nits, while LCDs reach around 250-300 nits
- LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, while LCDs use cold cathode fluorescent lamps
- LED monitors offer wider viewing angles of 178° compared to 160° for LCDs
- LED monitors have faster response times of 1-5ms, reducing motion blur and ghosting
- LED monitors are more expensive than LCDs, often by $50-$200

LED monitors have a higher brightness of up to 600 nits, while LCDs reach around 250-300 nits
When it comes to brightness, LED monitors offer a significant advantage over LCDs. LED monitors can achieve extremely high brightness levels, reaching up to 600 nits, while LCDs typically top out around 250-300 nits. This means that LED monitors can get much brighter and more vibrant, providing a more vivid viewing experience.
The higher brightness of LED monitors is due to their use of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) for backlighting. This technology allows for more precise control over screen brightness and better power management. As a result, LED monitors consume about 20-30% less power than LCD monitors while delivering superior brightness.
The higher brightness of LED monitors is particularly advantageous in well-lit rooms or outdoor environments. If you plan to use your monitor in a bright environment, an LED monitor with a higher nit rating will provide a clearer and more visible display. This makes LED monitors ideal for outdoor digital signage, commercial displays, and situations where maximum visibility is required.
Additionally, the higher brightness of LED monitors contributes to improved picture quality. LED monitors offer higher contrast ratios, deeper blacks, and more accurate colour reproduction. This results in images that appear more lifelike and detailed, with richer and more vibrant colours.
It's important to note that while LED monitors excel in brightness and image quality, LCD monitors have their advantages too. LCD monitors are generally more affordable, making them a cost-effective option for those on a tight budget. They also offer wider viewing angles than early-generation LEDs, ensuring consistent image quality for multiple viewers. Furthermore, LCD monitors have proven to be reliable technology, providing good performance and value over several decades.
Monitoring Data Usage: A Guide for Linksys Routers
You may want to see also

LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, while LCDs use cold cathode fluorescent lamps
The main difference between LCD and LED monitors is in their backlighting technology. LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, and these monitors use cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs) for backlighting. On the other hand, LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode, and these monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting.
LCD monitors use a layer of liquid crystal to control the passage of light. When an electric current is applied, the liquid crystals align to either allow or block light, creating the images we see on the display. This technology has been a cornerstone in the world of visual displays for decades.
Cold cathode fluorescent lamps, or CCFLs, are the light source for LCD screens. These lamps emit light that passes through the liquid crystal layer to create images. LCDs are extensively used in electronics, such as computer monitors and televisions. CCFLs are long, thin tubes that produce light through the interaction of electricity with mercury vapour inside the tube. They provide a consistent and uniform light source and are known for their long lifespan, high brightness, and low power consumption.
LED monitors, on the other hand, use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as their light source. LEDs produce light directly, without the need for a separate light source like CCFLs. Each diode emits its own light when an electric current passes through it. LED backlighting enables better control over individual pixels, resulting in sharper images and more uniform illumination across the screen.
LED monitors offer several advantages over LCD monitors. They consume less power, provide higher brightness levels, and have superior contrast ratios. LED technology is more energy-efficient, resulting in lower power consumption and reduced electricity bills. LED monitors also have a longer lifespan, typically lasting around 100,000 hours compared to 50,000 hours for LCDs.
In summary, LED monitors use light-emitting diodes for backlighting, providing improved visual clarity, colour accuracy, and contrast. LCD monitors, on the other hand, use cold cathode fluorescent lamps for backlighting and are known for their good colour reproduction and brightness. LED monitors offer superior performance but usually come with a higher price tag.
Choosing Studio Monitors: Room Size Matters
You may want to see also

LED monitors offer wider viewing angles of 178° compared to 160° for LCDs
LED monitors offer a wider viewing angle than LCD monitors. The viewing angle of an LED display is a reference value that includes both horizontal and vertical indicators. The horizontal viewing angle refers to the range of angles to the left and right of the screen, while the vertical viewing angle refers to the range above and below. LED monitors offer a wider viewing angle of 178° compared to 160° for LCDs. This means that colours and contrast remain more consistent when viewing the screen from different angles.
The wider viewing angle of LED monitors is due to the use of different backlighting technologies. LED monitors use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for backlighting, while LCD monitors typically use cold cathode fluorescent lamps (CCFLs). LEDs are placed evenly across the entire screen, allowing for local dimming and better contrast. This results in superior picture quality with better contrast ratios and deeper blacks compared to LCD displays.
The type of LED chip and its packaging can also impact the viewing angle. For example, Surface-Mount Device (SMD) LEDs offer wider viewing angles than Discrete LEDs because of their design, which allows light to disperse more broadly. Additionally, larger LEDs tend to have bigger lens surfaces, making it easier for light to disperse across a wider angle.
Wider viewing angles in commercial LED displays not only provide technical specifications but also engage viewers more effectively, encouraging longer viewing times and more significant interaction. This is why viewing angles are necessary for LED displays. However, there are also places where narrow viewing angles (less than 30 degrees) are used, such as highway or railway applications.
When deciding between an LCD and an LED monitor, it is important to consider factors such as purpose, budget, energy efficiency, picture quality, and screen size. For gaming, graphic design, or video editing, an LED monitor with full-array backlighting is often the better choice due to its superior picture quality and colour accuracy. If energy efficiency and a longer lifespan are priorities, LED monitors are also the better choice. On the other hand, if budget is a concern, LCD monitors offer good value and performance.
Monitoring Natural Gas Usage: Efficient Strategies for Conservation
You may want to see also

LED monitors have faster response times of 1-5ms, reducing motion blur and ghosting
LED monitors have faster response times, ranging from 1-5ms, which significantly reduces motion blur and ghosting. This is especially important for gamers and those watching action-packed movies, as it enhances the overall viewing experience by providing clearer visuals and reducing distractions.
The response time of a monitor refers to the amount of time it takes for pixels to switch from one colour to another. A fast response time ensures that the monitor can keep up with fast-moving objects on the screen, preventing motion blur and smearing. For example, when playing games or watching movies with constant movement, the pixels are constantly changing colours, and a quick response time ensures that the display can keep up with these changes.
LED monitors, with their superior response times, offer a smoother and more immersive experience. This is particularly beneficial for gamers, as it can improve accuracy and performance. Additionally, for those who spend a significant amount of time in front of a monitor, a faster response time can help reduce eye strain by providing a more comfortable viewing experience.
It is worth noting that while a fast response time is desirable, an overly quick response time can lead to inverse ghosting, where the pixels change colour too quickly and create a bright trail behind fast-moving objects. However, this issue can often be mitigated by adjusting the monitor's settings or utilising features like overdrive to find the optimal balance.
In summary, LED monitors' faster response times of 1-5ms enhance the viewing experience by reducing motion blur and ghosting, making them a preferred choice for gamers and those seeking a high-quality visual experience.
Viewing Your Website: Monitor Size Matters
You may want to see also

LED monitors are more expensive than LCDs, often by $50-$200
When it comes to choosing between an LED and an LCD monitor, there are several factors to consider, including performance, pros and cons, and price. LED monitors tend to perform better in areas like brightness, contrast, black levels, colour accuracy, and viewing angles. They are also thinner, more lightweight, and more energy-efficient than LCD monitors. Additionally, LED monitors have faster response times, reducing motion blur and ghosting, which is especially beneficial for gaming.
However, one of the main drawbacks of LED monitors is their higher price tag. LED monitors are generally more expensive than LCD monitors, often by $50-$200. This price difference can be a significant factor for consumers, especially those on a tight budget. The premium pricing of LED monitors makes them less accessible to some buyers, who may opt for the more affordable LCD option.
While LED monitors offer superior performance and image quality, the higher cost may not be justifiable for casual users who do not require the fastest response times and the highest colour accuracy. In such cases, an LCD monitor can be a more economical choice, providing good performance for day-to-day use at a lower price point.
It is worth noting that the price gap between LED and LCD monitors has narrowed in recent years as LED technology has become more common and accessible. Additionally, LED monitors tend to have a longer lifespan than LCDs, which may offset the higher initial cost over time. Nonetheless, for buyers with budget constraints, the difference in price can be a deciding factor when choosing between LED and LCD monitors.
Monitoring Table Sizes on Unix: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A nit is a unit of measurement that refers to the amount of light emitted from a surface or object. One nit is equal to one candela per square meter.
Nits help us understand the true brightness of a display and compare the brightness of different screens. Displays that are brighter require more power to operate, so nits can also help us compare the efficiency of different screens.
This depends on your needs and preferences. If you're using your device in a bright room, you'll want a higher nit count so the screen is still visible. If you're in a dark room, a lower nit count may be fine. Most monitors, TVs, and phones on the market today range from 250 to 600 nits, but some high-end models can go up to 1,000 nits or more.
A:
- Smartphones/Tablets: 200 to 1000+ nits
- Laptops/Monitors: 200 to 600+ nits
- TVs: 100 to 2000+ nits
- Projectors: 1000-2000 nits
- LED Walls/Screens: 1000-5000+ nits
LED monitors can achieve up to 600 nits, while LCD monitors typically max out around 250-300 nits. So, yes, LED monitors tend to have more nits than LCD monitors.







