Adobe Camera Raw is a non-destructive image-processing plugin that allows users to edit and export raw image files produced by digital cameras. It is not a standalone program but is launched in conjunction with Adobe Photoshop or Adobe After Effects. It can also be accessed through Adobe Bridge. The plugin allows users to view and edit raw files before opening them for further editing in Photoshop or exporting them to image formats such as JPEG or TIFF. Raw files contain uncompressed picture data that must be processed by software before they can be viewed. Adobe Camera Raw supports all modern raw formats, including CR2, CR3, NEF, ORF, and DNG files.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Import and enhance raw images |
| Supported Applications | Photoshop, Photoshop Elements, After Effects, Bridge, Lightroom |
| Supported Camera Models | Apple, Canon, Casio, Contax, DJI, DxO, Epson, Fujifilm, Google, GoPro, Hasselblad, Huawei, Kodak, Konica Minolta, Leaf, Leica, LG, Mamiya, Motorola, Nikon, Nokia, OM Digital Solutions, OnePlus, Olympus, Panasonic, Parrot, Pentax, PhaseOne, Pixii, Ricoh, Samsung, Sigma, Skydio, Sony, Xiaomi, Yuneec, Zeiss |
| File Format Support | Digital Negative (DNG), CR2, CR3, NEF, ORF |
| Editing Features | Crop, rotate, adjust exposure, colour temperature, contrast, sharpness, tone curves, colour grading, lens distortion correction, vignette, noise reduction, dodging, burning, cloning |
| Export Settings | Output file format, bit depth, resolution, colour space, compression ratio |
| Batch Processing | Yes |
| Subscription | Included with Adobe Creative Cloud packages for Photoshop or After Effects |
What You'll Learn

Adobe Camera Raw is a plugin for Photoshop and After Effects
Adobe Camera Raw is a powerful tool for photographers, allowing them to import and enhance raw image files from a wide range of cameras. It is a plugin that extends the functionality of Adobe Photoshop and Adobe After Effects, as well as other Adobe applications such as Adobe Bridge, Photoshop Elements, and Lightroom.
As a plugin for Photoshop and After Effects, Adobe Camera Raw enables users to work with raw image files directly within these applications. This integration provides a seamless editing experience, allowing photographers to utilise the advanced features of both Photoshop and After Effects while also benefiting from the capabilities of Camera Raw.
One of the key advantages of using Adobe Camera Raw is its ability to handle raw image files. Raw images contain unprocessed and uncompressed data from a camera's image sensor, providing greater flexibility in editing compared to JPEG or TIFF formats. With Camera Raw, photographers can adjust various aspects of their images, including white balance, tonal range, contrast, colour saturation, and sharpening. Moreover, the original camera raw data is preserved, giving users the freedom to reprocess their images and achieve their desired results.
The plugin is compatible with a broad range of camera models and supports various raw file formats. It also offers standard camera support for specific models, such as the DxO One. Adobe regularly updates Camera Raw to ensure compatibility with the latest cameras and to provide new features for Photoshop and Lightroom users.
Installing the Adobe Camera Raw plugin is a straightforward process. Users can download the appropriate installer file for their Adobe application and follow the installation instructions. Once installed, the plugin integrates seamlessly into the supported Adobe applications, providing easy access to its powerful raw image editing capabilities.
Charging Eufy Cameras: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

It allows you to edit and export raw image files
Adobe Camera Raw is a powerful tool for photographers, allowing them to import, edit, and enhance raw image files. It is a plugin that pops up when you open a raw file with Adobe Photoshop or Bridge. With Adobe Camera Raw, you can edit raw photos non-destructively, meaning the original camera raw data is preserved. It supports all modern raw formats, including CR2, CR3, NEF, ORF, and DNG files.
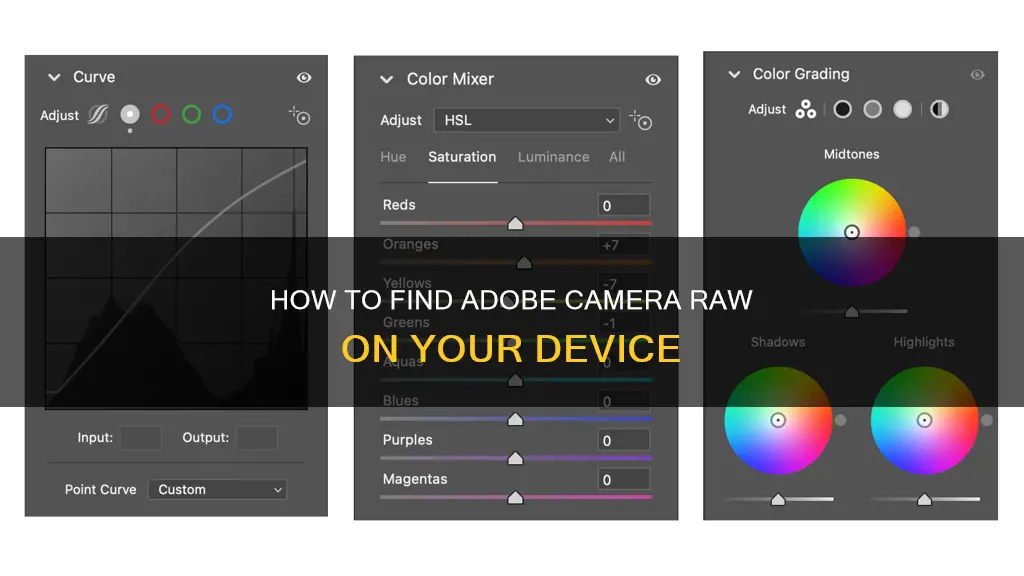
Adobe Camera Raw gives you a range of editing tools, including profiles, tone sliders, local adjustments, curves, clone brushes, and transform options. You can also import multiple images and edit them together, which is useful when working on a comprehensive series of images. Additionally, it allows you to choose your desired export settings, such as output file format, bit depth, resolution, color space, and compression ratio.
One of the key advantages of using Adobe Camera Raw is its integration with other Adobe applications. It is included as a plugin with Adobe Photoshop and After Effects, and it also adds functionality to Adobe Bridge. This means you can seamlessly move between these applications when working on your images.
When it comes to exporting your edited raw images, there are a few options. You can save the processed files in Digital Negative (DNG), JPEG, TIFF, or Photoshop (PSD) formats. Keep in mind that Adobe Camera Raw cannot save an image in the camera raw format. Instead, it allows you to export your edited raw images in more standard and widely-used formats.
Additionally, if you are using the Photos app on macOS, you can select the edited image and go to File > Export to export your modified raw photo as a conventional image format such as JPEG or TIFF. This process will convert your raw file to a standard image format while preserving your edits.
Space Tesla Camera: Did the Battery Die?
You may want to see also

Raw files are uncompressed and unprocessed
The benefit of this is that you have more freedom to manipulate aspects of the photo, such as brightness, colour, sharpness, and noise reduction, with minimal quality loss. This is because the raw file format preserves all of the data in an image without compression.
However, the downside of shooting in raw format is that it results in larger file sizes compared to compressed formats like JPEG. This is because the raw format does not compress the image data, so the files can take up more space on your camera's memory card and your computer's hard drive.
Another thing to consider is that you need special software to view and edit raw files. They cannot be simply shared or viewed like JPEG files. You need a raw converter and editor, such as Adobe Camera Raw, to view and edit them.
Overall, shooting in raw format can be beneficial if you want to have more control over the final image and are willing to sacrifice some storage space. It gives you the flexibility to make adjustments to the image without losing quality. However, it also requires additional time and software to process and edit the raw files.
Finding the Camaro's Battery: Fifth Generation
You may want to see also

Raw files contain more data than JPEGs or TIFFs
Adobe Camera Raw is a tool that lets you import and enhance raw images. Raw files contain more data than JPEGs or TIFFs. When you press the shutter button, your camera exposes light onto the sensor. The amplifier then sets the ISO to your required level to give a correct exposure. After that, the analog-to-digital converter sends the signal to the processor. If you choose JPG conversion, the data gets processed, coloured, sharpened, compressed, and written onto the memory card. However, if you choose a raw format, the procedure stops right after the digital conversion. What's written onto the card is raw pixel data.
Raw files contain more tonal information than a JPG file. They are like the digital equivalent of a film negative. Raw files are uncompressed and unprocessed, which means they are larger than JPEG or TIFF files. JPEG loses the most information during compression, while TIFF is uncompressed and contains more data than JPEG, resulting in a more detailed picture. However, because TIFF files contain more data, they take up more storage space.
When you shoot in JPEG, your camera automatically processes and enhances the image. You have little control over how this processing occurs. Shooting in raw gives you greater control because it doesn't lock you into the processing done by your camera. You can still edit JPEG and TIFF images in Camera Raw, but you will be editing pixels that were already processed by the camera. Raw files always contain the original, unprocessed pixels from the camera.
You can edit raw photos using Adobe Camera Raw, which comes with Photoshop. It acts like a plugin, opening in a separate window. It gives you the same tools as Lightroom, including profiles, tone sliders, local adjustments, curves, clone brushes, and transform options. With Adobe Camera Raw, you can edit raw photos non-destructively. It handles all modern raw formats such as CR2, CR3, NEF, ORF, or DNG files.
Minolta X-700: What Battery Powers This Classic Camera?
You may want to see also

Adobe Camera Raw is not a standalone program
Adobe Camera Raw is a non-destructive image processing plugin that allows you to edit and export the raw files produced by a digital camera. It is not a standalone program but is instead launched in conjunction with Adobe Photoshop or Adobe After Effects. With either of these programs installed, you can also access Camera Raw through Adobe Bridge.
The plugin allows you to view and edit raw files before opening them for further editing in Photoshop or exporting them to image formats such as JPEG or TIFF. Raw files are produced by digital cameras and contain uncompressed picture data that must be processed by software before they can be viewed.
Adobe Camera Raw is included as a plug-in with Adobe After Effects and Adobe Photoshop, adding functionality to Adobe Bridge. It gives these applications the ability to import and work with camera raw files, as well as JPEG and TIFF files. Camera Raw supports images up to 65,000 pixels long or wide and up to 512 megapixels.
While Camera Raw is not a standalone program, it is a powerful tool for editing and processing raw image files. It allows you to crop and rotate images, adjust exposure, colour temperature, contrast, and sharpness, and make complex changes using tone curves and colour grading tools. It is a popular choice for professional photographers and can be accessed through a subscription to Adobe's Creative Cloud packages that include either Photoshop or After Effects.
GoPro Cameras: Which Models Offer the Longest Battery Life?
You may want to see also







