Monitoring GPU performance is essential to ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently, especially when running GPU-intensive tasks. GPU or Graphics Processing Unit is a dedicated hardware component that accelerates graphics and video rendering. By keeping an eye on GPU usage, you can identify performance bottlenecks and take steps to optimise your system's performance. This can be done through various tools and methods, such as the built-in Task Manager in Windows or third-party applications like MSI Afterburner and NVIDIA Inspector, which allow you to monitor and limit GPU usage by individual processes. Additionally, for NVIDIA GPUs, the NVIDIA Control Panel provides detailed information about GPU utilisation and the NVIDIA System Management Interface (nvidia-smi) offers performance monitoring via the command line.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| GPU Usage | Can be found using Task Manager, MSI Afterburner, NVIDIA Inspector, or NVIDIA System Management Interface (nvidia-smi) |
| GPU Utilization | Can be viewed through the NVIDIA Control Panel or nvidia-smi |
| GPU Memory Usage | Can be monitored using nvidia-smi, nvtop, or atop |
What You'll Learn

Using the Task Manager
The Task Manager is a built-in tool in Windows that allows users to monitor the performance of their system and manage running processes. Here is how you can use it to monitor GPU performance:
Opening the Task Manager
To open the Task Manager, press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on your keyboard or right-click on the taskbar and select Task Manager from the menu.
Viewing GPU Performance
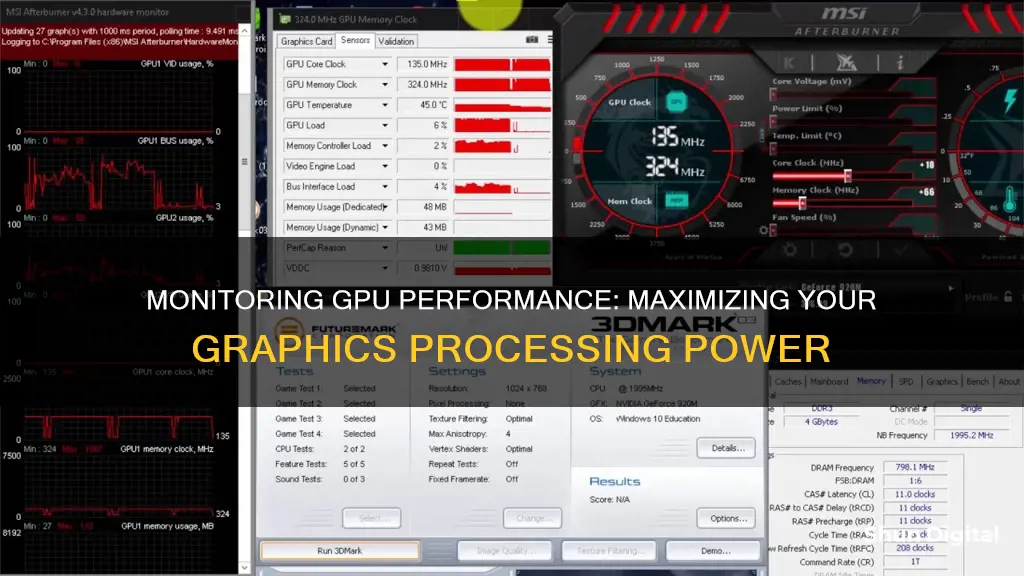
Once the Task Manager is open, navigate to the Performance tab. Here, you will be able to view your computer's overall system usage. Find the GPU option located on the left-hand side of the Performance tab and click on it. The Task Manager will then display real-time data on your GPU usage, including the GPU utilisation percentage, GPU engine and memory clock speed, and the dedicated video memory in use.
Customising GPU Usage Monitoring
The Windows Task Manager also lets you customise your GPU usage monitoring. Click on the gear icon next to the GPU option to access the settings menu. Here, you can choose to display additional information such as the GPU temperature and fan speed.
Monitoring GPU Usage by Process
To find GPU usage by process in Windows, click on the Performance tab in the Task Manager and select GPU from the left-hand menu to view the GPU usage of all running processes. By default, the Task Manager displays the GPU usage of processes in descending order of usage. You can click on the GPU column to sort the processes by ascending or descending order of usage.
Viewing an Application's GPU Usage
To view an application's GPU usage, open the Task Manager and click on the More details option at the bottom of the window if you see the standard, simple view. Then, on the Processes tab, right-click any column header and enable the GPU option. This adds a GPU column that lets you see the percentage of GPU resources each application is using. You can also enable the GPU Engine option to see which GPU engine an application is using.
Viewing an Application's Video Memory Usage
To view an application's video memory usage, switch to the Details tab in Task Manager. On the Details tab, right-click any column header, and then click the Select Columns option. Scroll down and enable the GPU, GPU Engine, Dedicated GPU Memory, and Shared GPU Memory columns. The Dedicated GPU Memory column shows how much memory an application is using on your GPU. If you have integrated graphics, this column shows how much of your normal system RAM is reserved exclusively for your graphics hardware. The Shared GPU Memory column shows how much memory an application is currently using for video features out of the computer's normal system RAM.
Monitoring Overall GPU Resource Usage
To monitor overall GPU resource usage, click the Performance tab and look for the GPU option in the sidebar—you may have to scroll down to see it. If your computer has multiple GPUs, you'll see multiple GPU options here. Windows displays real-time GPU usage, with different graphs depending on what's happening on your system. You can also see graphs of dedicated and shared GPU memory usage.
Differentiating Monitor Resolutions: 480x720 vs 800x480
You may want to see also

Third-party tools
GPU-Z
GPU-Z is a lightweight and user-friendly system utility designed to provide vital information about your video card and graphics processor. It is widely used by gamers and enthusiasts for its simplicity and accuracy. GPU-Z offers real-time monitoring of GPU temperature, clock speeds, memory usage, fan speed, and other essential metrics. It also provides detailed specifications of the GPU, including the graphics card model, GPU architecture, memory type, and driver versions. GPU-Z supports a wide range of graphics devices and is compatible with Windows operating systems.
HWMonitor
HWMonitor is a popular and comprehensive GPU monitor software that tracks hardware components such as the GPU, CPU, motherboard, and hard drive. It offers real-time metrics such as temperature, clock speeds, fan speed, and voltage for various GPU models. HWMonitor has different pricing plans, including a basic free version, a personal plan, a pro plan, and an enterprise plan.
Speccy
Speccy is a comprehensive system information tool that includes GPU monitoring capabilities. It offers real-time monitoring of GPU parameters such as temperature, clock speeds, and fan speed, presented in a clear and user-friendly interface. Speccy has a free basic version and a professional version with additional features and support.
MSI Afterburner
MSI Afterburner is a widely used GPU monitor software that offers an extensive range of features, including a real-time monitoring overlay. It provides detailed information about GPU temperature, clock speeds, fan speed, and usage percentages, which can be customized to display during gameplay. MSI Afterburner is compatible with Windows and various graphics card models.
HWiNFO
HWiNFO is a powerful system monitoring utility that provides in-depth information about hardware components, including the GPU. While not specifically designed for GPU monitoring, it offers comprehensive capabilities, making it an excellent choice. HWiNFO displays real-time GPU metrics such as temperature, clock speeds, voltages, power consumption, and utilization. It is compatible with a wide range of GPU models and is free for non-commercial use.
CAM
CAM is a gaming GPU monitoring software package that provides comprehensive information about a computer's hardware. It enables users to monitor the performance of graphics cards and manage their PCs efficiently. CAM offers features such as quick tracking, in-game monitoring, smart scheduling, a night mode option, and an intuitive interface. It is free to use and developed by the California-based company NZXT.
Geeks3D GPU Shark
Geeks3D GPU Shark is a lightweight and user-friendly GPU monitoring software optimized for Windows. It is compatible with GeForce and Radeon graphics cards and allows users to monitor GPU memory, clock speeds, vendor details, temperature, and BIOS versions. Geeks3D GPU Shark is free to use and provides simple navigation and an intuitive design.
Open Hardware Monitor
Open Hardware Monitor is a Windows-specific GPU monitoring application that runs on various Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems without installation. It allows users to monitor graphics cards, CPU, and memory consumption, providing real-time data on CPU and GPU temperatures, CPU load, GPU memory, and clock speed. Open Hardware Monitor has a simple interface and is free to use.
Understanding EDP LCD and Monitor Technology
You may want to see also

Targeting the right GPU
When it comes to choosing the right GPU, there are several factors to consider. Here are some key guidelines to help you make an informed decision:
Performance Needs
Match the GPU to your intended usage. If you're a casual gamer or web browser, an integrated graphics or entry-level GPU like the GTX 1650 or RX 6500 XT may suffice. For more demanding tasks such as high-end gaming or professional workloads, consider mid-range, high-end, or workstation GPUs. For example, the RTX 3060 or RX 6600 XT for mid-range, and the RTX A series or Radeon Pro for professional use.
Budget Constraints
Balance performance with cost. Determine your comfortable price range and research current GPU prices, availability, and brand offerings. Consider the value offered by different manufacturers and models to find the best fit for your budget.
Brand and Features
Explore brands like NVIDIA and AMD, each with its unique features. NVIDIA offers DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) for enhanced performance and image quality, while AMD is known for competitive pricing and FidelityFX Super Resolution (FSR). Evaluate additional features such as ray tracing, cooling solutions, and software ecosystems provided by each brand.
Compatibility
Ensure seamless integration by checking the power supply unit (PSU) requirements, physical dimensions, and compatibility with your motherboard's PCIe slot. Make sure the GPU will fit in your PC case and has the necessary connectors and wattage to meet its power requirements.
Future-proofing
Invest in a GPU that can accommodate future upgrades. Consider the expected lifespan, resale value, and reviews of different GPUs. Analyze the resolution and refresh rate of your monitor to ensure the GPU can handle your desired settings. Look for bundle deals or promotions to get the best value for your money.
By carefully considering these factors, you can make an informed decision when targeting the right GPU for your specific needs and budget constraints.
Wifi Adapter Monitor Mode: How to Check?
You may want to see also

Using the NVIDIA Control Panel
The NVIDIA Control Panel offers a range of features to improve performance and stability and access new features. It is an intuitive 3D application that allows for seamless monitoring of PC component characteristics, including GPU performance.
To launch the NVIDIA Control Panel, right-click on your desktop and choose the NVIDIA Control Panel from the dropdown menu, or use the Windows search function. Once in the Control Panel, you can view GPU utilisation by selecting 'Manage GPU Utilisation' under the 'Select a Task' pane in the 'Workstation' section. This will show you a list of the GPUs installed in your system, their utilisation, and whether ECC is enabled for each. You can also view a graph of GPU utilisation over time by clicking 'GPU Utilisation Graphs'.
The Control Panel also allows you to adjust your settings to increase frames per second and smooth gameplay. For example, you can turn on Low Latency Mode to lower latency and increase frame rates. You can also adjust the Power Management Mode to optimise the power-performance ratio of your graphics card. If you want to maximise performance, select 'Prefer Maximum Performance', which will allow your GPU to use maximum power but may cause it to run hotter.
Additionally, the NVIDIA Control Panel provides networking features that improve network throughput and reduce CPU utilisation. The FirstPacket technology improves performance for networked games and other latency-sensitive traffic by prioritising important applications. The DualNet technology doubles the network link speed and reduces CPU utilisation by offloading packet processing tasks to hardware.
Simple Ways to Check if Your Monitor Has Full RGB
You may want to see also

UNIX command-line utility
There are several UNIX command-line utilities for monitoring GPU performance. Here are some of the most commonly used ones:
- Nvidia-smi: This is a NVIDIA command-line utility that can be used to monitor the performance of NVIDIA GPU devices. It provides information such as memory usage, GPU utilization, temperature, and power draw.
- Nvtop: This is a command-line tool similar to "htop" but specifically designed for NVIDIA GPUs. It provides a nice graphical display of GPU devices, including GPU utilization, memory usage, and temperature.
- Intel-gpu-tools: This package includes the "intel_gpu_top" command, which displays a top-like summary of Intel GPU usage, similar to "nvidia-smi" but for Intel GPUs.
- Radeontop: This tool is used for AMD/ATI/Radeon cards and provides information about GPU utilization, memory usage, and temperature.
- Atop: This is a powerful UNIX command-line utility for monitoring various system resources, including CPU, GPU, memory, disk, and network usage. It logs system activity in 10-minute intervals, providing detailed reports on GPU usage over time.
- Gpustat: This is a simple command-line script that wraps "nvidia-smi" and provides an easy way to query and monitor GPU status, including memory usage and GPU utilization.
- Glances: This is a monitoring program with a GPU monitoring plugin. It can be used to monitor CPU, disk IO, disk space, network, and GPU performance.
These tools can be used to monitor GPU performance, memory usage, temperature, and other relevant metrics. They provide real-time updates and detailed reports, helping users optimize their GPU usage and identify any potential issues.
Choosing the Right Monitor: Key Considerations
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can monitor your GPU performance through the Task Manager, which is a built-in tool in Windows. To do this, open the Task Manager and click on the "Performance" tab. From there, you can select "GPU" from the left-hand menu to view the GPU usage of all running processes.
In the Task Manager, right-click on one of the columns in the "Processes" tab and click "GPU" to enable usage tracking. This will allow you to see which programs are using the GPU.
Yes, you can use third-party tools such as MSI Afterburner or NVIDIA Inspector to monitor and limit GPU usage.
You can use the NVIDIA System Management Interface (nvidia-smi) command-line utility to monitor the performance of NVIDIA GPU devices.