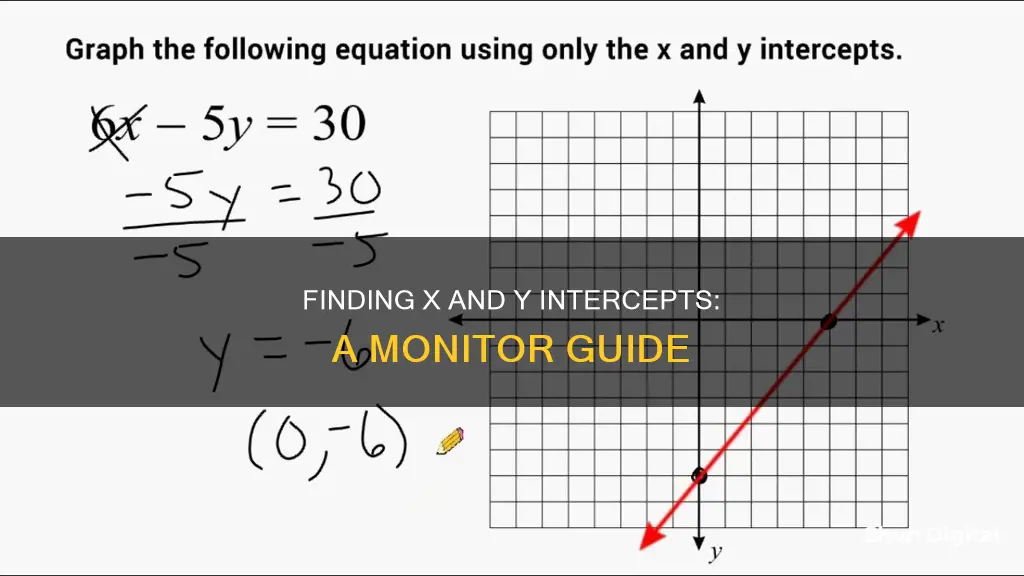
When dealing with graphs, it is often important to identify the x-intercept and y-intercept. The x-intercept is the point where the graph of a line crosses the x-axis, and the y-intercept is the point where the graph of a line crosses the y-axis. These points can be found algebraically by setting y = 0 and solving for x to find the x-intercept, and by setting x = 0 and solving for y to find the y-intercept. For example, to find the x-intercept of the equation y = 3x - 1, set y = 0: y = 3x - 1 --> 0 = 3x - 1 --> 1 = 3x --> 1/3 = x. So, the x-intercept is (1/3, 0). To find the y-intercept, set x = 0: y = 3x - 1 --> y = 3(0) - 1 --> y = -1. So, the y-intercept is (0, -1).
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| To find y-intercept | Set x = 0 and solve for y. The point will be (0, y) |
| To find x-intercept | Set y = 0 and solve for x. The point will be (x, 0) |
| To find y-intercept from the slope and a point | Write the equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Substitute the slope and the x and y coordinates for a point on the line to solve for b. |
| To find y-intercept from two points | Calculate the rise and run of the line, then divide rise by run to find the slope. Write the equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Substitute the slope and the x and y coordinates for a point on the line to solve for b. |
| To find y-intercept from the equation of the line | Plug in 0 for x in the line equation and solve for y. |
| To find y-intercept on a graphing calculator | Press the "Y=" button on the calculator and enter the equation. Press the "Zoom" button and select a zoom that includes the X and Y intercepts. Press the "Trace" button, then press "0" to move the cursor to the Y intercept. |
| To find x-intercept(s) on a graphing calculator | Press the "2nd" key, then the "Calc" key to access the trace menu. Scroll down to "Zero" and press "Enter". Use the arrow keys to scroll to the left and right of the X intercept and press "Enter". The X intercept will be displayed at the bottom of the screen. |
What You'll Learn

How to find x-intercepts: substitute y=0 and solve for x
To find the x-intercept of a line, you need to substitute y = 0 and solve for x. This is because the x-intercept is the point at which the line crosses the x-axis, and when y = 0, the line crosses this axis.
For example, let's say you want to find the x-intercept of the line 5x + 2y = 10. To do this, you would substitute y = 0 into the equation, giving you 5x + 2(0) = 10, which simplifies to 5x = 10, and finally x = 2. So, the x-intercept is (2, 0).
The x-intercept can be found for any equation in the form y = mx + b by substituting y = 0. This is known as the slope-intercept form, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. By substituting y = 0, you are finding the point at which the line crosses the x-axis, making x the only variable and thus solving for x.
The x-intercept can also be found for other forms of linear equations. For the general form of a straight line, ax + by + c = 0, the x-intercept can be found by putting y = 0, giving you x-intercept = -c/a. For the point-slope form, y - b = m(x - a), the x-intercept can be found by putting y = 0, giving you x-intercept = (am - b)/m.
Surveillance Signs: Is Your House Being Watched?
You may want to see also

How to find y-intercepts: substitute x=0 and solve for y
To find the y-intercept of a line, you can use the following methods:
Using the equation of the line
If you already know the equation of the line, you can find the y-intercept by setting x = 0 and solving for y. The y-intercept will be the value of y when x = 0. This method works because the y-intercept is the point where the line crosses the y-axis, and the y-axis is located at x = 0.
For example, let's find the y-intercept of the line 5x + 4y = 16. By setting x = 0, we get:
4y = 16
Y = 4
So, the y-intercept is (0, 4).
Using the slope and a point on the line
If you know the slope of the line and a point on the line, you can find the y-intercept by using the slope-intercept form of the equation of the line. The slope-intercept form is given by y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
For example, let's find the y-intercept of a line with a slope of 2 that passes through the point (-3, 4). First, we write the equation of the line in slope-intercept form:
Y = 2x + b
Next, we substitute the coordinates of the given point:
4 = 2(-3) + b
Finally, we solve for b:
4 = -6 + b
10 = b
So, the y-intercept is (0, 10).
Using two points on the line
If you know two points on the line, you can first find the slope of the line by calculating the "rise" and the "run" between the two points. Then, you can use the slope and one of the points to find the y-intercept, as shown in the previous method.
For example, let's find the y-intercept of a line that passes through the points (-1, 2) and (3, -4). First, we calculate the slope:
Rise = change in y-coordinates = -4 - 2 = -6
Run = change in x-coordinates = 3 - (-1) = 4
Slope = rise/run = -6/4 = -3
Now, we can use the slope-intercept form with the slope and either point:
Y = mx + b
Y = -3x + b
Using the point (-1, 2):
2 = -3(-1) + b
2 = 3 + b
5 = b
So, the y-intercept is (0, 5).
Removing the ASUS ROG Swift Monitor Stand: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

How to find y-intercept using slope and point
To find the y-intercept of a line when given the slope and a point on that line, you can use the equation of the line in slope-intercept form:
`y = mx + b`
Where:
- `m` is the slope of the line
- `b` is the y-intercept
- `x` and `y` are the coordinates of a point on the line
Method 1: Using the Slope and Point
- Write down the slope and the coordinates of the given point.
- Substitute the given slope for `m` in the equation `y = mx + b`.
- Replace `x` and `y` with the coordinates of the given point.
- Solve for `b`, which represents the y-intercept.
- Write the y-intercept as a coordinate point: `(0, b)`
Method 2: Using the Equation of the Line
If you already have the equation of the line, you can find the y-intercept by:
- Substituting `0` for `x` in the equation.
- Solving for `y`.
The answer you get for `y` is the y-intercept of the line.
Monitoring Data Usage: Mediacom's Essential Guide
You may want to see also

How to find y-intercept using two points
To find the y-intercept of a line using two points, you can follow these steps:
- Identify the Two Points: Let's denote the two points as Point 1 (x1, y1) and Point 2 (x2, y2). You can choose any two points on the line, as long as they are distinct.
- Calculate the Slope (m): The slope of a line is defined as the "rise" divided by the "run." You can calculate it using the formula: m = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1). Make sure to perform the calculations correctly, ensuring that you are subtracting the y-coordinates and x-coordinates, respectively.
- Use the Slope and One of the Points to Find the Y-Intercept: Now that you have the slope (m), you can use it along with either of the two points to find the y-intercept. The y-intercept is represented as "b" in the equation "y = mx + b." Plug in the values of m, x, and y from one of your points into this equation. This will give you an equation with only one variable, "b." Solve for "b," and you will have found the y-intercept.
- Plug the Values into the Slope-Intercept Form: Once you have both the slope (m) and the y-intercept (b), you can write the equation of the line in the slope-intercept form: y = mx + b. This equation represents the line that passes through your two chosen points.
For example, let's say you have the two points: Point 1 (-5, 10) and Point 2 (-3, 4). First, calculate the slope using the formula: m = (4 - 10) / (-3 - (-5)) = -3. Now, use this slope and either of the points to find the y-intercept. Let's use Point 2: 4 = -3(-3) + b. Simplify the equation: -5 = b. So, the y-intercept is (-5, 0). The equation of the line is y = -3x - 5.
This process allows you to determine the y-intercept of a line when you have two points on that line. It's important to note that the order of the points doesn't matter, as long as you are consistent in your calculations. Additionally, you can use any two points on the line, and you will always find the same y-intercept value since they all lie on the same line.
Connecting Your AP CPM Peter: Monitor Setup Guide
You may want to see also

How to find y-intercept using a graphing calculator
To find the y-intercept of a line using a graphing calculator, follow these steps:
- First, enter the equation into the calculator by pressing the "Y=" button and inputting the equation, ensuring that all parentheses and operators are included.
- Next, graph the equation by pressing the "Zoom" button and selecting an appropriate zoom that includes the X and Y intercepts.
- Then, find the Y-intercept by pressing the "Trace" button, followed by the "0" button. This will move the cursor to the Y-intercept, where X = 0, and the Y-coordinate will be displayed at the bottom of the screen.
Alternatively, you can find the y-intercept of a line without a graphing calculator by using the slope-intercept form of the equation, which is given as y = mx + b, where m is the slope of the line and b is the y-intercept. If you know the slope and a point on the line, substitute the slope and the x and y coordinates of the point into the equation and solve for b. For example, if the slope is 2 and the point is (-3,4), the equation would be 4 = 2(-3) + b, which simplifies to -2 = b, so the y-intercept is (-0, -2).
The Evolution of HDMI LCD Monitors: Understanding the Basics
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The x-intercept is the point at which a graph crosses the x-axis, at this point the y-coordinate is zero. The y-intercept is the point at which a graph crosses the y-axis, at this point the x-coordinate is zero.
To find the x-intercept, set y = 0 and solve for x. The point will be (x, 0).
To find the y-intercept, set x = 0 and solve for y. The point will be (0, y).
The standard form of a quadratic equation is written as y = ax^2 + bx + c, where x and y are variables. To find the y-intercept, substitute 0 for x and solve for y. The y-intercept is always equal to the value of c in the equation.
First, identify the slope and a point on the graph. Write a linear equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). Using the given point (x, y) and the slope m, rewrite the equation by substituting the appropriate values for x, y, and m. Solve the equation for b to identify the y-intercept.







