Finding the make and model of your monitor can be a difficult task, especially if you are using a desktop computer. While Windows 10 and 11 make it easy to access most of the under-the-hood details, you may need to dive into the registry to find specific details about your display.
In Windows 10, you can find advanced display information in the Settings > System > Display menu. Here, you can find details such as the manufacturer and model number, resolution, graphics card, and refresh rate.
In Windows 11, you can find display information in the Settings > System > Advanced Display Settings menu. This will show you details such as the display resolution, refresh rate, bit depth, colour format, and colour space. You can also access the monitor settings by clicking on Display adapter properties.
If you need more specific information, such as the monitor's serial number, you can use third-party utilities like NirSoft's DumpEDID or PowerShell scripts to retrieve this information.
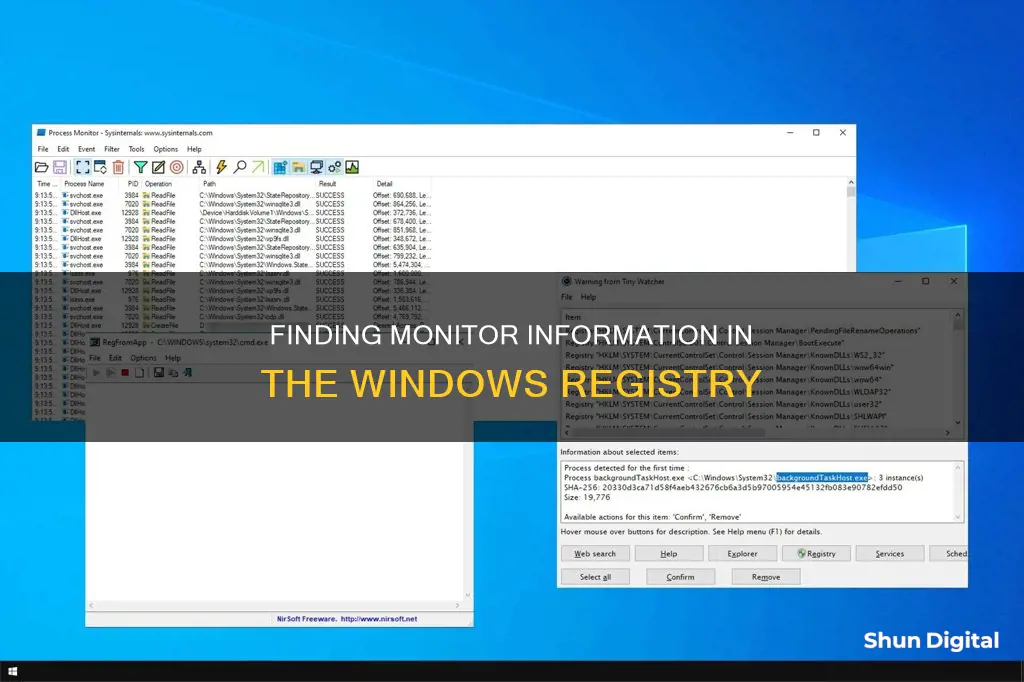
Additionally, if you want to track changes to specific registry keys, you can use tools like Microsoft Sysinternals Process Monitor. This tool allows you to filter and monitor specific registry keys, providing a detailed view of any changes made.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Registry key to determine monitor placement | HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Video |
| Registry key to determine monitor placement in Windows 7 | HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\GraphicsDrivers\Configuration |
| Command to get manufacturer and model of monitor | wmic desktopmonitor get Caption, MonitorType, MonitorManufacturer, Name |
| Tool to get manufacturer and model of monitor | DumpEDID utility by Nir Sofer |
| Registry key to determine AutoConfigURL | HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings\AutoConfigURL |
| Tool to determine what is changing the value of the AutoConfigURL registry key | Microsoft Sysinternals Process Monitor |
| Monitor details in Windows 10 | Settings > System > Display > Advanced Display Settings |
| Monitor details in Windows 11 | Settings > System > Display > Advanced Display Settings |
What You'll Learn

Monitor placement in a multi-monitor environment
When setting up a multi-monitor environment, it is important to consider the placement of your monitors for optimal functionality and comfort. Here are some tips for monitor placement in a multi-monitor setup:
- Ergonomics: Ensure that your seating position is comfortable and maintains good posture. Adjust your chair so that your back is supported, your feet are flat on the floor, and your forearms are resting on the desk at a 90-degree angle. This position will help reduce strain on your back, neck, and eyes.
- Designate Primary and Secondary Monitors: Choose one monitor as your primary display, which will be used for primary tasks such as typing or data entry. The secondary monitor can be used for reference materials, chats, or other supporting information. Typically, the primary monitor is placed directly in front of you, with the secondary monitor to the side.
- Adjust Monitor Height and Angle: Position your primary monitor at eye level to avoid neck strain. Ensure that the secondary monitor is adjusted to a similar height to maintain a comfortable viewing angle. You can use monitor arms or stands to adjust the height and angle of your monitors.
- Mouse Orientation: Point your mouse towards the primary screen to keep it within a comfortable reach. This prevents repetitive stress injuries that can occur when your elbow angle approaches 180 degrees.
- Screen Arrangement: Decide on the arrangement of your monitors based on your workflow and preferences. You can place the secondary monitor to the left or right of the primary monitor, or you can place one monitor above the other. Some people prefer a surround setup with one monitor in the middle and two monitors on either side. Experiment to find the arrangement that works best for you.
- Consistency Across Monitors: Ensure that your displays have consistent brightness, colour temperature, and resolution to reduce eye strain and provide a seamless visual experience across multiple monitors.
- Cable Management: With multiple monitors, cable management becomes crucial to avoid a cluttered workspace. Use cable ties or clips to organise and hide cables, ensuring they are connected securely to your computer and power sources.
- Test and Adjust: Once you have set up your monitors, test your configuration by performing typical tasks. Make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal comfort and productivity.
By following these tips, you can create a multi-monitor environment that enhances your productivity and provides a comfortable viewing experience. Remember to consider your personal preferences and workflow when arranging your monitors to create a customised and efficient workspace.
CPAP Usage Monitoring: Privacy or Health Concern?
You may want to see also

How to find monitor make and model
There are several ways to find out the make and model of your monitor. Here are some methods that can be used:
Physically checking the monitor
The maker's name is usually stamped on the monitor at the bottom of the bezel. When you power on your monitor, you may also see the maker's logo appear for a few seconds before the monitor enters sleep mode. The brand name or logo may also be placed behind the screen.
Using Windows Settings
On a Windows OS, go to Settings > System > Display. Here, you can find information about your monitor, including its brand name and model number. If you have multiple displays connected, click on the hierarchy under the colour profile to view all connected monitor brands and their model numbers.
You can also click on 'Advanced display settings' and then on 'Display Adapter properties' to access the graphics card properties, which will provide additional information for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Using the Device Manager
The Device Manager is an app that comes with the Windows operating system. To find the model of your monitor using this method:
- Type 'device manager' in the search bar.
- Click on the recommended Device Manager app.
- Select 'Monitors' from the list of devices.
- Double-click on 'Monitors' to view the list of monitors connected to your PC, along with their brand names and models.
Using the Command Prompt
Press WinKey + S to open an instant search on your Windows PC. Type 'command' or 'cmd' and press enter to open the command prompt. Then, type the following code:
Wmic desktopmonitor get Caption, MonitorType, MonitorManufacturer, Name
Press enter, and the command prompt will display the result, including the monitor manufacturer and model number.
Using third-party software
You can also use third-party software such as Belarc Advisor or MonitorInfoView to find your monitor's model. Belarc Advisor provides a comprehensive report on your computer system, including display information.
Curved Monitor Buying Guide: Size Considerations
You may want to see also

Monitor settings in Windows 11
To access the display settings in Windows 11, go to Settings > System > Display. Here, you can modify your display resolution, scale, and brightness. You can also configure the night light setting, which reduces blue light emissions to alleviate eye strain and improve sleep quality. Additionally, if your display supports HDR, you can enable it for a more immersive visual experience.
If you have multiple displays, you can rearrange and adjust their layout by dragging and dropping the numbered display icons in the "Multiple Displays" section of the Display panel. You can also use the Detect button to identify all connected displays.
To change the display brightness, you can either use the Brightness slider in the Action Center on the right side of the taskbar or go to Settings > System > Display. Some PCs can also automatically adjust the screen brightness based on lighting conditions or content.
Windows 11 also allows you to change the display resolution, scale, and layout. You can find these options in the Display settings under "Scale and Layout." Adjusting the scale will impact text size, application sizes, and other display component sizes.
For external displays, make sure your cables are properly connected to your PC or dock, and check for Windows updates before changing any settings. You can rearrange and adjust the layout of multiple displays by dragging and dropping the display icons in the Display settings.
Detaching the Monitor: Asus Zenbook's Easy Separation
You may want to see also

Using the Registry Editor to find monitor details
To find monitor details using the Registry Editor, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Registry Editor
Open the Registry Editor by pressing the Windows key + R, typing "regedit" into the Run box, and clicking "OK". Alternatively, you can access it by pressing the Windows key + X to open the Power Menu and selecting "Registry Editor".
Step 2: Navigate to the Monitor Sub-folder
Once the Registry Editor is open, navigate to the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Enum\
From there, you will need to find the sub-folder that corresponds to your monitor. The sub-folder will be named with a string of alphanumeric characters.
Step 3: Locate Monitor Details
Within the monitor sub-folder, you can find various details about your monitor. For example, you can find the monitor's name, manufacturer, model, serial number, week of manufacture, year of manufacture, and more.
Step 4: Back Up the Registry (Optional)
Before making any changes to the Registry, it is highly recommended to back it up. To do this, go to File in the top left corner of the Registry Editor and select Export. Choose a location to save the backup file and click "Save".
Step 5: Rename Your Monitor (Optional)
If you wish to rename your monitor, you can do so by following these steps:
- Right-click on "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE" and select "Find".
- Paste the driver key that you copied earlier and click "Find Next".
- Double-click on "FriendlyName" in the results.
- Replace the "Value data" with the new name you have chosen and click "OK".
- Close the Registry Editor and open the Device Manager by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting "Device Manager".
- Locate your monitor under the "Monitor" options, right-click on it, and select "Scan for hardware changes". Your monitor should now appear with the new name.
Step 6: Access Advanced Display Settings (Optional)
For additional monitor details, you can access the Advanced Display Settings by going to "Settings > System > Display" and scrolling down to click on "Advanced Display Settings". Here, you will find information such as the manufacturer, model number, resolution, graphics card, refresh rate, and more.
Step 7: Access Graphics Card Properties (Optional)
From the Advanced Display Settings, you can also click on "Display adapter properties" to access the graphics card properties for further information and troubleshooting options.
Step 8: Use System Information Application (Optional)
If you are unable to find the monitor details you need in the Registry Editor, you can use the System Information Application. To open it, type "system information" in the search box on the taskbar and click on the appropriate application. In the System Information window, expand the "Component options" under "System Summary" and click on "Display" to view the details of your monitor.
Opening a Philips LCD Monitor: Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Using Process Monitor to find registry changes
Process Monitor is a tool that can be used to track the various processes' activity in the Windows operating system. It is not a built-in system utility, so you must download it manually from the Microsoft website.
Process Monitor allows you to show how processes access files on disk, registry keys, and remote resources in real time. It combines the capabilities of two legacy Sysinternals utilities: FileMon and RegMon.
- Download Process Monitor from the Microsoft website.
- Extract the zip file contents to a folder of your choice.
- Run Process Monitor.
- If the Filter dialog doesn't open automatically, press Ctrl + L to open it.
- In the Filter dialog box, select the "Path" option and enter the registry key value you want to monitor.
- Click the "Add" button to add this filter.
- In the Process Monitor window, look for events with the "Result" column value of "NAME NOT FOUND". These events indicate a change was made to the registry key.
- The "Operation" column will show "RegSetValue" if the value was changed or "RegCreateKey" if a new key was created.
- The "Process Name" column will display the name of the process that made the change.
- The "Detail" column will show the exact value that was changed.
- To stop capturing events, go to the File menu and select "Capture Events".
By following these steps, you can use Process Monitor to find and track changes to registry keys in Windows.
Removing FPS Counter: ASUS VG245H Monitor Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can find your monitor in the Windows 7 registry by checking the following keys:
```
HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Video
```
In the innermost MonXXXXXXX sub-folders, you should find Attach.RelativeX and Attach.RelativeY values, which indicate the monitor's position relative to pixel 0,0.
In Windows 10, you can find the advanced display settings by going to Settings > System > Display and clicking on Advanced Display Settings. Here, you will find details such as the manufacturer, model number, resolution, graphics card, and refresh rate.
To find your monitor in the Windows 11 registry, go to Settings > System > Display and click on Advanced Display Settings. Under the Advanced Display window, you will find options such as Desktop Mode, Active Signal Mode, Bit Depth, Color Format, and Color Space. You can also access monitor settings by clicking on Display adapter properties.
You can use the wmic command in the Command Prompt to get the monitor's manufacturer and model information. Run the following command with administrator privileges:
```
wmic desktopmonitor get Caption, MonitorType, MonitorManufacturer, Name
```
You can use the Microsoft Sysinternals Process Monitor tool to track changes to specific registry values. Set a filter for the registry key you want to monitor, and look for events with the "NAME NOT FOUND" result, which indicates a change was made. The Process Name column will show the process responsible for the change.