Monitoring the performance of mutual funds is crucial to making informed decisions that lead to better returns. While financial experts are irreplaceable, investors should also have some knowledge about their investments. There are several ways to track mutual fund performance, including fund fact sheets, which are one-page documents published monthly by each mutual fund, providing an overview of the fund's performance and portfolio. Additionally, investors can refer to updates and review statements provided by advisors or intermediaries, or use websites and mobile apps that track scheme performance. It is also important to consider the fund's historical performance, fee structure, and risk-adjusted returns. By regularly evaluating mutual fund performance, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments.
What You'll Learn

Compare fund performance against a benchmark
When it comes to monitoring the performance of a mutual fund, it is important to compare it against a benchmark. This is because every fund has a benchmark used to track and measure its performance. By comparing a fund's performance against its benchmark, you can identify how well the fund is doing relative to the industry standard.
A good mutual fund is one that consistently outperforms its benchmark over the long term. When a fund generates higher returns than the benchmark, the excess is known as the 'alpha' of the fund. This alpha represents the added value that the fund has created compared to simply investing in the benchmark index. A positive alpha indicates that the fund has delivered returns above what would be expected based on its level of risk.
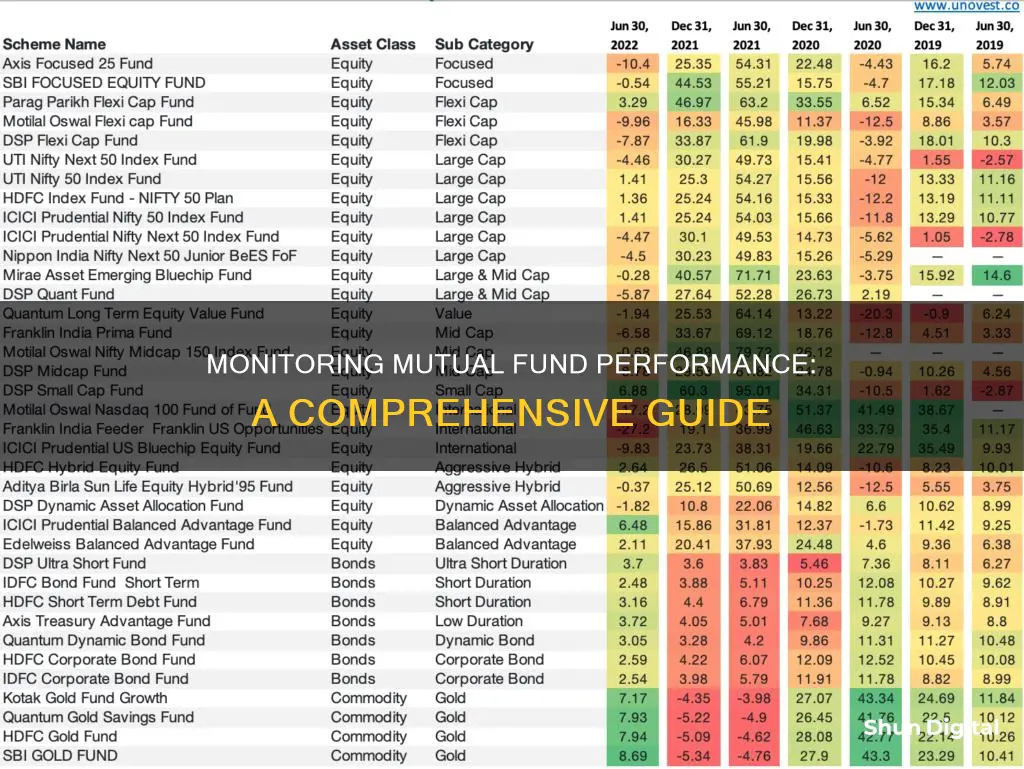
To evaluate the performance of a mutual fund against its benchmark, you can refer to the fund's fact sheet. A fact sheet is a basic document published monthly by each mutual fund, providing an overview of the fund's performance and portfolio. It includes information such as the fund's investment objective, the fund manager's name and experience, the latest assets under management (AUM), and the total expense ratio (TER). Additionally, the fact sheet will show the fund's performance relative to its benchmark, often using metrics such as CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate), beta, standard deviation, and the Sharpe ratio. These metrics allow you to analyse how the fund has performed in comparison to its benchmark during different market cycles.
By regularly reviewing the fund's fact sheet and comparing its performance against its benchmark, you can make informed decisions about your investment. It is important to remember that past performance does not guarantee future results, but analysing how a fund has fared against its benchmark can provide valuable insights into the fund's potential and help you assess if it is meeting your investment goals.
Fixing the ViewSonic VA 1930WM LCD Monitor: A Step-by-Step Guide
You may want to see also

Evaluate the fund's risk profile
Evaluating the risk profile of a mutual fund is essential to ensure that you are not sold a riskier fund than you can handle. Risk profiling is a process that helps you identify the optimal level of risk that is suitable for you as an investor. It is based on your risk appetite, which refers to the amount of risk you have the capacity to absorb. This is determined by factors such as your habits, behaviours, family orientation, attitude towards risk, age, income, number of dependents, etc.
Your risk profile is made up of three main components: your risk capacity, your risk tolerance, and the risk you need to take to achieve your financial goals.
- Risk capacity refers to your ability to take risks, which depends on factors that can be quantified, such as your age, income, and number of dependents.
- Risk tolerance refers to your willingness to take risks, indicating your emotional tolerance for market volatility and risk-taking in general. This is a psychological characteristic.
- Required risk is a mathematical calculation that helps you understand the level of risk needed to achieve your financial goals.
To assess your risk profile, you can use risk profiling tools and questionnaires, which are often available online. These tools will evaluate your need, ability, and willingness to take risks.
Once you understand your risk profile, you can match it with the risk profile of the mutual fund you wish to invest in. The risk profile of a mutual fund scheme is the degree of risk attached to the principal invested. This information can be found in the risk profile disclosure on the first page of a mutual fund's scheme information document (SID). Additionally, you can refer to the riskometer, which provides a pictorial representation of the fund's risk profile.
It is important to note that your risk profile may change over time as your life circumstances evolve. Therefore, it is recommended to assess your risk profile periodically to ensure that your investments remain aligned with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Finding the Elusive X and Y on Your Monitor
You may want to see also

Analyse the fund manager's tenure
When choosing a mutual fund, it's important to consider the fund manager's tenure. The current fund manager will receive credit for the three-year returns, but they won't be held entirely responsible for the returns over a longer period, such as ten years. This is an important consideration, as mutual funds are expected to be a long-term investment.
A fund manager's tenure can give you an idea of their skill and the level of risk associated with the fund. A longer tenure indicates that the manager has a successful track record, and their strategies are likely to be aligned with your investment goals. It also suggests that the fund is stable and has a lower risk of negative performance.
On the other hand, a shorter tenure could mean the manager is relatively inexperienced or that there have been frequent changes in management, which might indicate higher risk.
When evaluating a fund manager's tenure, it's essential to consider the fund's historical performance and how it aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Additionally, remember to assess the fund's performance over different market cycles, as this can provide insights into the manager's ability to navigate various economic conditions.
You can find information about the fund manager, including their tenure and experience, in the fund's fact sheet, which is typically published monthly and is readily available on the mutual fund's website. This document provides an overview of the fund's strategy, performance, and portfolio composition, making it a valuable tool for investors when deciding whether to invest or not.
Best Places to Buy Desktop Monitors
You may want to see also

Understand the fee structure
The fee structure of a mutual fund is an important aspect to consider when monitoring its performance. Mutual fund companies charge a fee for their services and expertise, which can impact the overall returns of your investment. Here are some key points to consider when understanding the fee structure:
- Expense Ratio: The expense ratio is the fee charged by the fund house to manage your portfolio. This includes manager fees, distribution costs, investor transaction fees, and other charges. While it may seem small at first, it can significantly impact your investments over time. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the expense ratio when evaluating a mutual fund.
- Total Expense Ratio (TER): The TER represents the overall expenses of a mutual fund as a percentage of its total assets. It includes the management fee, distribution costs, and other operational expenses. High TERs can eat into your investment returns, so it is important to analyse the TER before investing in a fund.
- Fund Management Charges: These charges cover the cost of managing the fund, including the fund manager's salary and other administrative expenses.
- Other Costs: Mutual funds may also incur other costs, such as distribution and marketing expenses, that are not included in the expense ratio. It is important to consider these additional costs when evaluating the fee structure of a mutual fund.
- Comparison with Peers: When assessing the fee structure, compare the expenses of the mutual fund with those of its peers. This will help you determine if the fees are reasonable and in line with industry standards.
- Performance vs. Fees: Evaluate whether the fund's performance justifies the fees charged. A higher-fee fund does not automatically translate to better performance. Consider other parameters such as historical performance, risk-adjusted returns, and the fund manager's skill before making a decision.
- Review Fee Structure Regularly: The fee structure of mutual funds can change over time. It is important to periodically review the fees and expenses associated with your investments to ensure they remain competitive and aligned with your investment goals.
Understanding the fee structure of a mutual fund is crucial in monitoring its performance. By considering the expense ratio, TER, fund management charges, and other associated costs, you can make informed decisions about your investments and ensure that the fees do not outweigh the potential returns. Remember to compare fees with similar funds and assess whether the fund's performance justifies the costs.
Connecting Your Xbox to the New MSI Monitor
You may want to see also

Check historical performance data
Checking historical performance data is an important step in monitoring mutual fund performance. While past performance is not always indicative of future results, it can give you an idea of the fund's consistency and the skill of the fund manager. Here are some key considerations when reviewing historical performance data:
- Time Periods: Evaluate the fund's performance over different time periods, such as one year, three years, five years, or since its inception. This will give you a broader perspective on how the fund has fared over time.
- Market Cycles: Consider the fund's performance across different market cycles. For example, how did it perform during market highs and lows? This will help you understand how the fund navigates through various economic conditions.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns: Analyze the fund's risk-adjusted returns, which are the returns generated relative to the risks taken. This will help you assess if the fund is providing adequate returns for the level of risk you are taking.
- Performance Benchmarks: Compare the fund's performance against relevant benchmarks, such as the Nifty, BSE Sensex, or BSE 200. This will give you a frame of reference to evaluate how the fund has performed relative to the overall market.
- Peer Comparison: Shortlist a few comparable funds and conduct a peer comparison. This will help you contextualize the fund's performance relative to other similar investment options.
- Fund Manager Tenure: Consider the tenure of the fund manager, especially when evaluating long-term performance. The current fund manager may not be responsible for the returns generated over the entire period.
- Consistency: Look for consistency in the fund's performance. A fund that consistently performs well across different market conditions may indicate a more reliable investment option.
- Fund Fact Sheets: Utilize fund fact sheets, which are one-page documents published monthly by mutual funds. These provide key information about the fund's performance, portfolio composition, investment objectives, fees, and risks. They are designed to be easily understandable for the average investor and can be found on the mutual fund's website.
Best Places to Buy Marshall Monitor Headphones
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
It is recommended to evaluate the performance of your mutual fund every six months to a year, depending on the tenure of the investment. Evaluating the fund's performance in a shorter period will not give an accurate insight.
A fund fact sheet is a basic one-page document that gives an overview of a mutual fund scheme, with a special emphasis on the disclosure of scheme performance and portfolio. It is published every month by each mutual fund and can be found on the mutual fund's website. It is a great starting point for evaluating a mutual fund scheme before investing and for keeping track of the fund's performance.
Some key things to look out for when monitoring your mutual fund's performance include the fund's historical performance data, fee structure, risk-adjusted returns, and performance against the index. It is also important to define your investment goals and shortlist a few peer funds to compare.
There are several tools and resources available to track the performance of your mutual fund. You can use fund screener tools offered by FinTech firms and third-party websites. Additionally, you can refer to websites, mobile apps, and business papers that provide information and updates on mutual fund performance. Seeking guidance from financial experts, such as mutual fund distributors or investment advisors, can also be helpful.