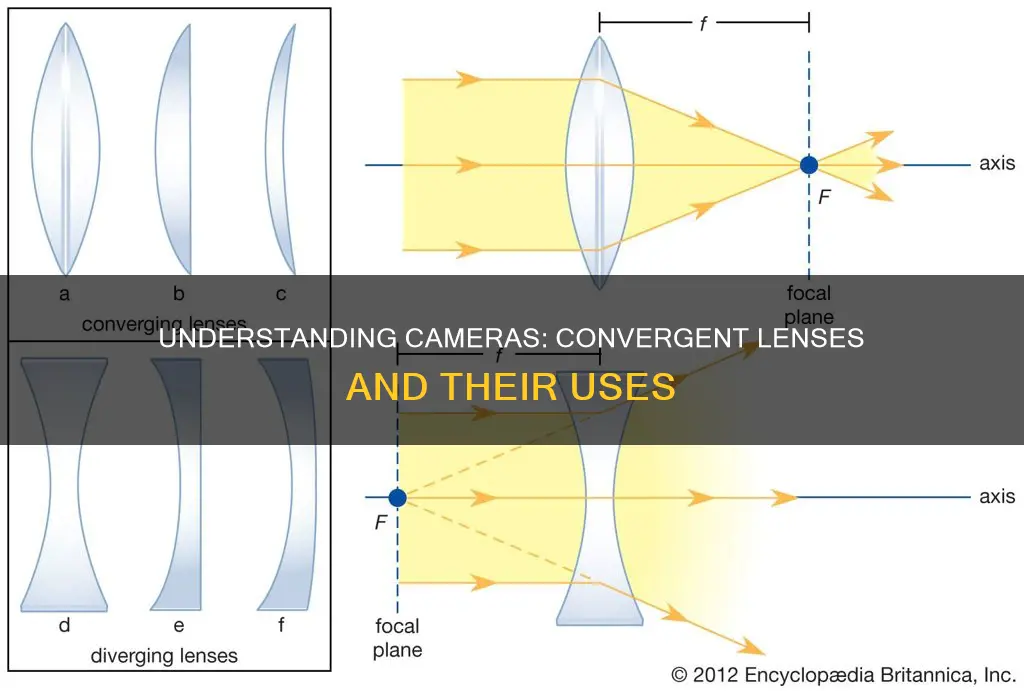
Cameras use converging lenses to focus and magnify images. A converging lens, also known as a positive lens, converges light rays from a source to meet at a single point called the focus. This is achieved by bending the light rays inwards. The distance from the centre of the lens to the point where the refracted light rays meet is known as the focal length.
Most camera lenses consist of a converging lens, followed by a diverging lens, and then a second converging lens. The first lens controls the level of magnification by moving towards or away from the object. The light then passes through the diverging lens, which flips the inverted image. Finally, the last converging lens inverts the image once more and delivers it to the back of the camera, where it is printed on film or digital media.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Lens type | Converging |
| Lens shape | Convex |
| Lens thickness | Thicker in the middle than at the edges |
| Light rays | Converge at a single point on the other side of the lens |
| Lens function | Focuses light |
| Lens use | Magnifying glasses, cameras, eyeglasses, microscopes, telescopes |
What You'll Learn

Converging lenses are used to focus light in cameras
Converging lenses, also known as convex lenses, are used in cameras to focus light from an object onto the film or digital sensor. The lens converges the incoming light onto a single point, known as the principal focus, allowing the camera to capture a clear image.
A converging lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. When light rays pass through a converging lens, they are refracted and bent inwards towards the centre of the lens. This is due to the outward curvature of the lens surface. The degree of curvature determines how much the light rays are refracted. Lenses with a higher curvature will have a shorter focal length as the light is bent more sharply.
In a camera, the converging lens is usually the first in a sequence of lenses. It controls the level of image magnification by moving towards or away from the object. The light then passes through a diverging lens, which flips the inverted image, before passing through a final converging lens. This inverts the image once more and delivers it to the back of the camera, where it is printed onto film or a digital media surface.
Converging lenses are also used in other optical devices such as microscopes, magnifying glasses, and telescopes. They are essential components in everyday items like eyeglasses, where they correct vision by focusing light onto the retina.
Analog Camera Lenses: Interchangeable or Not?
You may want to see also

They are used to magnify images in cameras
Cameras use converging lenses to magnify and focus images. The photographic lens is made up of several optical elements working together. Both convex and concave lenses are used in the manufacture of photographic lenses for various reasons, including the reduction of aberration and the function of telephoto and zoom lenses.
A converging lens, also known as a positive lens, is a lens that converges light rays coming from a source to meet or 'converge' at a single point called the focus. The point where all light rays converge is called the 'Principal Focus'. The distance from the centre of the lens to the point of focus is known as the Focal Length.
Convex lenses are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. This is the opposite of concave lenses, which are thicker towards the edges of the frame. Convex lenses are used in prescription glasses and photographic lenses, while concave lenses are used to correct nearsightedness.
Converging lenses are used in magnifying glasses, microscopes, telescopes, binoculars, and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia.
Polarized Camera Lenses: Worth the Investment?
You may want to see also

Converging lenses are used to correct farsightedness
Converging lenses, also known as convex lenses, are used to correct farsightedness, or hyperopia. These lenses are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges, and they have the ability to converge light rays from a source to meet at a single point called the focus or principal focus. This is achieved through refraction, which is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another with a different refractive index.
In the context of vision correction, converging lenses are used to treat hyperopia, where individuals can see objects that are close to them but struggle with focusing on distant objects. The converging lens helps to focus light onto the retina, assisting the eye in forming a clear image. This is achieved by converging the incoming light onto the retina, ensuring proper illumination and allowing the eye to form a sharp image.
Converging lenses are commonly used in eyeglasses to correct hyperopia. They are also used in cameras, where they focus light from an object onto the film or digital sensor, producing clear and sharp images. The lens system's objective lens is typically a converging lens, and varying its focal length allows photographers to capture a variety of scenes, from landscapes to portraits.
In addition to their use in eyeglasses and cameras, converging lenses also find application in scientific instruments such as microscopes and telescopes. These instruments often employ a combination of converging and diverging lenses to magnify and clarify the view of tiny or distant objects.
Interchangeable Lenses: Mirrorless Camera Flexibility Explored
You may want to see also

Converging lenses are used in microscopes
Converging lenses, also known as convex lenses, are thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges. They are used in a variety of optical instruments to focus light on a specific point, known as the focal point. The focal length of a converging lens determines how light is refracted and images are formed.
In a simple microscope, the first lens at the end produces a magnified and inverted image. The second lens further magnifies this image and inverts it, and the final lens (the eyepiece) delivers the magnified, upright image of the object viewed in front of the first lens. By adjusting the distance between the first lens and the object, the magnification of the image delivered to the eyepiece can be controlled.
Converging lenses are also used in other optical devices such as eyeglasses, cameras, and telescopes. In eyeglasses, they help correct farsightedness by focusing light onto the retina. In cameras, they are used to focus and magnify images, and in telescopes, they are used for image magnification.
Understanding APS-C Camera and Lens Cropping: What's the Difference?
You may want to see also

Converging lenses are used in magnifying glasses
Converging lenses are convex lenses, which are thicker in the middle with tapering ends. They are used to direct light towards a particular object. They are used in magnifying glasses to focus light and magnify the object being viewed. The lens is fixed inside a frame with a handle.
Converging lenses are also used in cameras to focus light and create clear images. They are responsible for bringing the image into focus on the image plane (the image sensor or photographic film at the back of the camera).
Converging lenses are further used in microscopes, telescopes, binoculars, and optical projectors. They can also be used to correct farsightedness in prescription glasses.
In summary, converging lenses are an essential component in various optical devices, including magnifying glasses, cameras, microscopes, and telescopes, where they play a crucial role in focusing light and creating clear, magnified images.
T3 Lenses: Universal Fit or Camera-Specific?
You may want to see also







